Abstract
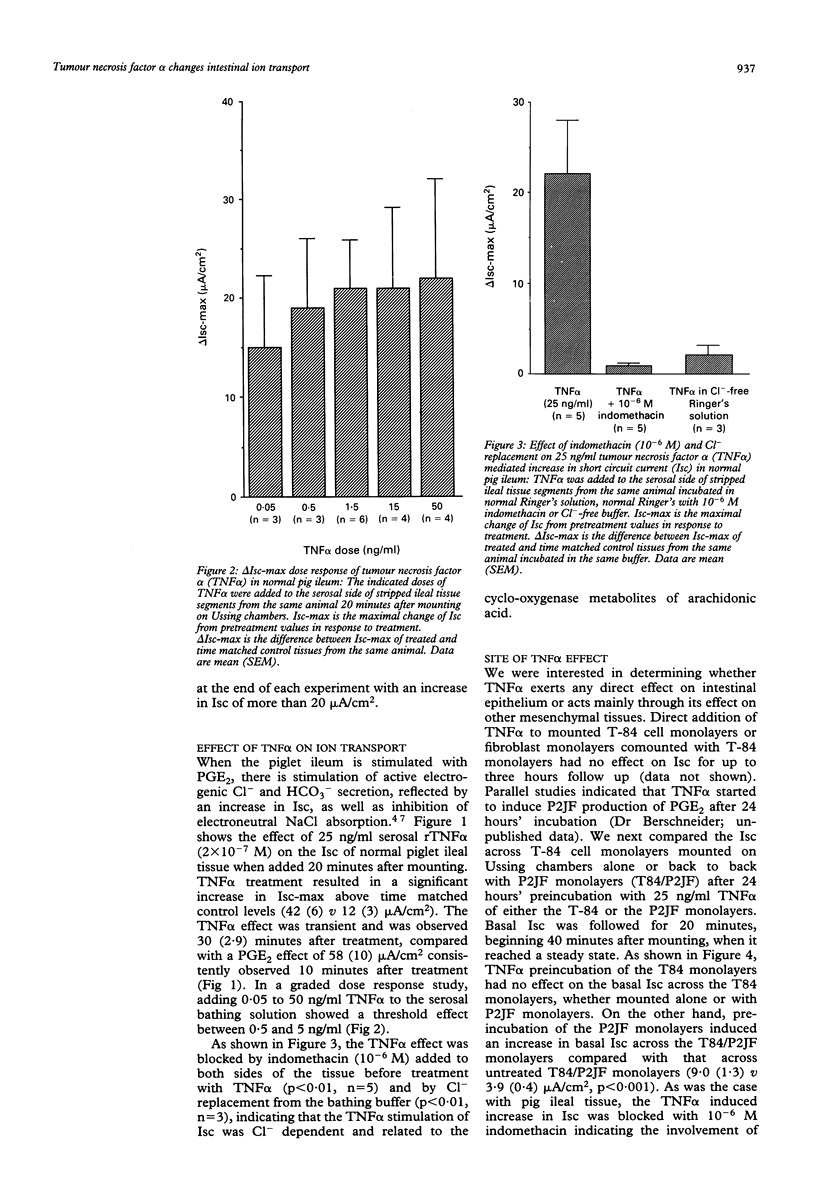
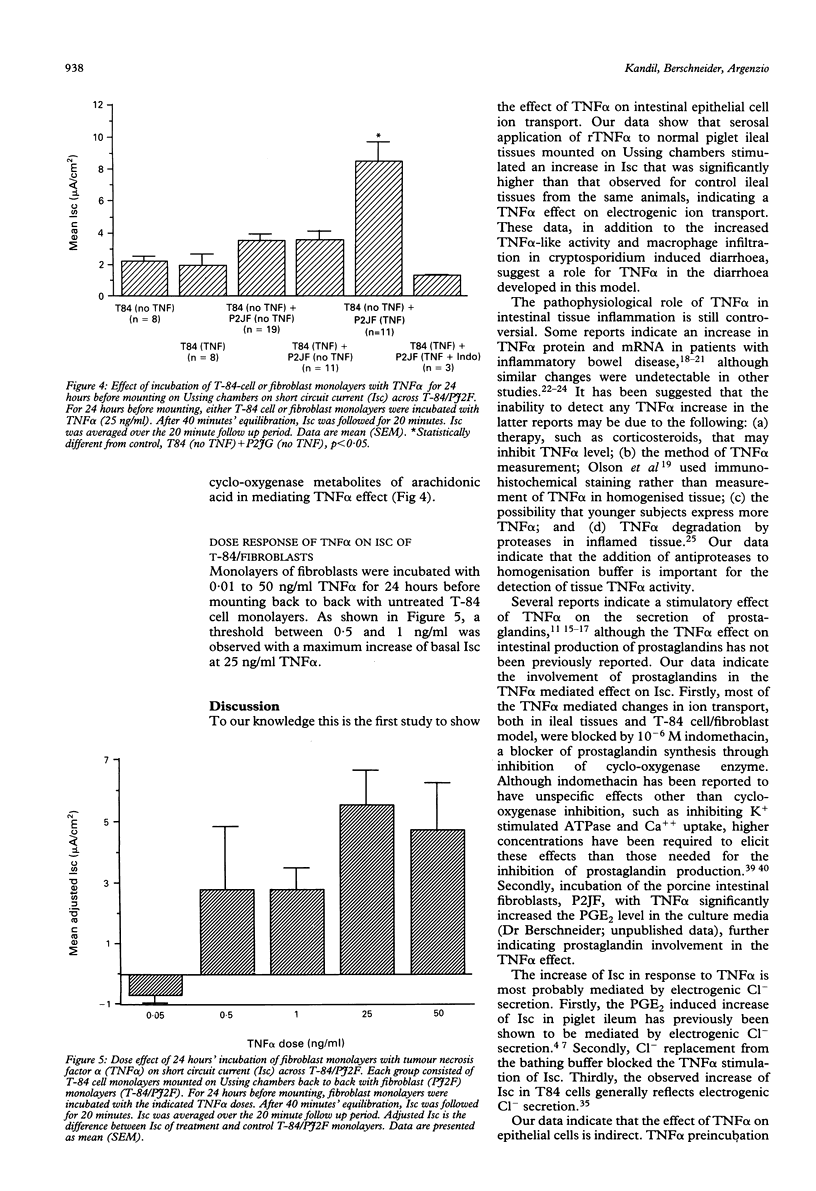
Prostaglandins stimulate electrogenic anion secretion and inhibit sodium chloride absorption in cryptosporidium induced pig diarrhoea. Because tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) is an early mediator of inflammation and stimulates prostaglandin secretion, we investigated its effect on intestinal ion transport. Cryptosporidium infected pig ileum showed higher macrophage infiltration and tissue TNF alpha-like activity than uninfected tissues (p < 0.05, n = 4 and p < 0.05, n = 12, respectively). TNF alpha treatment of control porcine ileal mucosa increased the short circuit current (Isc), a measurement of net anion secretion in this model (p < 0.001, n = 23). This effect was blocked by 10(-6) M indomethacin and Cl- replacement. Neither acute treatment nor preincubation of colonic intestinal epithelial cell monolayers (T84) with TNF alpha stimulated the Isc. However, co-mounting of TNF alpha preincubated pig jejunal fibroblasts (P2JF) monolayers back to back with untreated T84 monolayers dose-dependently induced an indomethacin sensitive increase in Isc compared with values in untreated co-mounted monolayers (p < 0.001, n = 11). These data suggest that in infectious diarrhoea, TNF alpha may induce Cl- secretion through a paracrine mechanism involving prostaglandin release from subepithelial cells, for example fibroblasts.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argenzio R. A., Lecce J., Powell D. W. Prostanoids inhibit intestinal NaCl absorption in experimental porcine cryptosporidiosis. Gastroenterology. 1993 Feb;104(2):440–447. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90412-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argenzio R. A., Liacos J. A. Endogenous prostanoids control ion transport across neonatal porcine ileum in vitro. Am J Vet Res. 1990 May;51(5):747–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argenzio R. A., Liacos J. A., Levy M. L., Meuten D. J., Lecce J. G., Powell D. W. Villous atrophy, crypt hyperplasia, cellular infiltration, and impaired glucose-Na absorption in enteric cryptosporidiosis of pigs. Gastroenterology. 1990 May;98(5 Pt 1):1129–1140. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90325-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauldry S. A., McCall C. E., Cousart S. L., Bass D. A. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha priming of phospholipase A2 activation in human neutrophils. An alternative mechanism of priming. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1277–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bern M. J., Sturbaum C. W., Karayalcin S. S., Berschneider H. M., Wachsman J. T., Powell D. W. Immune system control of rat and rabbit colonic electrolyte transport. Role of prostaglandins and enteric nervous system. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jun;83(6):1810–1820. doi: 10.1172/JCI114086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berschneider H. M., Powell D. W. Fibroblasts modulate intestinal secretory responses to inflammatory mediators. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):484–489. doi: 10.1172/JCI115610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J., Foster E. S., Budinger M. E., Hayslett J. P. Mechanism of electroneutral sodium chloride absorption in distal colon of the rat. Gastroenterology. 1987 Sep;93(3):449–455. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90905-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braegger C. P., Nicholls S., Murch S. H., Stephens S., MacDonald T. T. Tumour necrosis factor alpha in stool as a marker of intestinal inflammation. Lancet. 1992 Jan 11;339(8785):89–91. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90999-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M., Wise W. C., Halushka P. V. Prostaglandin-independent inhibition of calcium transport by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: differential effects of carboxylic acids and piroxicam. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Oct;227(1):84–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cominelli F., Nast C. C., Clark B. D., Schindler R., Lierena R., Eysselein V. E., Thompson R. C., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin 1 (IL-1) gene expression, synthesis, and effect of specific IL-1 receptor blockade in rabbit immune complex colitis. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):972–980. doi: 10.1172/JCI114799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven P. A., DeRubertis F. R. Profiles of eicosanoid production by superficial and proliferative colonic epithelial cells and sub-epithelial colonic tissue. Prostaglandins. 1986 Sep;32(3):387–399. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(86)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran R. D., Billiar T. R., Stuehr D. J., Ochoa J. B., Harbrecht B. G., Flint S. G., Simmons R. L. Multiple cytokines are required to induce hepatocyte nitric oxide production and inhibit total protein synthesis. Ann Surg. 1990 Oct;212(4):462–471. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199010000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells and dermal fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):2163–2168. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., McRoberts J. A., Mandel K. G., Tisdale L. D., Masui H. A human colonic tumor cell line that maintains vectorial electrolyte transport. Am J Physiol. 1984 Feb;246(2 Pt 1):G204–G208. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.2.G204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham D. M., Arkins S., Edwards C. K., 3rd, Dantzer R., Kelley K. W. Role of interferon-gamma in counteracting the suppressive effects of transforming growth factor-beta 2 and glucocorticoids on the production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Dec;48(6):473–481. doi: 10.1002/jlb.48.6.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias J. A., Gustilo K., Baeder W., Freundlich B. Synergistic stimulation of fibroblast prostaglandin production by recombinant interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3812–3816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie M. B., McHugh D. D. Migration of neutrophils across endothelial monolayers is stimulated by treatment of the monolayers with interleukin-1 or tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3309–3317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granström E., Kindahl H. Radioimmunoassay of prostaglandins and thromboxanes. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Res. 1978;5:119–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs K. L., Sartor R. B., Haskill S. Cytokine messenger RNA profiles in inflammatory bowel disease mucosa detected by polymerase chain reaction amplification. Gastroenterology. 1992 Nov;103(5):1587–1595. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91182-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karayalcin S. S., Sturbaum C. W., Wachsman J. T., Cha J. H., Powell D. W. Hydrogen peroxide stimulates rat colonic prostaglandin production and alters electrolyte transport. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):60–68. doi: 10.1172/JCI114715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhnert P., Wüthrich C., Peterhans E., Pauli U. The porcine tumor necrosis factor-encoding genes: sequence and comparative analysis. Gene. 1991 Jun 30;102(2):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90075-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudanna C., Miron S., Berton G., Rossi F. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha/cachectin activates the O2(-)-generating system of human neutrophils independently of the hydrolysis of phosphoinositides and the release of arachidonic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jan 15;166(1):308–315. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91946-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson L. D., Powell D. W. Bradykinin-stimulated eicosanoid synthesis and secretion by rabbit ileal components. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jun;252(6 Pt 1):G783–G790. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.252.6.G783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecce J. G., Coalson J. A. Diets for rearing colostrum-free piglets with an automatic feeding device. J Anim Sci. 1976 Mar;42(3):622–629. doi: 10.2527/jas1976.423622x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmmann V., Benninghoff B., Dröge W. Tumor necrosis factor-induced activation of peritoneal macrophages is regulated by prostaglandin E2 and cAMP. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):587–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman S. N., Sartor R. B. Examining the role of inflammatory cytokines in chronic inflammatory bowel disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1993 Apr;16(3):239–240. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199304000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald T. T., Hutchings P., Choy M. Y., Murch S., Cooke A. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma production measured at the single cell level in normal and inflamed human intestine. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Aug;81(2):301–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb03334.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden P. A., Ballermann B. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha activates soluble guanylate cyclase in bovine glomerular mesangial cells via an L-arginine-dependent mechanism. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1843–1852. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden P. A., Brock T. A., Ballermann B. J. Glomerular endothelial cells respond to calcium-mobilizing agonists with release of EDRF. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):F1295–F1303. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.5.F1295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier B., Radeke H. H., Selle S., Younes M., Sies H., Resch K., Habermehl G. G. Human fibroblasts release reactive oxygen species in response to interleukin-1 or tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Biochem J. 1989 Oct 15;263(2):539–545. doi: 10.1042/bj2630539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ming W. J., Bersani L., Mantovani A. Tumor necrosis factor is chemotactic for monocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1469–1474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murch S. H., Lamkin V. A., Savage M. O., Walker-Smith J. A., MacDonald T. T. Serum concentrations of tumour necrosis factor alpha in childhood chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1991 Aug;32(8):913–917. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.8.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedwin G. E., Svedersky L. P., Bringman T. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Goeddel D. V. Effect of interleukin 2, interferon-gamma, and mitogens on the production of tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2492–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pescovitz M. D., Lunney J. K., Sachs D. H. Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies reactive with porcine PBL. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):368–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racusen L. C., Binder H. J. Effect of prostaglandin on ion transport across isolated colonic mucosa. Dig Dis Sci. 1980 Dec;25(12):900–904. doi: 10.1007/BF01308038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radeke H. H., Meier B., Topley N., Flöge J., Habermehl G. G., Resch K. Interleukin 1-alpha and tumor necrosis factor-alpha induce oxygen radical production in mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1990 Feb;37(2):767–775. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. S., Warhurst G., Turnberg L. A. Synthesis and degradation of prostaglandin E2 in the epithelial and sub-epithelial layers of the rat intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 13;713(3):684–687. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90331-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spenney J. G., Mize K. S. Inhibition of gastric K+ ATPase by phenylbutazone and indomethacin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Jul 1;26(13):1241–1245. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topley N., Floege J., Wessel K., Hass R., Radeke H. H., Kaever V., Resch K. Prostaglandin E2 production is synergistically increased in cultured human glomerular mesangial cells by combinations of IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha 1. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 15;143(6):1989–1995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weymer A., Huott P., Liu W., McRoberts J. A., Dharmsathaphorn K. Chloride secretory mechanism induced by prostaglandin E1 in a colonic epithelial cell line. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1828–1836. doi: 10.1172/JCI112175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



