Abstract
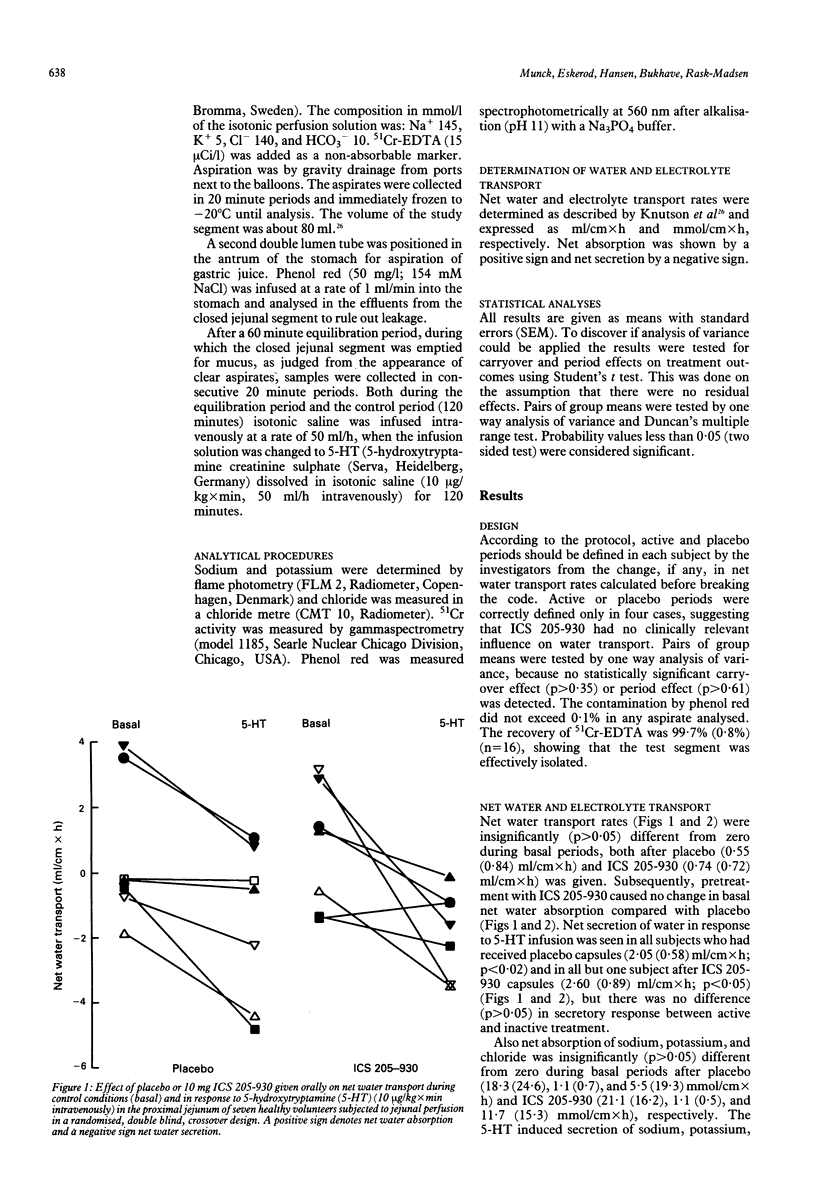
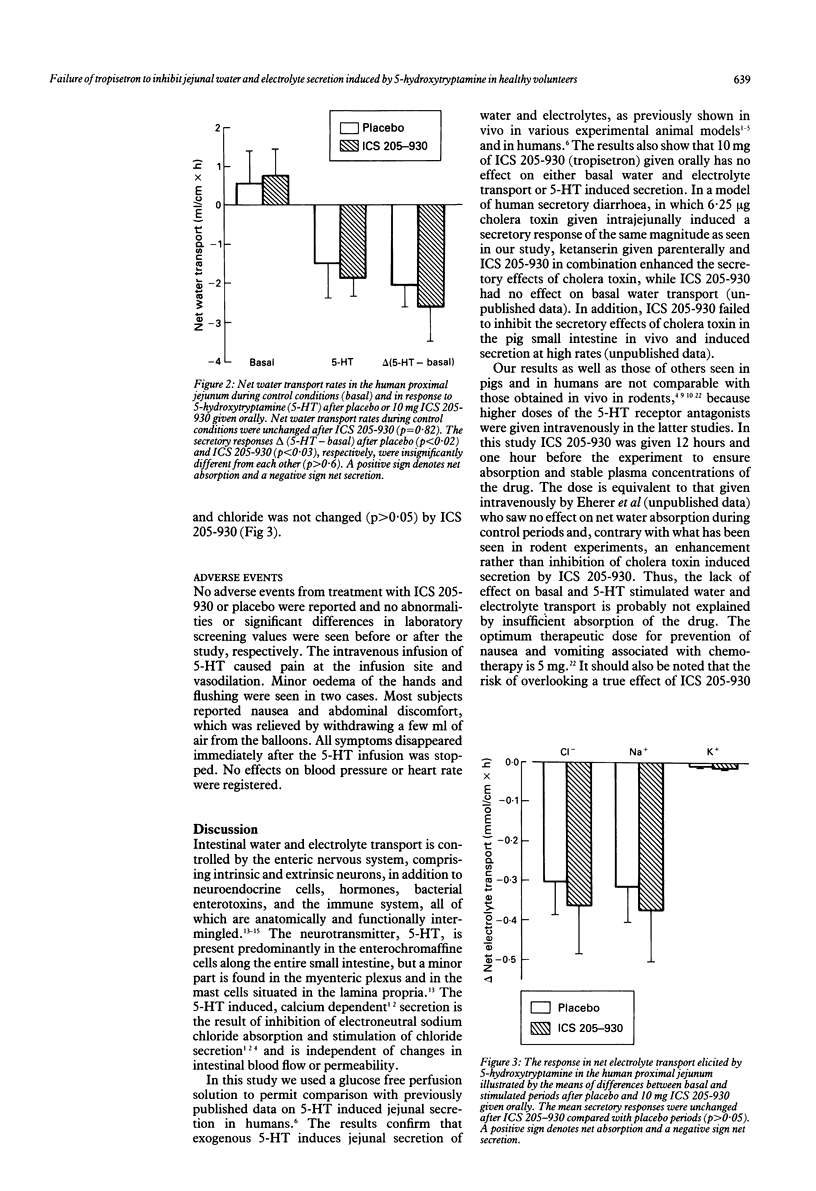
The effects of the 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT3) receptor antagonist, ICS 205-930 (tropisetron), on basal and 5-HT induced jejunal secretion of water and electrolytes were examined using a double blind, randomised crossover design. In seven healthy volunteers steady state perfusions of the proximal jejunum were performed twice with the Loc-I-Gut tube after 5+5 mg ICS 205-930 or placebo capsules were given. After equilibration for 60 minutes and completion of a 120 minute basal period 5-HT (10 micrograms/kg x min intravenously) was infused for 120 minutes. Net water absorption (mean (SEM)) in the basal period was 0.55 (0.84) ml/cm x h and 0.74 (0.72) ml/cm x h after placebo and ICS 205-930, respectively (p > 0.05). Infusion of 5-HT caused significant net secretion of water after placebo (2.05 (0.58) ml/cm x h; p < 0.02) as well as ICS 205-930 (2.60 (0.89) ml/cm x h; p < 0.05). As ICS 205-930 excerted no effects on either basal or 5-HT induced water and electrolyte transport in the intact human jejunum the compound is probably not efficacious as an anti-secretory drug in patients with 5-HT induced diarrhoea.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Accarino A. M., Azpiroz F., Malagelada J. R. Symptomatic responses to stimulation of sensory pathways in the jejunum. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 1):G673–G677. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.263.5.G673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. V., Coupe M. O., Morris J. A., Hodgson H. J., Bloom S. R. Remission of symptoms in carcinoid syndrome with a new 5-hydroxytryptamine M receptor antagonist. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 May 2;294(6580):1129–1129. doi: 10.1136/bmj.294.6580.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bern M. J., Sturbaum C. W., Karayalcin S. S., Berschneider H. M., Wachsman J. T., Powell D. W. Immune system control of rat and rabbit colonic electrolyte transport. Role of prostaglandins and enteric nervous system. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jun;83(6):1810–1820. doi: 10.1172/JCI114086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berschneider H. M., Powell D. W. Fibroblasts modulate intestinal secretory responses to inflammatory mediators. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):484–489. doi: 10.1172/JCI115610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beubler E., Badhri P., Schirgi-Degen A. 5-HT receptor antagonists and heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin-induced effects in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep 4;219(3):445–450. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90486-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beubler E., Horina G. 5-HT2 and 5-HT3 receptor subtypes mediate cholera toxin-induced intestinal fluid secretion in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1990 Jul;99(1):83–89. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91233-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beubler E., Kollar G., Saria A., Bukhave K., Rask-Madsen J. Involvement of 5-hydroxytryptamine, prostaglandin E2, and cyclic adenosine monophosphate in cholera toxin-induced fluid secretion in the small intestine of the rat in vivo. Gastroenterology. 1989 Feb;96(2 Pt 1):368–376. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91560-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunsson I., Sjöqvist A., Jodal M., Lundgren O. Mechanisms underlying the small intestinal fluid secretion caused by arachidonic acid, prostaglandin E1 and prostaglandin E2 in the rat in vivo. Acta Physiol Scand. 1987 Aug;130(4):633–642. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1987.tb08186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchheit K. H. Inhibition of cholera toxin-induced intestinal secretion by the 5-HT3 receptor antagonist ICS 205-930. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;339(6):704–705. doi: 10.1007/BF00168665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J., Wang Y. Z., Frieling T., Wood J. D. Neural 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors regulate chloride secretion in guinea pig distal colon. Am J Physiol. 1991 Nov;261(5 Pt 1):G833–G840. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.261.5.G833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe S. E., Perdue M. H. Gastrointestinal food hypersensitivity: basic mechanisms of pathophysiology. Gastroenterology. 1992 Sep;103(3):1075–1095. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donowitz M., Binder H. J. Jejunal fluid and electrolyte secretion in carcinoid syndrome. Am J Dig Dis. 1975 Dec;20(12):1115–1122. doi: 10.1007/BF01070754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donowitz M., Tai Y. H., Asarkof N. Effect of serotonin on active electrolyte transport in rabbit ileum, gallbladder, and colon. Am J Physiol. 1980 Dec;239(6):G463–G472. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1980.239.6.G463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardcastle J., Hardcastle P. T., Redfern J. S. Action of 5-hydroxytryptamine on intestinal ion transport in the rat. J Physiol. 1981 Nov;320:41–55. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendriks R., Bornstein J. C., Furness J. B. Evidence for two types of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor on secretomotor neurons of the guinea-pig ileum. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Apr;339(4):409–414. doi: 10.1007/BF00736055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itasaka S., Shiratori K., Takahashi T., Ishikawa M., Kaneko K., Suzuki Y. Stimulation of intramural secretory reflex by luminal distension pressure in rat distal colon. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jul;263(1 Pt 1):G108–G114. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.263.1.G108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson L., Odlind B., Hällgren R. A new technique for segmental jejunal perfusion in man. Am J Gastroenterol. 1989 Oct;84(10):1278–1284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan K., Kane A., Asarkof N., Wicks J., Guerina V., Kellum J., Baron S., Gintzler A. R., Donowitz M. Entamoeba histolytica causes intestinal secretion: role of serotonin. Science. 1983 Aug 19;221(4612):762–764. doi: 10.1126/science.6308760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misiewicz J. J., Waller S. L., Kiley N. Effect of oral prostaglandin E1 on intestinal transit in man. Lancet. 1969 Mar 29;1(7596):648–651. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck L. K., Mertz-Nielsen A., Westh H., Bukhave K., Beubler E., Rask-Madsen J. Prostaglandin E2 is a mediator of 5-hydroxytryptamine induced water and electrolyte secretion in the human jejunum. Gut. 1988 Oct;29(10):1337–1341. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.10.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson O., Cassuto J., Larsson P. A., Jodal M., Lidberg P., Ahlman H., Dahlström A., Lundgren O. 5-Hydroxytryptamine and cholera secretion: a histochemical and physiological study in cats. Gut. 1983 Jun;24(6):542–548. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.6.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rask-Madsen J., Bukhave K., Beubler E. Influence on intestinal secretion of eicosanoids. J Intern Med Suppl. 1990;732:137–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.1990.tb01486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöqvist A., Cassuto J., Jodal M., Lundgren O. Actions of serotonin antagonists on cholera-toxin-induced intestinal fluid secretion. Acta Physiol Scand. 1992 Jul;145(3):229–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1992.tb09360.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobhani I., Vidon N., Huchet B., Rambaud J. C. Human jejunal secretion induced by prostaglandin E1: a dose-response study. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;31(4):433–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1991.tb05559.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinner M. J., McFadden D., Sherlock D., Jaffe B. M. Verapamil reversal of serotonin-induced jejunal secretion of water and electrolytes in awake dogs. Gastroenterology. 1986 Mar;90(3):515–519. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)91102-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn K. M. Tropisetron. A review of the clinical experience. Drugs. 1992;43 (Suppl 3):11–22. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199200433-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


