Abstract
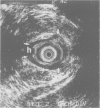
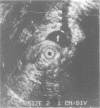
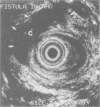
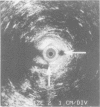
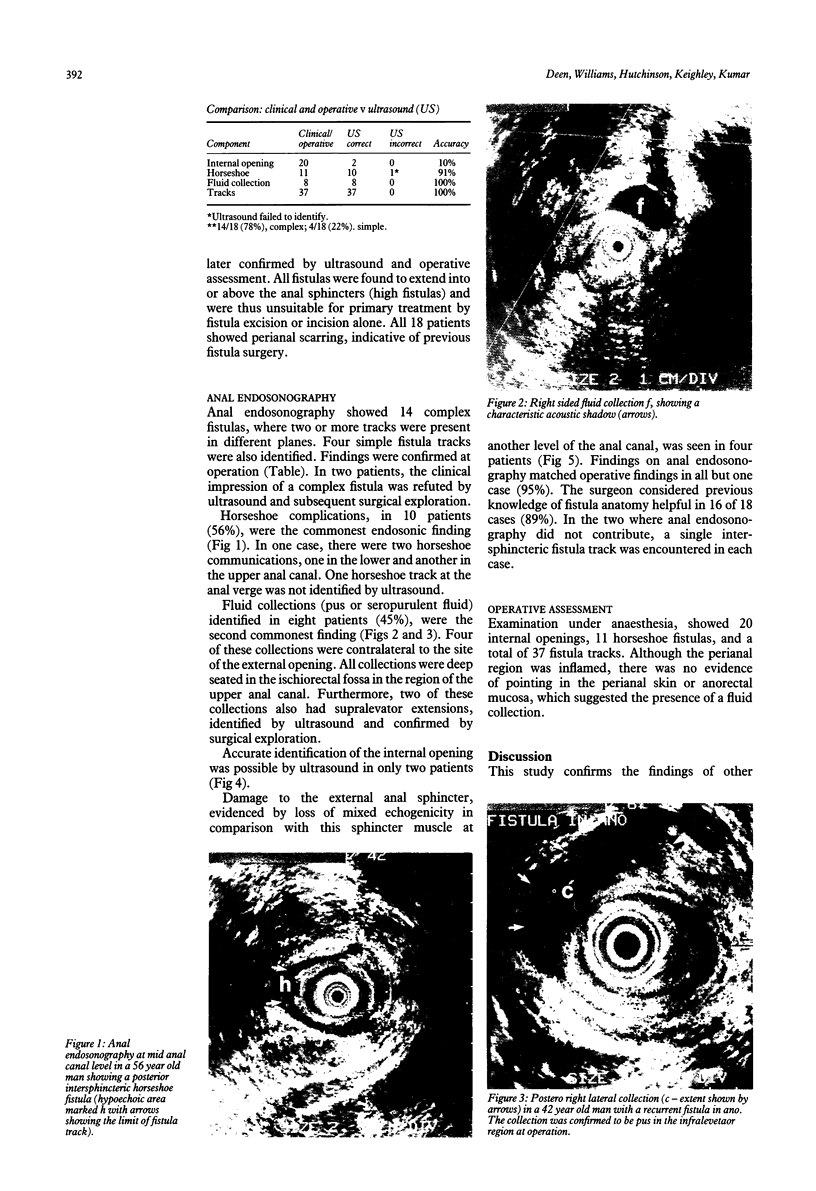
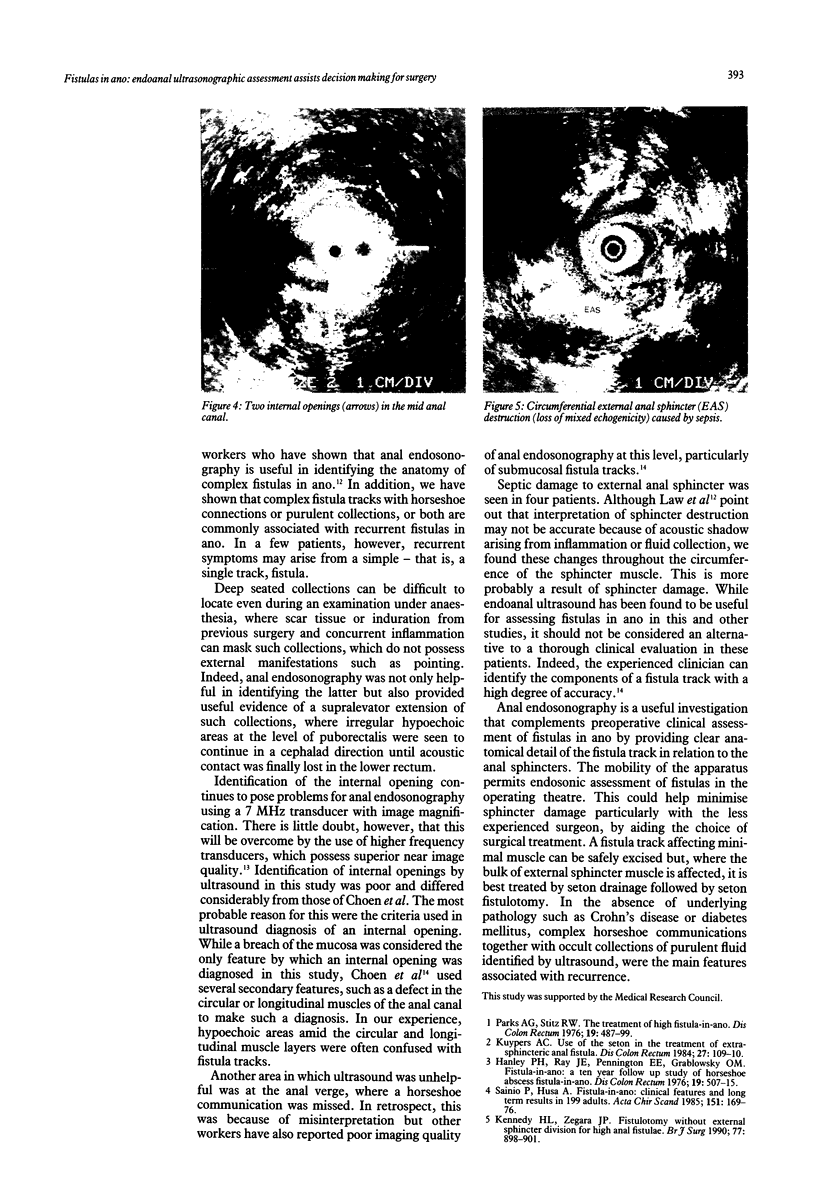
Eighteen patients with a clinical impression of a complex fistula in ano, had anal endosonography to delineate the anatomy of the fistula track and identify associated areas of sepsis. The clinical impression of a complex fistula was refuted by endosonography and subsequent surgical exploration in two cases. Horseshoe tracks were identified in nine (50%) patients and fluid collections, not evident on clinical examination were identified in eight (45%) patients. Accurate identification of the internal opening with a 7 MHz transducer was possible in two (11%) cases. External sphincter damage was evident in four (22%) patients. Surgical findings matched endosonographic appearances in all but one case (94%). Anal endosonography is an accurate and minimally invasive method of delineating the relation of fistula tracks to the anal sphincters and identifying deep areas of sepsis in relation to such fistulas.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Choen S., Burnett S., Bartram C. I., Nicholls R. J. Comparison between anal endosonography and digital examination in the evaluation of anal fistulae. Br J Surg. 1991 Apr;78(4):445–447. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800780418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirocco W. C., Reilly J. C. Challenging the predictive accuracy of Goodsall's rule for anal fistulas. Dis Colon Rectum. 1992 Jun;35(6):537–542. doi: 10.1007/BF02050532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanley P. H., Ray J. E., Pennington E. E., Grablowsky O. M. Fistula-in-ano: a ten-year follow-up study of horseshoe-abscess fistula-in-ano. Dis Colon Rectum. 1976 Sep;19(6):507–515. doi: 10.1007/BF02590943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy H. L., Zegarra J. P. Fistulotomy without external sphincter division for high anal fistulae. Br J Surg. 1990 Aug;77(8):898–901. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800770818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuypers H. C. Use of the seton in the treatment of extrasphincteric anal fistula. Dis Colon Rectum. 1984 Feb;27(2):109–110. doi: 10.1007/BF02553987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law P. J., Talbot R. W., Bartram C. I., Northover J. M. Anal endosonography in the evaluation of perianal sepsis and fistula in ano. Br J Surg. 1989 Jul;76(7):752–755. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800760737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks A. G., Stitz R. W. The treatment of high fistula-in-ano. Dis Colon Rectum. 1976 Sep;19(6):487–499. doi: 10.1007/BF02590941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sainio P., Husa A. Fistula-in-ano. Clinical features and long-term results of surgery in 199 adults. Acta Chir Scand. 1985;151(2):169–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schouten W. R., van Vroonhoven T. J. Treatment of anorectal abscess with or without primary fistulectomy. Results of a prospective randomized trial. Dis Colon Rectum. 1991 Jan;34(1):60–63. doi: 10.1007/BF02050209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Rothenberger D. A., Nemer F. D., Goldberg S. M. Fistula-in-ano in Crohn's disease. Results of aggressive surgical treatment. Dis Colon Rectum. 1991 May;34(5):378–384. doi: 10.1007/BF02053687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]