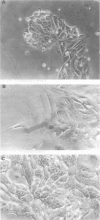
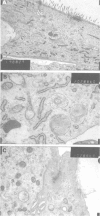
Abstract
Gall bladder epithelial cells serve numerous biological functions and abnormalities in their function are important in the pathogenesis of several gall bladder diseases. Direct studies on cell function are rare due to lack of reliable methods to culture this epithelium. This study reports a reliable and reproducible method of harvesting and culturing gall bladder epithelial cells. Normal bovine gall bladder epithelium, obtained within 20 minutes of slaughter, was rinsed with modified Hanks's balanced salt solution, the mucosa separated and incubated in trypsin--EDTA solution at 37 degrees C. The cells were isolated and resuspended in Dulbeco's modification of Eagles' medium containing 10% fetal calf serum and, after filtration and centrifugation, were plated under aseptic conditions. The growth rate was established by flow cytometry and the morphological characteristics of the growing cells by electron microscopy. Gall bladder epithelial cells grew successfully and visible clusters of cells were present by day two, confluency being reached at 8 to 10 days in collagen coated plates and 12 to 14 days in uncoated plates. Electron microscopy showed typical gall bladder epithelia with microvilli, tight junctions, and mucus droplets. This method proved reliable and reproducible for the culture of gall bladder epithelial cells and should allow direct studies of the biological properties of these cells in human tissue.
Full text
PDF

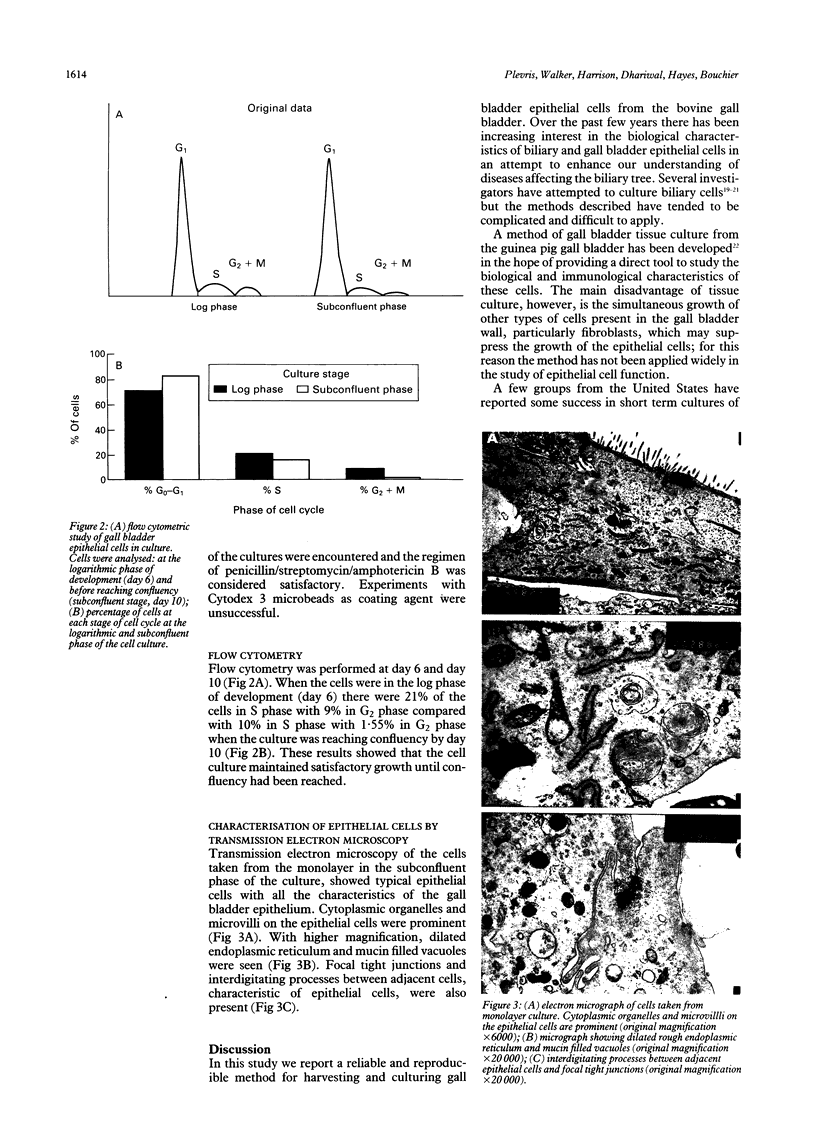

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DIAMOND J. M. TRANSPORT OF SALT AND WATER IN RABBIT AND GUINEA PIG GALL BLADDER. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Sep;48:1–14. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M. Recent developments in solute and water transport across the gall bladder epithelium. Gastroenterology. 1966 May;50(5):692–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elhamady M. S., Hopwood D., Milne G., Ross P., Bouchier I. A. Tissue culture of guinea-pig gall-bladder epithelium. J Pathol. 1983 Jul;140(3):221–235. doi: 10.1002/path.1711400305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelarden R. T., Rose R. C. Electrical properties and diffusion potentials in the gallbladder of man, monkey, dog, goose and rabbit. J Membr Biol. 1974;19(1):37–54. doi: 10.1007/BF01869969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant A. G., Billing B. H. The isolation and characterization of a bile ductule cell population from normal and bile-duct ligated rat livers. Br J Exp Pathol. 1977 Jun;58(3):301–310. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintze K., Petersen K. U., Olles P., Saverymuttu S. H., Wood J. R. Effects of bicarbonate on fluid and electrolyte transport by the guinea pig gallbladder: a bicarbonate-chloride exchange. J Membr Biol. 1979 Mar 28;45(1-2):43–59. doi: 10.1007/BF01869294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii M., Vroman B., LaRusso N. F. Isolation and morphologic characterization of bile duct epithelial cells from normal rat liver. Gastroenterology. 1989 Nov;97(5):1236–1247. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91695-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacyna M. R., Ross P. E., Bakar M. A., Hopwood D., Bouchier I. A. Characteristics of cholesterol absorption by human gall bladder: relevance to cholesterolosis. J Clin Pathol. 1987 May;40(5):524–529. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.5.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacyna M. R., Ross P. E., Bakar M. A., Hopwood D., Bouchier I. A. Characteristics of cholesterol absorption by human gall bladder: relevance to cholesterolosis. J Clin Pathol. 1987 May;40(5):524–529. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.5.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacyna M. R., Ross P. E., Hopwood D., Bouchier I. A. The effect of secretin on sodium ion absorption by the isolated human gallbladder. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1989 Jun;3(3):293–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1989.tb00216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar U., Jordan T. W. Isolation and culture of biliary epithelial cells from the biliary tract fraction of normal rats. Liver. 1986 Dec;6(6):369–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1986.tb00306.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. P., LaMont J. T., Carey M. C. Role of gallbladder mucus hypersecretion in the evolution of cholesterol gallstones. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jun;67(6):1712–1723. doi: 10.1172/JCI110209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. P., LaMont J. T., Carey M. C. Role of gallbladder mucus hypersecretion in the evolution of cholesterol gallstones. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jun;67(6):1712–1723. doi: 10.1172/JCI110209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda D., Lee S. P., Hayashi A. Long-term culture and partial characterization of dog gallbladder epithelial cells. Lab Invest. 1991 May;64(5):682–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevris J. N., Hayes P. C., Harrison D. J., Bouchier I. A. Evidence of hydrogen ion secretion from the human gall bladder in vitro. Gut. 1992 Apr;33(4):554–559. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.4.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rege R. V., Moore E. W. Evidence for H+ secretion by the in vivo canine gallbladder. Gastroenterology. 1987 Feb;92(2):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90118-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rege R. V., Nahrwold D. L., Moore E. W. Absorption of biliary calcium from the canine gallbladder: protection against the formation of calcium-containing gallstones. J Lab Clin Med. 1987 Oct;110(4):381–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuss L. Ion transport across gallbladder epithelium. Physiol Rev. 1989 Apr;69(2):503–545. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.2.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vindeløv L. L., Christensen I. J., Nissen N. I. A detergent-trypsin method for the preparation of nuclei for flow cytometric DNA analysis. Cytometry. 1983 Mar;3(5):323–327. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990030503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]