Abstract
We report the results of a randomized trial to assess the impact of an innovative ethics curriculum on the knowledge and confidence of 85 medical house officers in a university hospital programme, as well as their responses to a simulated clinical case. Twenty-five per cent of the house officers received a lecture series (Limited Intervention or LI), 25 per cent received lectures and case conferences, with an ethicist in attendance (Extensive Intervention or EI), and 50 per cent served as controls. A post-intervention questionnaire was administered. Knowledge scores did not differ among the groups. Confidence regarding ethical issues was significantly greater in the aggregate intervention group (3.9 on a 1 to 5 scale) compared to the control group (3.6). Confidence regarding procedural issues related to ethics was significantly higher for the EI group than for the controls (4.0 v 2.8). Responses to a simulated case showed that significantly fewer house officers in the EI group would intubate a patient for whom such therapy would be futile (EI = 57 per cent, LI = 87 per cent, Controls = 82 per cent). We conclude that ethics education can have an impact on house officers' confidence and their responses to a simulated case, and that the EI was more effective than the LI. Such results have implications regarding the implementation of ethics education during residency.
Full text
PDF

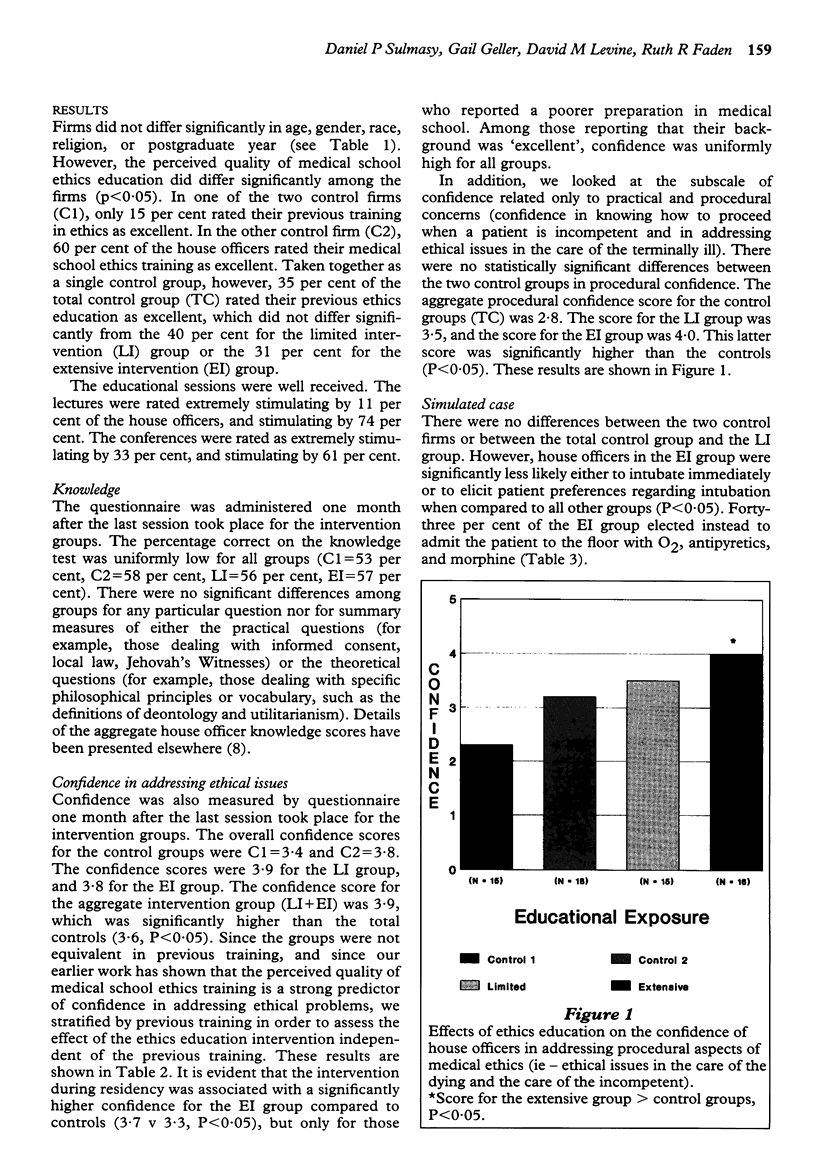
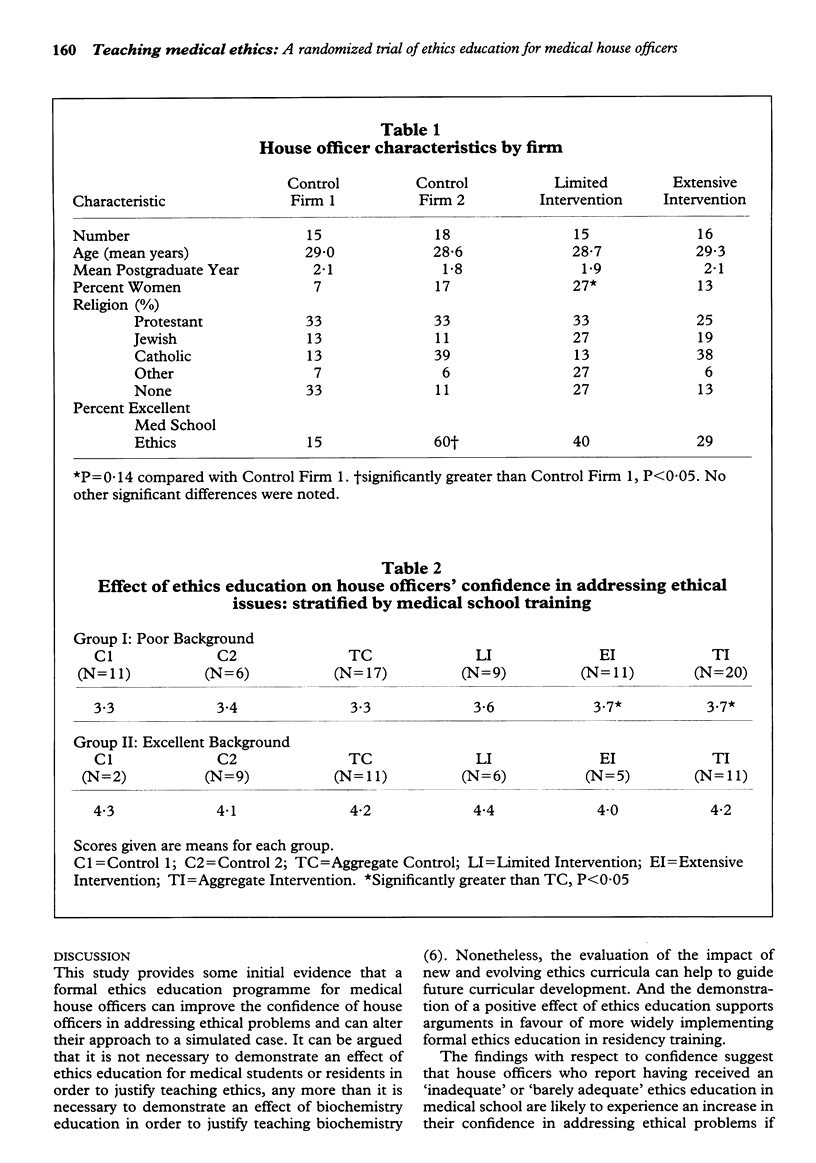
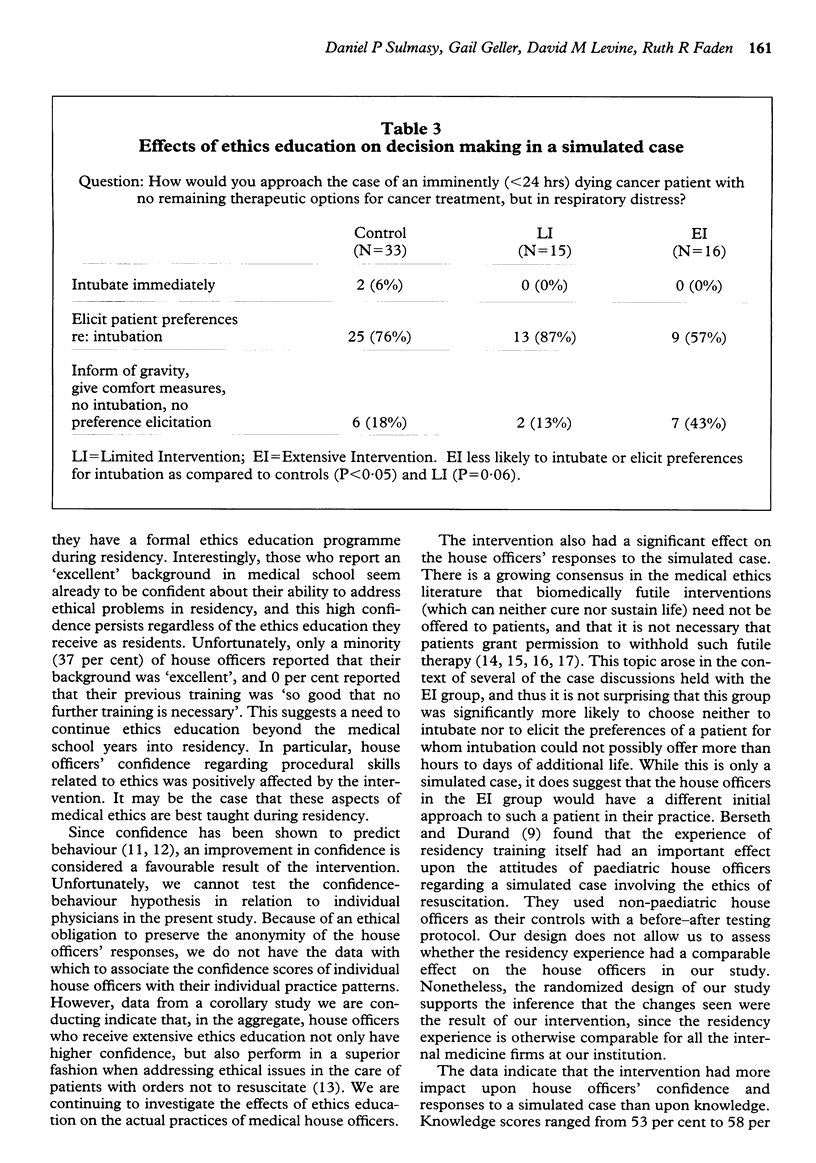


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bandura A., Adams N. E., Beyer J. Cognitive processes mediating behavioral change. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1977 Mar;35(3):125–139. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.35.3.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berseth C. L., Durand R. Evaluating the effect of a human values seminar series on ethical attitudes toward resuscitation among pediatric residents. Mayo Clin Proc. 1990 Mar;65(3):337–343. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)62534-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culver C. M., Clouser K. D., Gert B., Brody H., Fletcher J., Jonsen A., Kopelman L., Lynn J., Siegler M., Wikler D. Basic curricular goals in medical ethics. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 24;312(4):253–256. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501243120430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. M., Kaynard J. Unique educational program in critical care medicine for the general internist. J Gen Intern Med. 1993 Mar;8(3):126–129. doi: 10.1007/BF02599755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber-Langendoen K. Resuscitation of patients with metastatic cancer. Is transient benefit still futile? Arch Intern Med. 1991 Feb;151(2):235–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller G., Levine D. M., Mamon J. A., Moore R. D., Bone L. R., Stokes E. J. Knowledge, attitudes, and reported practices of medical students and house staff regarding the diagnosis and treatment of alcoholism. JAMA. 1989 Jun 2;261(21):3115–3120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon G. H., Tolle S. W. Discussing life-sustaining treatment. A teaching program for residents. Arch Intern Med. 1991 Mar;151(3):567–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langdon L. O., Jonsen A. R. The experience of the American Board of Internal Medicine. Hastings Cent Rep. 1983 Jun;13(3):26–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkel W. T., Margolis R. B., Smith R. C. Teaching humanistic and psychosocial aspects of care: current practices and attitudes. J Gen Intern Med. 1990 Jan-Feb;5(1):34–41. doi: 10.1007/BF02602307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles S. H., Lane L. W., Bickel J., Walker R. M., Cassel C. K. Medical ethics education: coming of age. Acad Med. 1989 Dec;64(12):705–714. doi: 10.1097/00001888-198912000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino E. D., Hart R. J., Jr, Henderson S. R., Loeb S. E., Edwards G. Relevance and utility of courses in medical ethics. A survey of physicians' perceptions. JAMA. 1985 Jan 4;253(1):49–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino E. D. Teaching medical ethics: some persistent questions and some responses. Acad Med. 1989 Dec;64(12):701–703. doi: 10.1097/00001888-198912000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneiderman L. J., Jecker N. S., Jonsen A. R. Medical futility: its meaning and ethical implications. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Jun 15;112(12):949–954. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-12-949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulmasy D. P., Geller G., Faden R., Levine D. M. The quality of mercy. Caring for patients with 'do not resuscitate' orders. JAMA. 1992 Feb 5;267(5):682–686. doi: 10.1001/jama.267.5.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulmasy D. P., Geller G., Levine D. M., Faden R. Medical house officers' knowledge, attitudes, and confidence regarding medical ethics. Arch Intern Med. 1990 Dec;150(12):2509–2513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson T., Brody H. Futility and the ethics of resuscitation. JAMA. 1990 Sep 12;264(10):1276–1280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner S. J. Futility in context. JAMA. 1990 Sep 12;264(10):1295–1296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


