Abstract
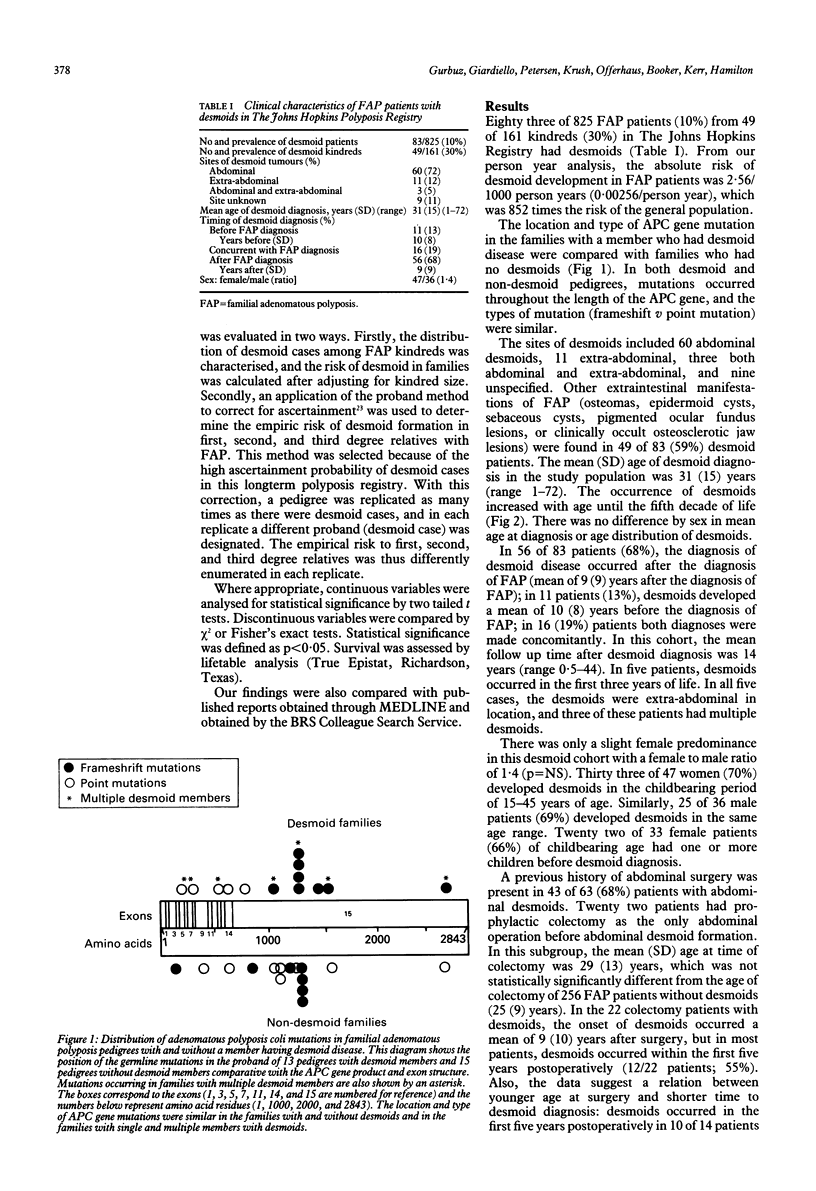
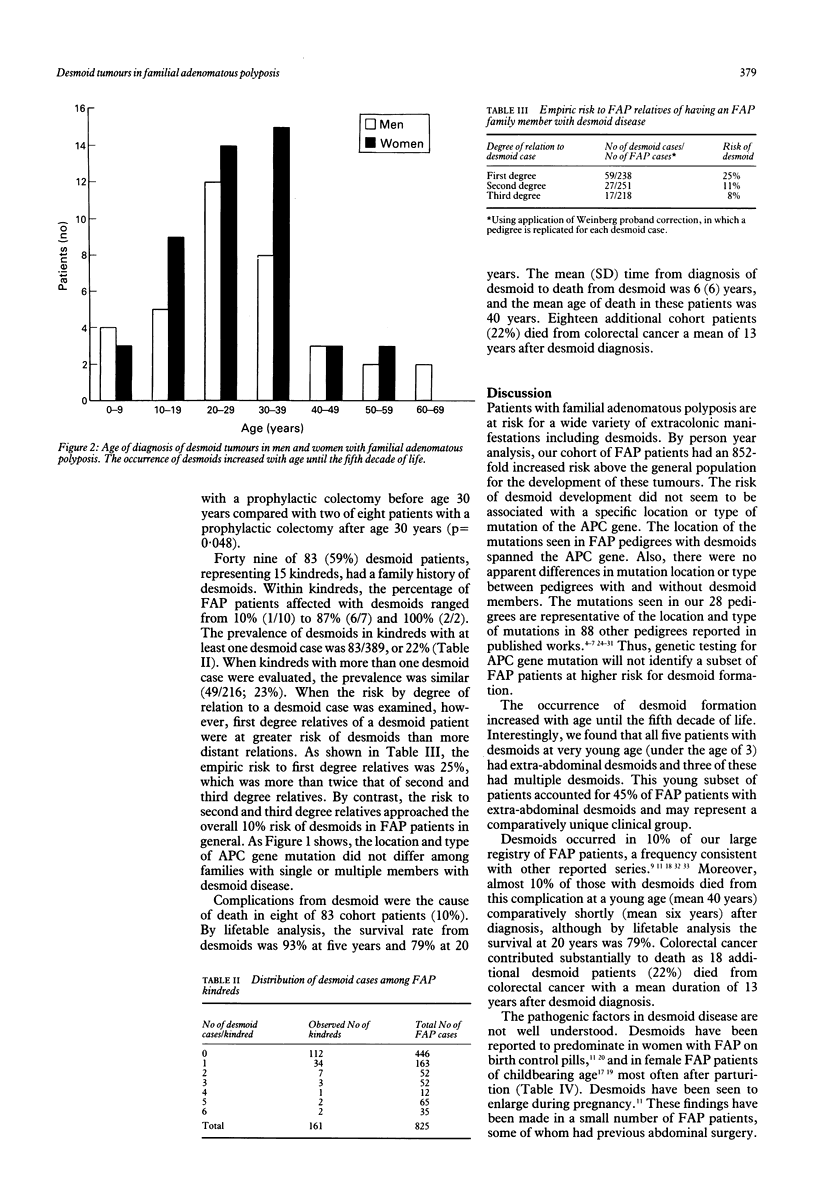
Desmoids are rare, benign fibromatous lesions, which can arise in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), a disorder caused by germline adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene mutation. This study investigated the risk of desmoids in FAP, the relation between specific APC gene mutations and desmoid formation, and the clinical characteristics of FAP patients with desmoids. Eighty three of 825 FAP patients (10%) from 49 of 161 kindreds (30%) had desmoids. The absolute risk of desmoids in FAP patients was 2.56/1000 person years; comparative risk was 852 times the general population. APC gene mutations were similar in families with and without desmoids. The female/male ratio was 1.4 (p = NS). Previous abdominal surgery was noted in 68% of patients with abdominal desmoids (55% developed within five years postoperatively). Desmoid risk in FAP family members of a desmoid patient was 25% in first degree relatives v 8% in third degree relatives. Desmoids are a comparatively common complication of FAP associated with surgical trauma and familial aggregation. Desmoid development was not linked to specific APC gene mutations and was not found predominantly in women. Studies of chemopreventive therapy, given within five years after abdominal surgery, should be considered in FAP patients with a family history of desmoid disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bussey H. J. Extracolonic lesions associated with polyposis coli. Proc R Soc Med. 1972 Mar;65(3):294–294. doi: 10.1177/003591577206500332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottrell S., Bicknell D., Kaklamanis L., Bodmer W. F. Molecular analysis of APC mutations in familial adenomatous polyposis and sporadic colon carcinomas. Lancet. 1992 Sep 12;340(8820):626–630. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92169-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHN I., JONSSON N., LUNDH G. DESMOID TUMOURS. A SERIES OF 33 CASES. Acta Chir Scand. 1963 Oct;126:305–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fee H. J., Elkins R. C., Jones E. L. Gardner's syndrome. Unusual presentation of abdominal pain. Am J Surg. 1972 May;123(5):532–534. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(72)90214-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodde R., van der Luijt R., Wijnen J., Tops C., van der Klift H., van Leeuwen-Cornelisse I., Griffioen G., Vasen H., Khan P. M. Eight novel inactivating germ line mutations at the APC gene identified by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1162–1168. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90032-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groden J., Thliveris A., Samowitz W., Carlson M., Gelbert L., Albertsen H., Joslyn G., Stevens J., Spirio L., Robertson M. Identification and characterization of the familial adenomatous polyposis coli gene. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):589–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey J. C., Quan S. H., Fortner J. G. Gardner's syndrome complicated by mesenteric desmoid tumors. Surgery. 1979 Apr;85(4):475–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwama T., Mishima Y., Utsunomiya J. The impact of familial adenomatous polyposis on the tumorigenesis and mortality at the several organs. Its rational treatment. Ann Surg. 1993 Feb;217(2):101–108. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199302000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. L., Cornell W. P. Gardner's syndrome; review of the literature and report on a family. Arch Surg. 1966 Feb;92(2):287–300. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1966.01320200127020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones I. T., Jagelman D. G., Fazio V. W., Lavery I. C., Weakley F. L., McGannon E. Desmoid tumors in familial polyposis coli. Ann Surg. 1986 Jul;204(1):94–97. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198607000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Järvinen H. J. Desmoid disease as a part of familial adenomatous polyposis coli. Acta Chir Scand. 1987;153(5-6):379–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakousis C. P., Berjian R. A., Lopez R., Rao U. Mesenteric fibromatosis in Gardner's syndrome. Arch Surg. 1978 Aug;113(8):998–1000. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1978.01370200092018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzbrunner B., Ritter S., Domingo J., Rosenthal C. J. Remission of rapidly growing desmoid tumors after tamoxifen therapy. Cancer. 1983 Dec 15;52(12):2201–2204. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19831215)52:12<2201::aid-cncr2820521204>3.0.co;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Nilbert M. C., Su L. K., Vogelstein B., Bryan T. M., Levy D. B., Smith K. J., Preisinger A. C., Hedge P., McKechnie D. Identification of FAP locus genes from chromosome 5q21. Science. 1991 Aug 9;253(5020):661–665. doi: 10.1126/science.1651562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemmer S., Pascoe L., DeCosse J. Occurrence of desmoids in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis of the colon. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Oct;28(2):385–392. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAdam W. A., Goligher J. C. The occurrence of desmoids in patients with familial polyposis coli. Br J Surg. 1970 Aug;57(8):618–631. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800570816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi Y., Ando H., Nagase H., Nishisho I., Horii A., Miki Y., Mori T., Utsunomiya J., Baba S., Petersen G. Germ-line mutations of the APC gene in 53 familial adenomatous polyposis patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4452–4456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagase H., Miyoshi Y., Horii A., Aoki T., Ogawa M., Utsunomiya J., Baba S., Sasazuki T., Nakamura Y. Correlation between the location of germ-line mutations in the APC gene and the number of colorectal polyps in familial adenomatous polyposis patients. Cancer Res. 1992 Jul 15;52(14):4055–4057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishisho I., Nakamura Y., Miyoshi Y., Miki Y., Ando H., Horii A., Koyama K., Utsunomiya J., Baba S., Hedge P. Mutations of chromosome 5q21 genes in FAP and colorectal cancer patients. Science. 1991 Aug 9;253(5020):665–669. doi: 10.1126/science.1651563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitamo J. J., Scheinin T. M., Häyry P. The desmoid syndrome. New aspects in the cause, pathogenesis and treatment of the desmoid tumor. Am J Surg. 1986 Feb;151(2):230–237. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. C., Rogers S. W., Gardner E. J. Spontaneous mesenteric fibromatosis in Gardner's syndrome. Cancer. 1981 Feb 1;47(3):597–601. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810201)47:3<597::aid-cncr2820470329>3.0.co;2-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH W. G. Desmoid tumors in familial multiple polyposis. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 1959 Jan 21;34(2):31–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stella A., Lonoce A., Resta N., Gentile M., Susca F., Mareni C., Brescia G., Origoni P., Montero M. P., Guanti G. Familial adenomatous polyposis: identification of a new frameshift mutation of the APC gene in an Italian family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 15;184(3):1357–1363. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80032-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell W. R., Gerner R. E. Indomethacin and ascorbate inhibit desmoid tumors. J Surg Oncol. 1980;15(1):85–90. doi: 10.1002/jso.2930150113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell W. R. Treatment of intra-abdominal and abdominal wall desmoid tumors with drugs that affect the metabolism of cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate. Ann Surg. 1975 Mar;181(3):299–302. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197503000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis Y., MacDonald F., Rindl P. M., Hulten M., McKeown C., Morton D. G., Keighley M. R., Fodde R., van der Luijt R., Khan P. M. Germline APC mutation familial adenomatous polyposis in Indian family. Lancet. 1992 Oct 24;340(8826):1035–1035. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93045-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



