Abstract
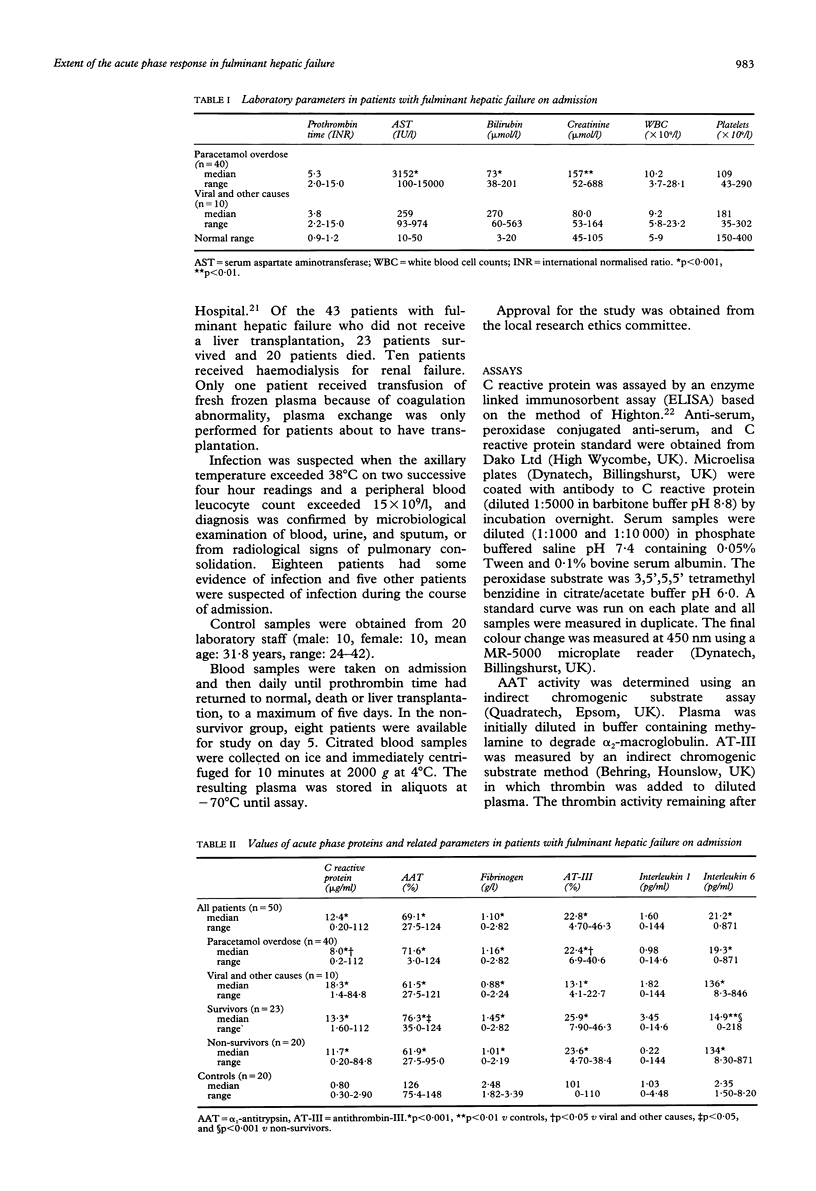
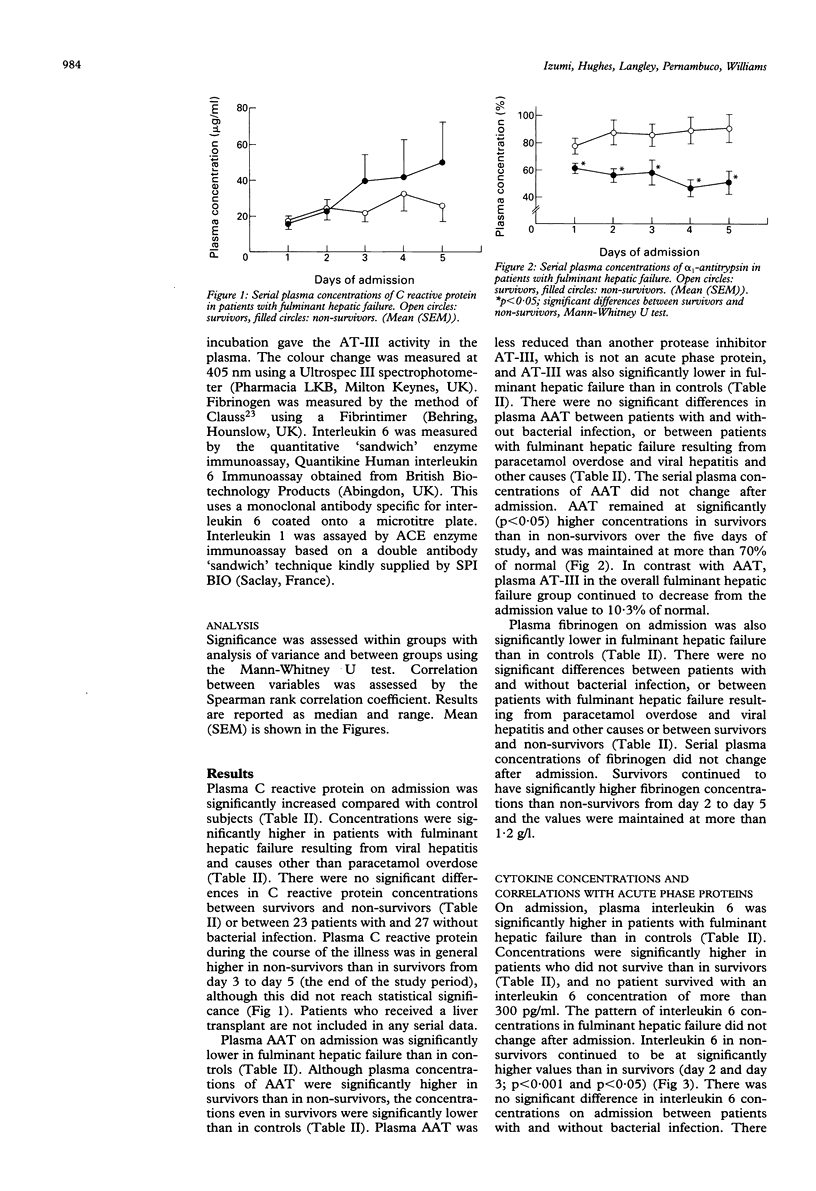
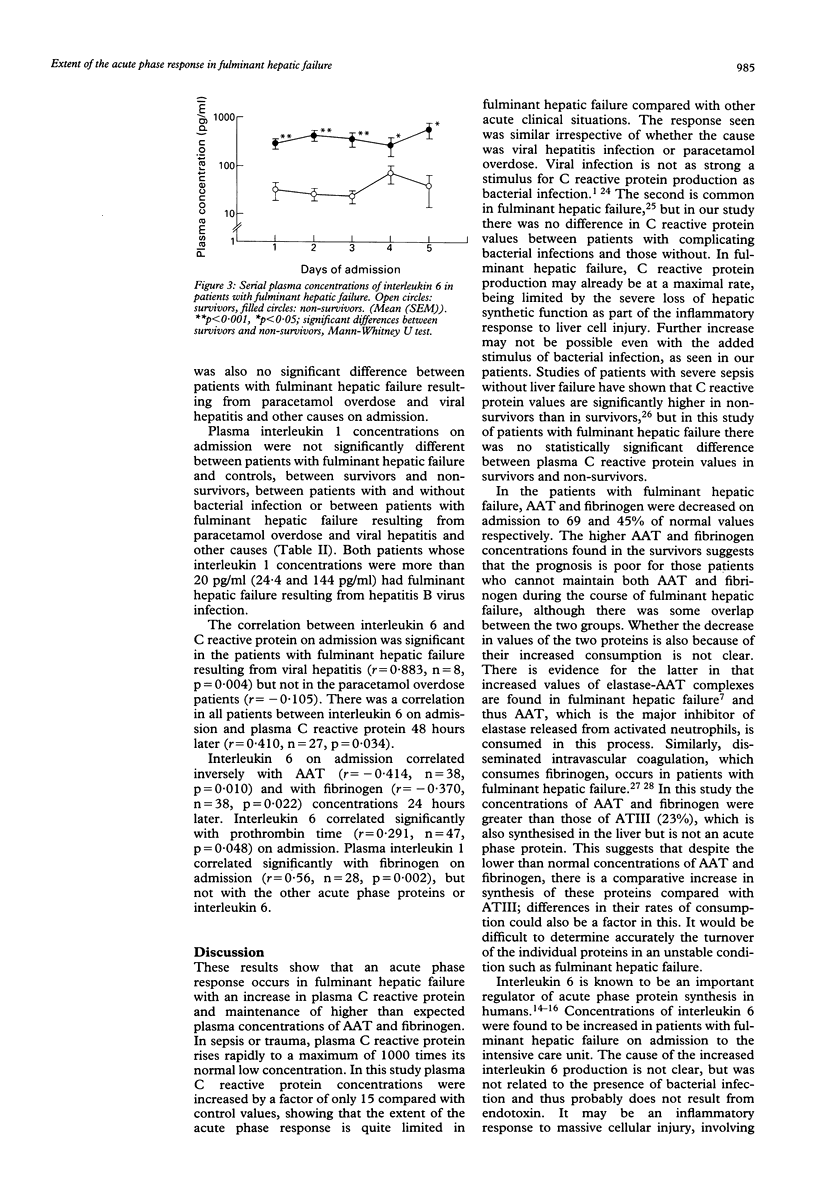
The extent of the acute phase response and the relation between acute phase proteins and cytokines in plasma was investigated in 50 patients with fulminant hepatic failure. On admission, C reactive protein was significantly higher in fulminant hepatic failure (median: 12.4 micrograms/ml, range:0.2-112 micrograms/ml) than in 20 controls (median: 0.8 microgram/ml, range: 0.3-2.9 micrograms/ml, p < 0.001). Serial measurements showed that plasma C reactive protein increased daily after admission until day 5, the end of the study period. alpha 1-Antitrypsin (AAT) (median: 69.1%, range: 27.5-124%) and fibrinogen (median: 1.10 g/l, range: 0-2.82 g/l) were significantly lower in fulminant hepatic failure on admission than in controls (AAT: median: 126%, range: 75.4-149%; fibrinogen: median 2.48 g/l, range: 1.82-3.39 g/l, p < 0.001) and did not change subsequently. Both AAT and fibrinogen were maintained at significantly higher concentrations in survivors than in those who did not. Bacterial infection occurred in 23 patients during the course of fulminant hepatic failure, but did not influence the concentrations of these three proteins. Interleukin 6 was significantly higher in fulminant hepatic failure (median: 21.2 pg/ml, range: 0-871 pg/ml) than in controls (median: 2.4 pg/ml, range: 1.5-8.2 pg/ml, p < 0.001). There was a significant correlation between interleukin 6 and the C reactive protein concentrations in patients with viral hepatitis on admission and in all patients 48 hours later, consistent with other evidence that interleukin 6 stimulates synthesis of this acute phase protein.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertina R. M., van Wijngaarden A., Reinalda-Poot J., Poort S. R., Bom V. J. Determination of plasma protein S--the protein cofactor of activated protein C. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Apr 22;53(2):268–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAUSS A. Gerinnungsphysiologische Schnellmethode zur Bestimmung des Fibrinogens. Acta Haematol. 1957 Apr;17(4):237–246. doi: 10.1159/000205234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell J. V., Geiger T., Gross V., Andus T., Walter E., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Heinrich P. C. Plasma clearance, organ distribution and target cells of interleukin-6/hepatocyte-stimulating factor in the rat. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Nov 1;177(2):357–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell J. V., Gómez-Lechón M. J., David M., Andus T., Geiger T., Trullenque R., Fabra R., Heinrich P. C. Interleukin-6 is the major regulator of acute phase protein synthesis in adult human hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 2;242(2):237–239. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80476-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell J. V., Gómez-Lechón M. J., David M., Fabra R., Trullenque R., Heinrich P. C. Acute-phase response of human hepatocytes: regulation of acute-phase protein synthesis by interleukin-6. Hepatology. 1990 Nov;12(5):1179–1186. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell J. V., Gómez-Lechón M. J., David M., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Heinrich P. C. Recombinant human interleukin-6 (IL-6/BSF-2/HSF) regulates the synthesis of acute phase proteins in human hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 23;232(2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80766-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delers F., Mangeney M., Raffa D., Vallet-Colom I., Daveau M., Tran-Quang N., Davrinches C., Chambaz J. Changes in rat liver mRNA for alpha-1-acid-glycoprotein, apolipoprotein E, apolipoprotein B and beta-actin after mouse recombinant tumor necrosis factor injection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 May 30;161(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91563-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckert F. Behaviour of antithrombin 3 in liver disease. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1973;19:109–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong Y., Moldawer L. L., Marano M., Wei H., Tatter S. B., Clarick R. H., Santhanam U., Sherris D., May L. T., Sehgal P. B. Endotoxemia elicits increased circulating beta 2-IFN/IL-6 in man. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2321–2324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger T., Andus T., Klapproth J., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Heinrich P. C. Induction of rat acute-phase proteins by interleukin 6 in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 1988 May;18(5):717–721. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath D. I., Cruickshank A., Gudgeon M., Jehanli A., Shenkin A., Imrie C. W. Role of interleukin-6 in mediating the acute phase protein response and potential as an early means of severity assessment in acute pancreatitis. Gut. 1993 Jan;34(1):41–45. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. D., Lane D. A., Ireland H., Langley P. G., Gimson A. E., Williams R. Fibrinogen derivatives and platelet activation products in acute and chronic liver disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Jun;68(6):701–707. doi: 10.1042/cs0680701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirik F. R., Podor T. J., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Loskutoff D. J., Carson D. A., Lotz M. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide and inflammatory mediators augment IL-6 secretion by human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):144–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapproth J., Castell J., Geiger T., Andus T., Heinrich P. C. Fate and biological action of human recombinant interleukin 1 beta in the rat in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Aug;19(8):1485–1490. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb-Bachofen V. A review on the biological properties of C-reactive protein. Immunobiology. 1991 Sep;183(1-2):133–145. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80193-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner I. The acute phase response: an overview. Methods Enzymol. 1988;163:373–383. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)63037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley P. G., Forbes A., Hughes R. D., Williams R. Thrombin-antithrombin III complex in fulminant hepatic failure: evidence for disseminated intravascular coagulation and relationship to outcome. Eur J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;20(6):627–631. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1990.tb01911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley P. G., Hughes R. D., Rolando N., Williams R. Increased elastase-alpha 1-antitrypsin complex in fulminant hepatic failure: relationship to bacterial infection and activation of coagulation. Clin Chim Acta. 1991 Aug 30;200(2-3):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(91)90092-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley P. G., Williams R. Physiological inhibitors of coagulation in fulminant hepatic failure. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1992 Jun;3(3):243–247. doi: 10.1097/00001721-199206000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinkovic S., Jahreis G. P., Wong G. G., Baumann H. IL-6 modulates the synthesis of a specific set of acute phase plasma proteins in vivo. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):808–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto Y., Nouri-Aria K. T., Meager A., Alexander G. J., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Enhanced tumour necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in fulminant hepatic failure. Lancet. 1988 Jul 9;2(8602):72–74. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson K., Olsson I. Neutral proteases of human granulocytes. III. Interaction between human granulocyte elastase and plasma protease inhibitors. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1974 Dec;34(4):349–355. doi: 10.3109/00365517409049891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohzato H., Yoshizaki K., Nishimoto N., Ogata A., Tagoh H., Monden M., Gotoh M., Kishimoto T., Mori T. Interleukin-6 as a new indicator of inflammatory status: detection of serum levels of interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein after surgery. Surgery. 1992 Feb;111(2):201–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka Y., Murata A., Nishijima J., Yasuda T., Hiraoka N., Ohmachi Y., Kitagawa K., Yasuda T., Toda H., Tanaka N. Circulating interleukin 6 as a useful marker for predicting postoperative complications. Cytokine. 1992 Jul;4(4):298–304. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(92)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramadori G., Sipe J. D., Dinarello C. A., Mizel S. B., Colten H. R. Pretranslational modulation of acute phase hepatic protein synthesis by murine recombinant interleukin 1 (IL-1) and purified human IL-1. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):930–942. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramadori G., Van Damme J., Rieder H., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. Interleukin 6, the third mediator of acute-phase reaction, modulates hepatic protein synthesis in human and mouse. Comparison with interleukin 1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Aug;18(8):1259–1264. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolando N., Harvey F., Brahm J., Philpott-Howard J., Alexander G., Gimson A., Casewell M., Fagan E., Williams R. Prospective study of bacterial infection in acute liver failure: an analysis of fifty patients. Hepatology. 1990 Jan;11(1):49–53. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840110110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiratori Y., Moriwaki H., Kawashima Y., Ando K., Asano F., Shimazaki M., Ohnishi H., Muto Y., Okuno M. Elevated interleukin-6 levels in sera of patients with fulminant hepatitis. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1991 Apr;26(2):233–233. doi: 10.1007/BF02811089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trey C., Davidson C. S. The management of fulminant hepatic failure. Prog Liver Dis. 1970;3:282–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Oers M. H., Van der Heyden A. A., Aarden L. A. Interleukin 6 (IL-6) in serum and urine of renal transplant recipients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Feb;71(2):314–319. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


