Abstract
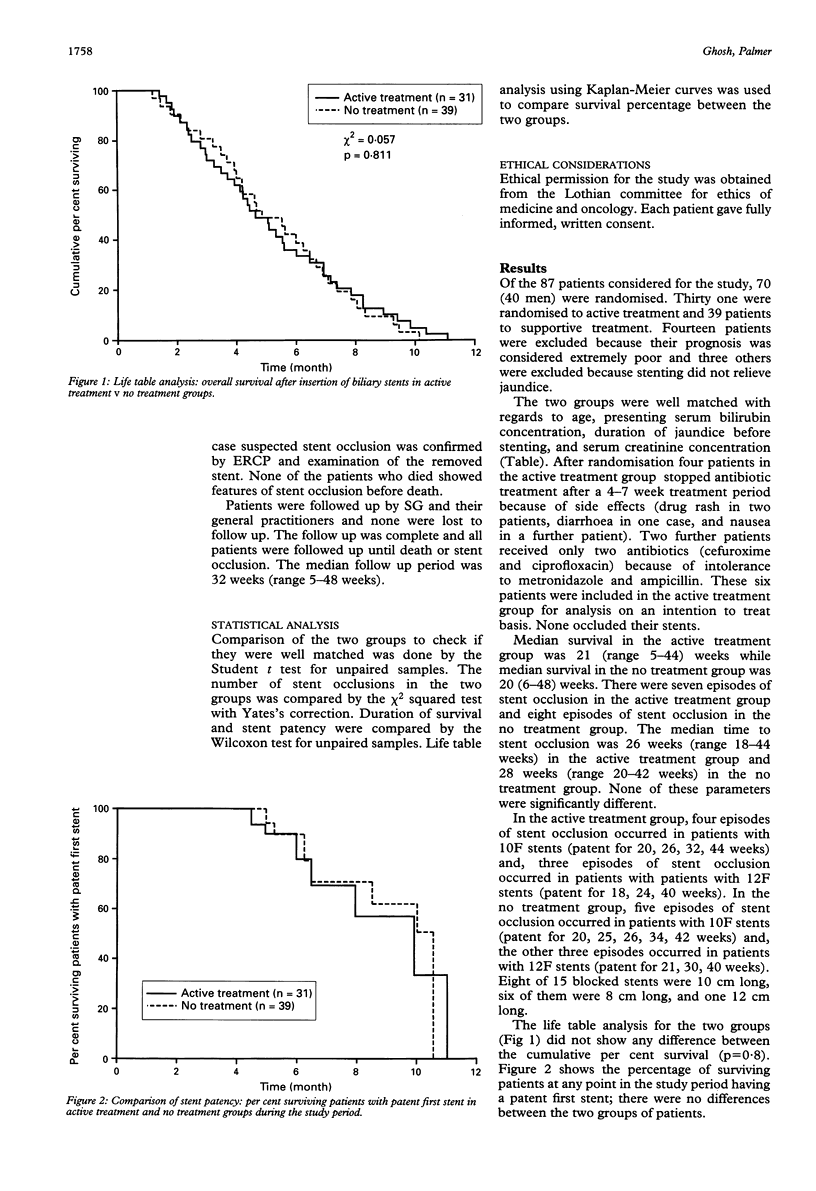
This study reports an open randomised controlled trial of cyclical antibiotics and ursodeoxycholic acid in prevention of plastic biliary stent occlusion. Seventy patients with malignant distal bile duct obstruction were randomised to either active treatment with cyclical antibiotics (ampicillin, metronidazole, ciprofloxacin) and ursodeoxycholic acid or no treatment after successful stent insertion. The two groups were well matched. The follow up was complete with stent occlusion or death being the end points. There was no difference in the incidence of stent occlusion between the two groups and the overall survival was similar. In conclusion, this study did not show any benefit of treatment with antibiotics and ursodeoxycholic acid in prolonging stent patency or improving survival.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Costerton J. W., Cheng K. J., Geesey G. G., Ladd T. I., Nickel J. C., Dasgupta M., Marrie T. J. Bacterial biofilms in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:435–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frakes J. T., Johanson J. F., Stake J. J. Optimal timing for stent replacement in malignant biliary tract obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc. 1993 Mar-Apr;39(2):164–167. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(93)70058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jazrawi R. P., de Caestecker J. S., Goggin P. M., Britten A. J., Joseph A. E., Maxwell J. D., Northfield T. C. Kinetics of hepatic bile acid handling in cholestatic liver disease: effect of ursodeoxycholic acid. Gastroenterology. 1994 Jan;106(1):134–142. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(94)94899-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knyrim K., Wagner H. J., Pausch J., Vakil N. A prospective, randomized, controlled trial of metal stents for malignant obstruction of the common bile duct. Endoscopy. 1993 Mar;25(3):207–212. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1010294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung J. W., Ling T. K., Kung J. L., Vallance-Owen J. The role of bacteria in the blockage of biliary stents. Gastrointest Endosc. 1988 Jan-Feb;34(1):19–22. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(88)71223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Shimakura K., Akamatsu T. Factors affecting the patency of stents in malignant biliary obstructive disease: univariate and multivariate analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1991 Jul;86(7):843–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J. M., Out M. M., Groen A. K., Huibregtse K., Jansen P. L., van Marle J., Tytgat G. N. A placebo-controlled study on the efficacy of aspirin and doxycycline in preventing clogging of biliary endoprostheses. Gastrointest Endosc. 1989 Nov-Dec;35(6):485–489. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(89)72895-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speer A. G., Cotton P. B., MacRae K. D. Endoscopic management of malignant biliary obstruction: stents of 10 French gauge are preferable to stents of 8 French gauge. Gastrointest Endosc. 1988 Sep-Oct;34(5):412–417. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(88)71407-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speer A. G., Cotton P. B., Rode J., Seddon A. M., Neal C. R., Holton J., Costerton J. W. Biliary stent blockage with bacterial biofilm. A light and electron microscopy study. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Apr;108(4):546–553. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-4-546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward A., Brogden R. N., Heel R. C., Speight T. M., Avery G. S. Ursodeoxycholic acid: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy. Drugs. 1984 Feb;27(2):95–131. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198427020-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Caestecker J. S., Jazrawi R. P., Petroni M. L., Northfield T. C. Ursodeoxycholic acid in chronic liver disease. Gut. 1991 Sep;32(9):1061–1065. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.9.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


