Abstract
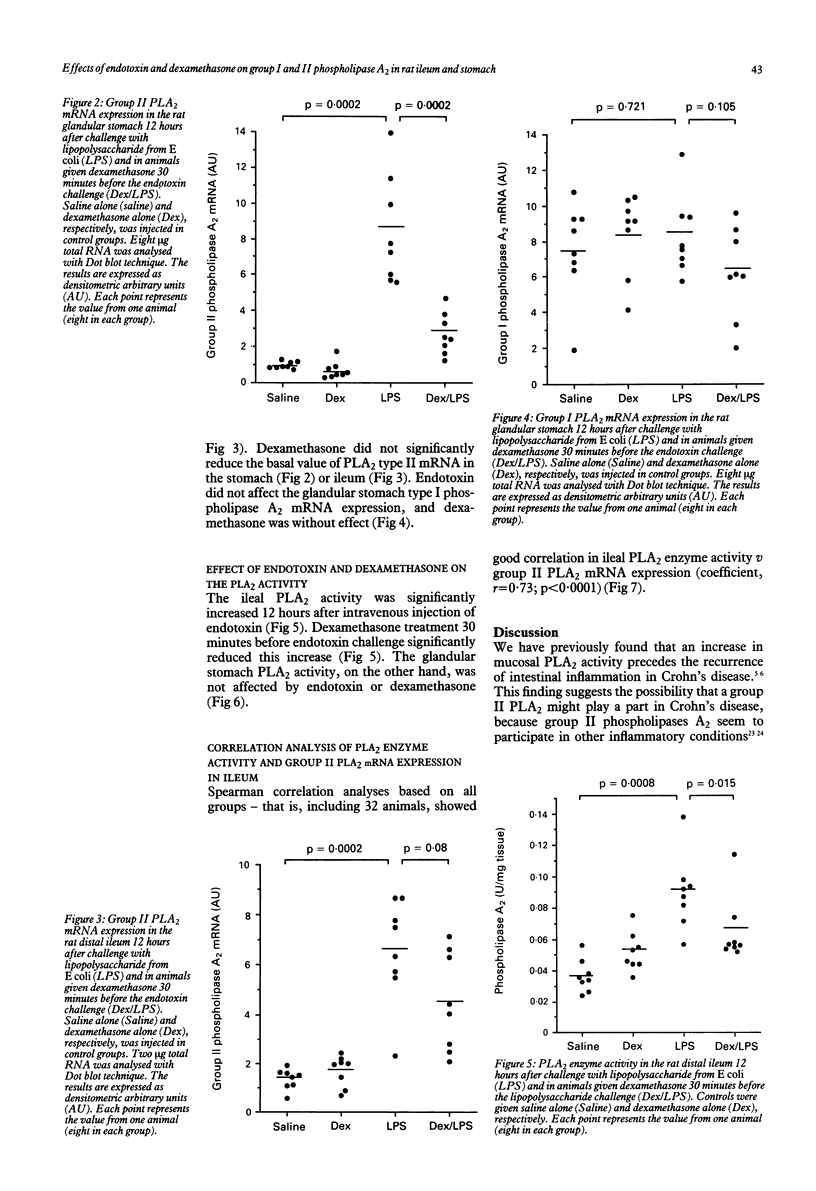
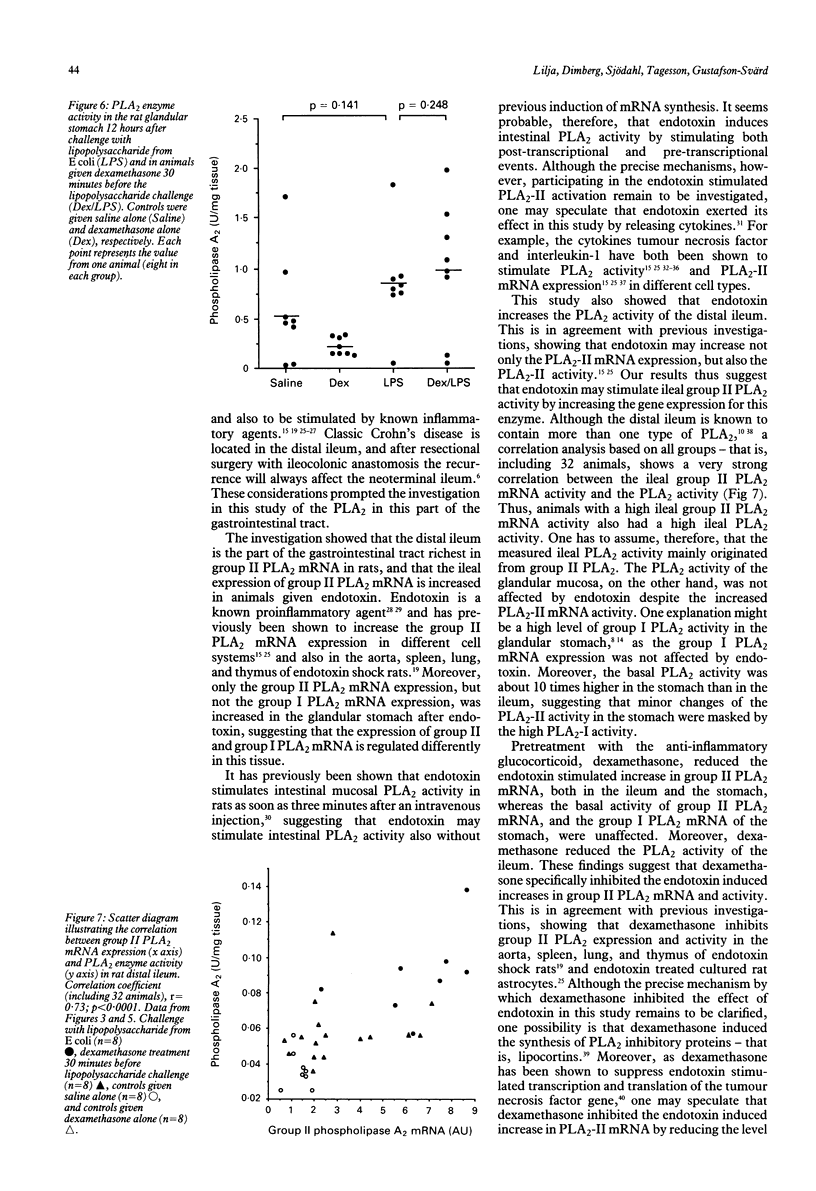
Phospholipase A2 (EC 3.1.1.4) is a key enzyme in inflammation and is thought to play an important part in inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. To investigate the nature and regulation of phospholipase A2 activity in the gastrointestinal mucosa, the distribution of messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) for group II phospholipase A2 in various parts of the rat gastrointestinal tract was studied, as well as the influence of endotoxin or dexamethasone, or both, on the group I and II phospholipase A2 mRNA expression and activity in the rat glandular stomach and distal ileum. The results show that (a) group II phospholipase A2 is present along the whole gastrointestinal tract, but in particularly large amounts in the distal ileum, (b) endotoxin increases group II, but not group I, phospholipase A2 mRNA expression in the glandular stomach and distal ileum, and (c) dexamethasone reduces the endotoxin induced increases in group II phospholipase mRNA expression and activity in the gastrointestinal mucosa. These findings suggest that phospholipase A2 of type II is a mediator of endotoxin effects in the gastrointestinal mucosa and that its expression at the mRNA level can be inhibited by corticosteroids.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomalaski J. S., Steiner M. R., Simon P. L., Clark M. A. IL-1 increases phospholipase A2 activity, expression of phospholipase A2-activating protein, and release of linoleic acid from the murine T helper cell line EL-4. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):155–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozdech J. M., Farmer R. G. Diagnosis of Crohn's disease. Hepatogastroenterology. 1990 Feb;37(1):8–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colten H. R. Tissue-specific regulation of inflammation. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 Jan;72(1):1–7. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.72.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowl R. M., Stoller T. J., Conroy R. R., Stoner C. R. Induction of phospholipase A2 gene expression in human hepatoma cells by mediators of the acute phase response. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2647–2651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitch E. A., Specian R. D., Berg R. D. Induction of early-phase tolerance to endotoxin-induced mucosal injury, xanthine oxidase activation, and bacterial translocation by pretreatment with endotoxin. Circ Shock. 1992 Mar;36(3):208–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimberg J., Gustafson-Svärd C., Weström B., Tagesson C., Söderkvist P. Group I phospholipase A2 mRNA expression in rat glandular stomach and pancreas. Ontogenic development and effects of cortisone acetate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Feb 28;1130(1):47–51. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90460-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gassama-Diagne A., Rogalle P., Fauvel J., Willson M., Klaébé A., Chap H. Substrate specificity of phospholipase B from guinea pig intestine. A glycerol ester lipase with broad specificity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13418–13424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson-Svärd C., Tagesson C., Boll R. M., Kald B. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha potentiates phospholipase A2-stimulated release and metabolism of arachidonic acid in cultured intestinal epithelial cells (INT 407). Scand J Gastroenterol. 1993 Apr;28(4):323–330. doi: 10.3109/00365529309090250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrikson R. L., Krueger E. T., Keim P. S. Amino acid sequence of phospholipase A2-alpha from the venom of Crotalus adamanteus. A new classification of phospholipases A2 based upon structural determinants. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4913–4921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inada M., Tojo H., Kawata S., Tarui S., Okamoto M. Induction of group II-like phospholipase A2 by lipopolysaccharide in the liver of BCG-primed rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 14;174(3):1077–1083. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91530-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaki J., Ohara O., Nakamura E., Tamaki M., Ono T., Kanda A., Yoshida N., Teraoka H., Tojo H., Okamoto M. cDNA cloning and sequence determination of rat membrane-associated phospholipase A2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):1030–1036. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90777-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kald B., Olaison G., Sjödahl R., Tagesson C. Novel aspect of Crohn's disease: increased content of platelet-activating factor in ileal and colonic mucosa. Digestion. 1990;46(4):199–204. doi: 10.1159/000200346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Hession C., Johansen B., Hayes G., McGray P., Chow E. P., Tizard R., Pepinsky R. B. Structure and properties of a human non-pancreatic phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5768–5775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurihara H., Nakano T., Takasu N., Arita H. Intracellular localization of group II phospholipase A2 in rat vascular smooth muscle cells and its possible relationship to eicosanoid formation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 3;1082(3):285–292. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(91)90204-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauritsen K., Laursen L. S., Bukhave K., Rask-Madsen J. In vivo profiles of eicosanoids in ulcerative colitis, Crohn's colitis, and Clostridium difficile colitis. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jul;95(1):11–17. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90284-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauritsen K., Laursen L. S., Bukhave K., Rask-Madsen J. Inflammatory intermediaries in inflammatory bowel disease. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1989;4(2):75–90. doi: 10.1007/BF01646865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansbach C. M., 2nd Phospholipases: old enzymes with new meaning. Gastroenterology. 1990 May;98(5 Pt 1):1369–1382. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90359-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami T., Tojo H., Shinomura Y., Tarui S., Okamoto M. Raised serum activity of phospholipase A2 immunochemically related to group II enzyme in inflammatory bowel disease: its correlation with disease activity of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1992 Jul;33(7):914–921. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.7.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee A. B., Cordella-Miele E., Miele L. Regulation of extracellular phospholipase A2 activity: implications for inflammatory diseases. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;11(3):233–243. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Arita H. Enhanced expression of group II phospholipase A2 gene in the tissues of endotoxin shock rats and its suppression by glucocorticoid. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 29;273(1-2):23–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81042-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Ohara O., Teraoka H., Arita H. Group II phospholipase A2 mRNA synthesis is stimulated by two distinct mechanisms in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 12;261(1):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80663-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara O., Tamaki M., Nakamura E., Tsuruta Y., Fujii Y., Shin M., Teraoka H., Okamoto M. Dog and rat pancreatic phospholipases A2: complete amino acid sequences deduced from complementary DNAs. J Biochem. 1986 Mar;99(3):733–739. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka S., Arita H. Inflammatory factors stimulate expression of group II phospholipase A2 in rat cultured astrocytes. Two distinct pathways of the gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9956–9960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olaison G., Sjödahl R., Tagesson C. Increased phospholipase A2 activity of Ileal mucosa in Crohn's disease. Digestion. 1988;41(3):136–141. doi: 10.1159/000199765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parant M., Le Contel C., Parant F., Chedid L. Influence of endogenous glucocorticoid on endotoxin-induced production of circulating TNF-alpha. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 1991 Aug;10(4):265–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pind S., Kuksis A. Association of the intestinal brush-border membrane phospholipase A2 and lysophospholipase activities (phospholipase B) with a stalked membrane protein. Lipids. 1989 May;24(5):357–362. doi: 10.1007/BF02535141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata T., Nakamura E., Tsuruta Y., Tamaki M., Teraoka H., Tojo H., Ono T., Okamoto M. Presence of pancreatic-type phospholipase A2 mRNA in rat gastric mucosa and lung. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 23;1007(1):124–126. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90141-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalkwijk C., Pfeilschifter J., Märki F., van den Bosch H. Interleukin-1 beta, tumor necrosis factor and forskolin stimulate the synthesis and secretion of group II phospholipase A2 in rat mesangial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 15;174(1):268–275. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90515-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalkwijk C., Vervoordeldonk M., Pfeilschifter J., Märki F., van den Bosch H. Cytokine- and forskolin-induced synthesis of group II phospholipase A2 and prostaglandin E2 in rat mesangial cells is prevented by dexamethasone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 15;180(1):46–52. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81252-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senegas-Balas F., Balas D., Verger R., de Caro A., Figarella C., Ferrato F., Lechene P., Bertrand C., Ribet A. Immunohistochemical localization of intestinal phospholipase A2 in rat paneth cells. Histochemistry. 1984;81(6):581–584. doi: 10.1007/BF00489538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakir K. M., O'Brian J. T., Gartner S. L. Enhanced phospholipase A2 activity in rat plasma, liver, and intestinal mucosa following endotoxin treatment: a possible explanation for the protective effect of indomethacin in endotoxic shock. Metabolism. 1985 Feb;34(2):176–182. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(85)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon P., Stenson W. F. Enhanced synthesis of leukotriene B4 by colonic mucosa in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1984 Mar;86(3):453–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara H., Amabe Y., Komatsubara T., Tojo H., Okamoto M., Wakano Y., Ishida H. Group II phospholipase A2 induced by interleukin-1 beta in cultured rat gingival fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jun 8;304(1):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80591-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smedh K., Olaison G., Sjödahl R. Initiation of anastomotic recurrence of Crohn's disease after ileocolic resection. Onset proximal to the junction and preceded by increased phospholipase A2 activity. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1992 Aug;27(8):691–694. doi: 10.3109/00365529209000141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solito E., Raugei G., Melli M., Parente L. Dexamethasone induces the expression of the mRNA of lipocortin 1 and 2 and the release of lipocortin 1 and 5 in differentiated, but not undifferentiated U-937 cells. FEBS Lett. 1991 Oct 21;291(2):238–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81293-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagesson C., Sjödahl R. Studies of the phospholipase A2 activity of rat ileal mucosa. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1985 Jan;20(1):25–30. doi: 10.3109/00365528509089628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Pruzanski W., Stefanski E., Ellies L. G., Aubin J. E., Sos A., Melcher A. Extracellular phospholipase A2 secretion is a common effector pathway of interleukin-1 and tumour necrosis factor action. Immunol Lett. 1991 Jun;28(3):187–193. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(91)90002-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Scott K., Smith G., Rajkovic I., Stefanski E., Schouten B. D., Singh R., Pruzanski W. Serum phospholipase A2 enzyme activity and immunoreactivity in a prospective analysis of patients with septic shock. Life Sci. 1992;50(11):807–811. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90186-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



