Abstract
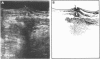
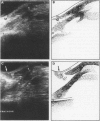
Transrectal ultrasonography is of clinical value in anorectal carcinoma and in inflammatory diseases of the anorectum. In this study a rigid linear endorectal probe was used to examine 15 patients with endoscopically and biopsy proved diagnosis of solitary rectal ulcer syndrome. In 13 of the 15 patients the rectal wall was thicker (mean (SEM) 5.7 (0.4) mm; normal values: 2.8 (0.1) mm) near the rectal ulcer. In all these cases the muscularis propria layer exceeded the maximum normal diameter of 2 mm. In nine of the 15 patients the normal rectal wall echo-structure, with five distinct layers, was disturbed and there was fading of the borders between the mucosa and the muscularis propria. Poor relaxation of the puborectalis muscle during straining was seen on ultrasound in 11 patients, as was intussusception of the rectal wall. The obvious enlargement of the muscularis propria points to a chronic mechanical load on the rectal wall. The ulcerative lesions are formed in this area of overloaded rectal wall. The direct visualisation of the puborectalis muscle during dynamic transrectal ultrasonography indicates that the fact that it does not relax is an important element in the pathogenesis of solitary rectal ulcer syndrome.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boscaini M., Moscini P. L., Montori A. Transrectal ultrasonography: interpretation of normal intestinal wall structure for the preoperative staging of rectal cancer. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1986;123:87–98. doi: 10.3109/00365528609091868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford M. J., Anderson J. R., Gilmour H. M., Holt S., Sircus W., Heading R. C. Clinical spectrum of "solitary ulcer" of the rectum. Gastroenterology. 1983 Jun;84(6):1533–1540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goei R., Baeten C., Janevski B., van Engelshoven J. The solitary rectal ulcer syndrome: diagnosis with defecography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987 Nov;149(5):933–936. doi: 10.2214/ajr.149.5.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt U., Feifel G., Ecker K. W. Rectal endosonography. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol. 1989 Jul;3(3):531–541. doi: 10.1016/0950-3528(89)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulsmans F. J., Tio T. L., Reeders J. W., Tytgat G. N. Transrectal US in the diagnosis of localized colitis cystica profunda. Radiology. 1991 Oct;181(1):201–203. doi: 10.1148/radiology.181.1.1887033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihre T. Intussusception of the rectum and the solitary ulcer syndrome. Ann Med. 1990 Dec;22(6):419–423. doi: 10.3109/07853899009147281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. N., Lubowski D. Z., Swash M., Henry M. M. Is paradoxical contraction of puborectalis muscle of functional importance? Dis Colon Rectum. 1987 Sep;30(9):667–670. doi: 10.1007/BF02561685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law P. J., Bartram C. I. Anal endosonography: technique and normal anatomy. Gastrointest Radiol. 1989 Fall;14(4):349–353. doi: 10.1007/BF01889235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. S. "Solitary" rectal ulcer syndrome. Are "solitary" rectal ulcer syndrome and "localized" colitis cystica profunda analogous syndromes caused by rectal prolapse? Gastroenterology. 1987 Jan;92(1):243–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberg B. Differentialdiagnose akut entzündlicher Dickdarmerkrankungen durch Kolonsonographie. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1987 Mar 6;112(10):382–385. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1068061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberg B. Sonographic features of colonic Crohn's disease: comparison of in vivo and in vitro studies. J Clin Ultrasound. 1990 Mar-Apr;18(3):161–166. doi: 10.1002/jcu.1870180304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackle E. J., Manton Mills J. O., Parks T. G. The investigation of anorectal dysfunction in the solitary rectal ulcer syndrome. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1990 Feb;5(1):21–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00496145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madigan M. R., Morson B. C. Solitary ulcer of the rectum. Gut. 1969 Nov;10(11):871–881. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.11.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahieu P. H. Barium enema and defaecography in the diagnosis and evaluation of the solitary rectal ulcer syndrome. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1986 Apr;1(2):85–90. doi: 10.1007/BF01648412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrom W. J., Wong W. D., Rothenberger D. A., Jensen L. L., Goldberg S. M. Endorectal ultrasound in the preoperative staging of rectal tumors. A learning experience. Dis Colon Rectum. 1990 Aug;33(8):654–659. doi: 10.1007/BF02150740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen S. N., Riis P. Rectal wall thickness measured by ultrasound in chronic inflammatory diseases of the colon. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1985 Jan;20(1):109–114. doi: 10.3109/00365528509089641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snooks S. J., Nicholls R. J., Henry M. M., Swash M. Electrophysiological and manometric assessment of the pelvic floor in the solitary rectal ulcer syndrome. Br J Surg. 1985 Feb;72(2):131–133. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800720221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun W. M., Read N. W., Donnelly T. C., Bannister J. J., Shorthouse A. J. A common pathophysiology for full thickness rectal prolapse, anterior mucosal prolapse and solitary rectal ulcer. Br J Surg. 1989 Mar;76(3):290–295. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800760323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tio T. L., Mulder C. J., Wijers O. B., Sars P. R., Tytgat G. N. Endosonography of peri-anal and peri-colorectal fistula and/or abscess in Crohn's disease. Gastrointest Endosc. 1990 Jul-Aug;36(4):331–336. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(90)71059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjandra J. J., Fazio V. W., Church J. M., Lavery I. C., Oakley J. R., Milsom J. W. Clinical conundrum of solitary rectal ulcer. Dis Colon Rectum. 1992 Mar;35(3):227–234. doi: 10.1007/BF02051012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Outryve M. J., Pelckmans P. A., Michielsen P. P., Van Maercke Y. M. Value of transrectal ultrasonography in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1991 Nov;101(5):1171–1177. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90064-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Womack N. R., Williams N. S., Mist J. H., Morrison J. F. Anorectal function in the solitary rectal ulcer syndrome. Dis Colon Rectum. 1987 May;30(5):319–323. doi: 10.1007/BF02555447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]