Abstract
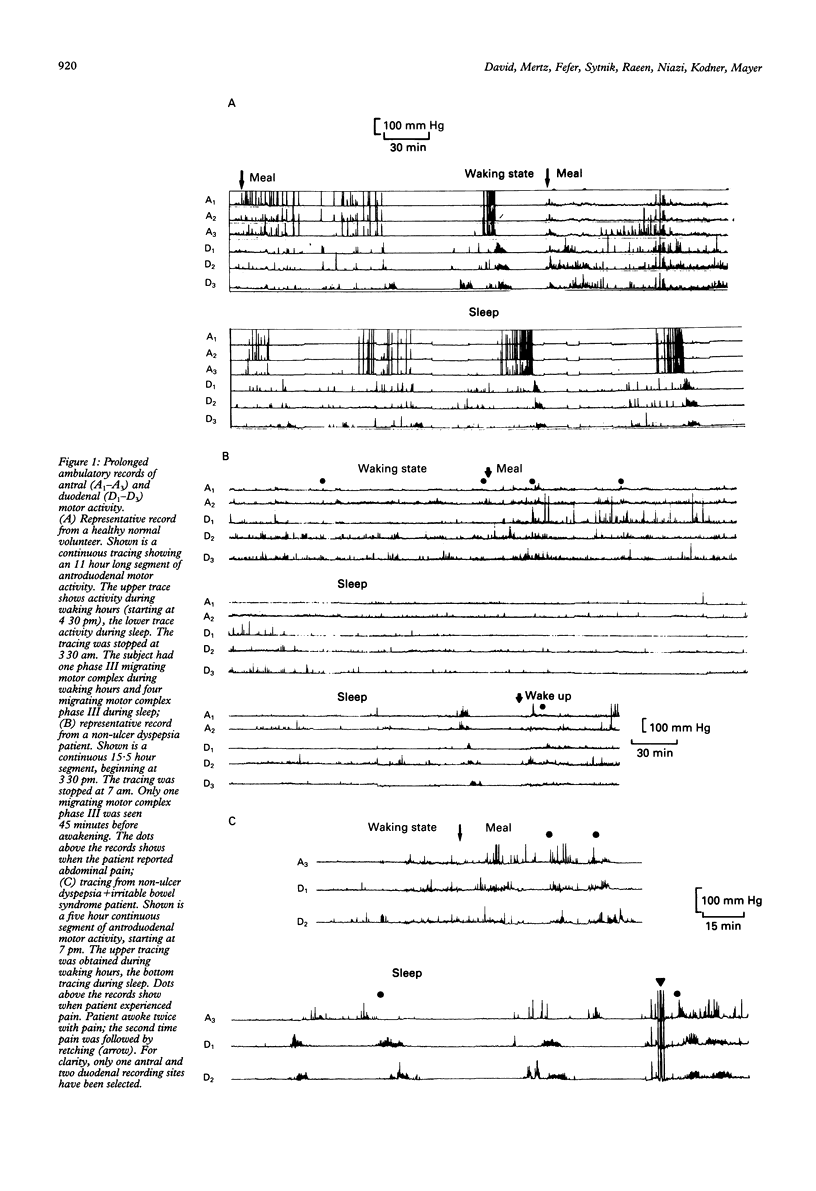
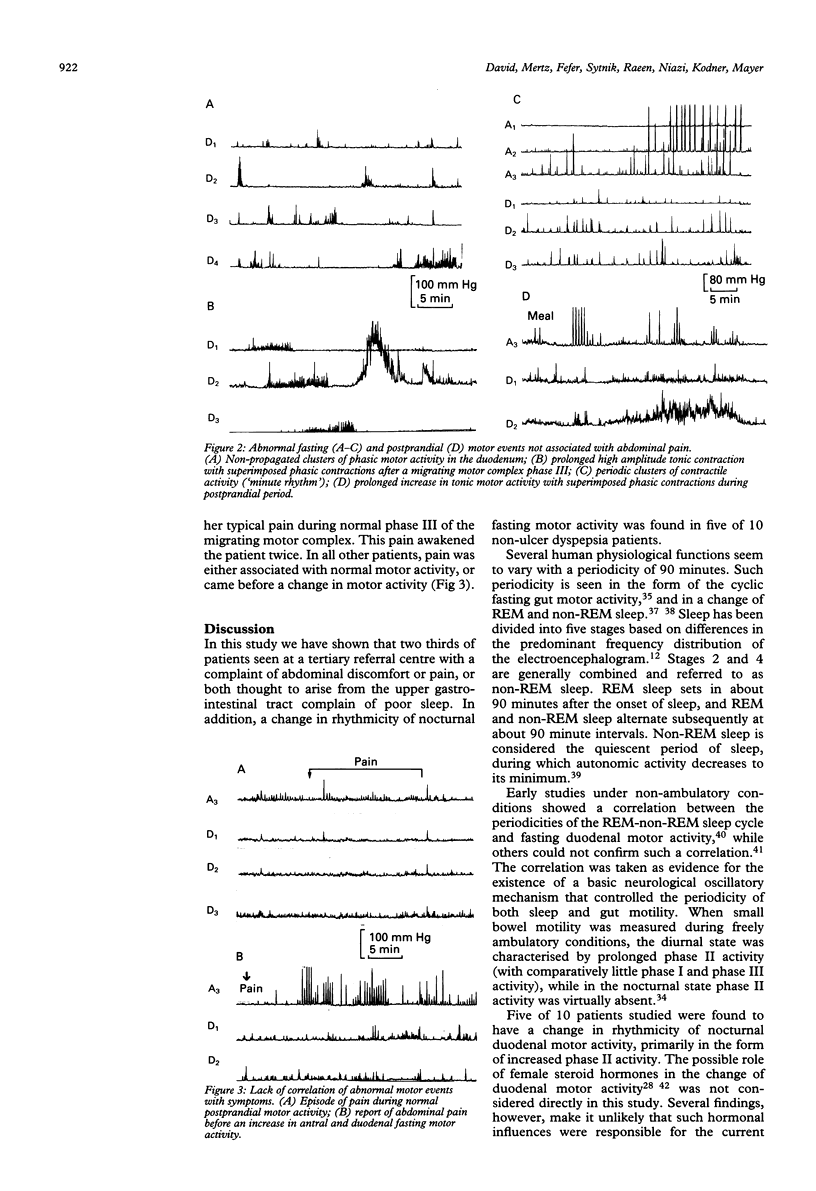
The prevalence of sleep disturbances was studied in patients with severe non-ulcer dyspepsia. It was also considered if the change in sleep pattern was associated with changes in the rhythmic fasting motor activity of the gastrointestinal tract, and if motor events correlate with the patient's symptoms. Motor activity in the duodenum was monitored over a 24 hour period under freely ambulatory conditions in 10 healthy controls and in 10 patients with severe non-ulcer dyspepsia using a transnasally placed catheter with six solid state pressure transducers connected to a digital data logging device. Symptoms and sleep disturbance were assessed by questionnaire and diary. Based on their symptoms, the patients were separated into two groups: those with dyspepsia symptoms only (non-ulcer dyspepsia; n = 5) and those with dyspepsia and additional functional symptoms thought to arise from the lower gastrointestinal tract (non-ulcer dyspepsia+irritable bowel syndrome; n = 5). When compared with either the control or the non-ulcer dyspepsia+irritable bowel syndrome group, non-ulcer dyspepsia patients had a considerably decreased number of migrating motor complexes during the nocturnal period (0.7 v 4.6), a decreased percentage of nocturnal phase I (5.2% v 78.0%), and an increased percentage of the nocturnal period in phase II (94% v 15.4%). Patients with non-ulcer dyspepsia+irritable bowel syndrome were not different from normal controls. Four of the non-ulcer dyspepsia patients and all of the non-ulcer dyspepsia+irritable bowel syndrome patients reported difficulties with sleep. Clusters of high amplitude tonic and phasic activity, not accompanied by subjective reports of discomfort were noted in several patients in both groups during the study. In eight of 10 patients, abdominal pain was reported during normal motor activity, while in one patient, pain correlated with phase III of the migrating motor complex. In contrast with previous reports in patients with irritable bowel syndrome, our findings suggest an abnormality of diurnal rhythmicity--shown in changed sleep and changed rhythmic duodenal motor activity--in patients with chronic abdominal pain thought to arise from the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbara L., Camilleri M., Corinaldesi R., Crean G. P., Heading R. C., Johnson A. G., Malagelada J. R., Stanghellini V., Wienbeck M. Definition and investigation of dyspepsia. Consensus of an international ad hoc working party. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 Aug;34(8):1272–1276. doi: 10.1007/BF01537277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boissevain M. D., McCain G. A. Toward an integrated understanding of fibromyalgia syndrome. I. Medical and pathophysiological aspects. Pain. 1991 Jun;45(3):227–238. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(91)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce L. A., Behsudi F. M. Progesterone effects on three regional gastrointestinal tissues. Life Sci. 1979 Aug 27;25(9):729–734. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilleri M., Neri M. Motility disorders and stress. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 Nov;34(11):1777–1786. doi: 10.1007/BF01540058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chediak A. D., Demirozu M. C., Nay K. N. Alpha EEG sleep produced by balloon catheterization of the esophagus. Sleep. 1990 Aug;13(4):369–370. doi: 10.1093/sleep/13.4.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. A., Diamant N. E. Small intestinal motility in fasted and postprandial states: effect of transient vagosympathetic blockade. Am J Physiol. 1987 Mar;252(3 Pt 1):G301–G308. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.252.3.G301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J., Dodds W. J., Friedman R. H., Sekiguchi T., Hogan W. J., Arndorfer R. C., Petrie D. J. Mechanism of gastroesophageal reflux in recumbent asymptomatic human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):256–267. doi: 10.1172/JCI109667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everson G. T. Gastrointestinal motility in pregnancy. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1992 Dec;21(4):751–776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch P. M., Ingram D. M., Henstridge J. D., Catchpole B. N. Relationship of fasting gastroduodenal motility to the sleep cycle. Gastroenterology. 1982 Sep;83(3):605–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann E. The 90-minute sleep-dream cycle. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1968 Mar;18(3):280–286. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1968.01740030024004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellow J. E., Borody T. J., Phillips S. F., Tucker R. L., Haddad A. C. Human interdigestive motility: variations in patterns from esophagus to colon. Gastroenterology. 1986 Aug;91(2):386–395. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90573-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellow J. E., Gill R. C., Wingate D. L. Prolonged ambulant recordings of small bowel motility demonstrate abnormalities in the irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1990 May;98(5 Pt 1):1208–1218. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90335-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellow J. E., Gill R. C., Wingate D. L. Prolonged ambulant recordings of small bowel motility demonstrate abnormalities in the irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1990 May;98(5 Pt 1):1208–1218. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90335-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellow J. E., Phillips S. F. Altered small bowel motility in irritable bowel syndrome is correlated with symptoms. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jun;92(6):1885–1893. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90620-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerlin P. Postprandial antral hypomotility in patients with idiopathic nausea and vomiting. Gut. 1989 Jan;30(1):54–59. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein K. B. Controlled treatment trials in the irritable bowel syndrome: a critique. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jul;95(1):232–241. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90319-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar D., Thompson P. D., Wingate D. L., Vesselinova-Jenkins C. K., Libby G. Abnormal REM sleep in the irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1992 Jul;103(1):12–17. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91089-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malagelada J. R., Stanghellini V. Manometric evaluation of functional upper gut symptoms. Gastroenterology. 1985 May;88(5 Pt 1):1223–1231. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning A. P., Thompson W. G., Heaton K. W., Morris A. F. Towards positive diagnosis of the irritable bowel. Br Med J. 1978 Sep 2;2(6138):653–654. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6138.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max M. B., Culnane M., Schafer S. C., Gracely R. H., Walther D. J., Smoller B., Dubner R. Amitriptyline relieves diabetic neuropathy pain in patients with normal or depressed mood. Neurology. 1987 Apr;37(4):589–596. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.4.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxton D. G., Morris J., Whorwell P. J. More accurate diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome by the use of 'non-colonic' symptomatology. Gut. 1991 Jul;32(7):784–786. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.7.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCain G. A., Scudds R. A. The concept of primary fibromyalgia (fibrositis): clinical value, relation and significance to other chronic musculoskeletal pain syndromes. Pain. 1988 Jun;33(3):273–287. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(88)90285-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mearin F., Cucala M., Azpiroz F., Malagelada J. R. The origin of symptoms on the brain-gut axis in functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology. 1991 Oct;101(4):999–1006. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90726-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldofsky H., Scarisbrick P. Induction of neurasthenic musculoskeletal pain syndrome by selective sleep stage deprivation. Psychosom Med. 1976 Jan-Feb;38(1):35–44. doi: 10.1097/00006842-197601000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldofsky H. Sleep and fibrositis syndrome. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1989 Feb;15(1):91–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr W. C., Robinson M. G. The sleeping gut. Med Clin North Am. 1981 Nov;65(6):1359–1376. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31476-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott L. D., Lester R., Van Thiel D. H., Wald A. Pregnancy-related changes in small intestinal myoelectric activity in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1983 Feb;84(2):301–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talley N. J., Camilleri M., Orkin B. A., Kramlinger K. G. Effect of cyclical unipolar depression on upper gastrointestinal motility and sleep. Gastroenterology. 1989 Sep;97(3):775–777. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90653-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talley N. J., Phillips S. F., Melton J., 3rd, Wiltgen C., Zinsmeister A. R. A patient questionnaire to identify bowel disease. Ann Intern Med. 1989 Oct 15;111(8):671–674. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-111-8-671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talley N. J., Phillips S. F. Non-ulcer dyspepsia: potential causes and pathophysiology. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Jun;108(6):865–879. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-6-865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talley N. J., Phillips S. F., Wiltgen C. M., Zinsmeister A. R., Melton L. J., 3rd Assessment of functional gastrointestinal disease: the bowel disease questionnaire. Mayo Clin Proc. 1990 Nov;65(11):1456–1479. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)62169-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talley N. J., Shuter B., McCrudden G., Jones M., Hoschl R., Piper D. W. Lack of association between gastric emptying of solids and symptoms in nonulcer dyspepsia. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1989 Dec;11(6):625–630. doi: 10.1097/00004836-198912000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talley N. J. Spectrum of chronic dyspepsia in the presence of the irritable bowel syndrome. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1991;182:7–10. doi: 10.3109/00365529109109530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talley N. J., Zinsmeister A. R., Schleck C. D., Melton L. J., 3rd Dyspepsia and dyspepsia subgroups: a population-based study. Gastroenterology. 1992 Apr;102(4 Pt 1):1259–1268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triadafilopoulos G., Simms R. W., Goldenberg D. L. Bowel dysfunction in fibromyalgia syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 1991 Jan;36(1):59–64. doi: 10.1007/BF01300088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veale D., Kavanagh G., Fielding J. F., Fitzgerald O. Primary fibromyalgia and the irritable bowel syndrome: different expressions of a common pathogenetic process. Br J Rheumatol. 1991 Jun;30(3):220–222. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/30.3.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldron B., Cullen P. T., Kumar R., Smith D., Jankowski J., Hopwood D., Sutton D., Kennedy N., Campbell F. C. Evidence for hypomotility in non-ulcer dyspepsia: a prospective multifactorial study. Gut. 1991 Mar;32(3):246–251. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.3.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whorwell P. J., McCallum M., Creed F. H., Roberts C. T. Non-colonic features of irritable bowel syndrome. Gut. 1986 Jan;27(1):37–40. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunus M., Masi A. T., Calabro J. J., Miller K. A., Feigenbaum S. L. Primary fibromyalgia (fibrositis): clinical study of 50 patients with matched normal controls. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Aug;11(1):151–171. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(81)90096-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


