Abstract
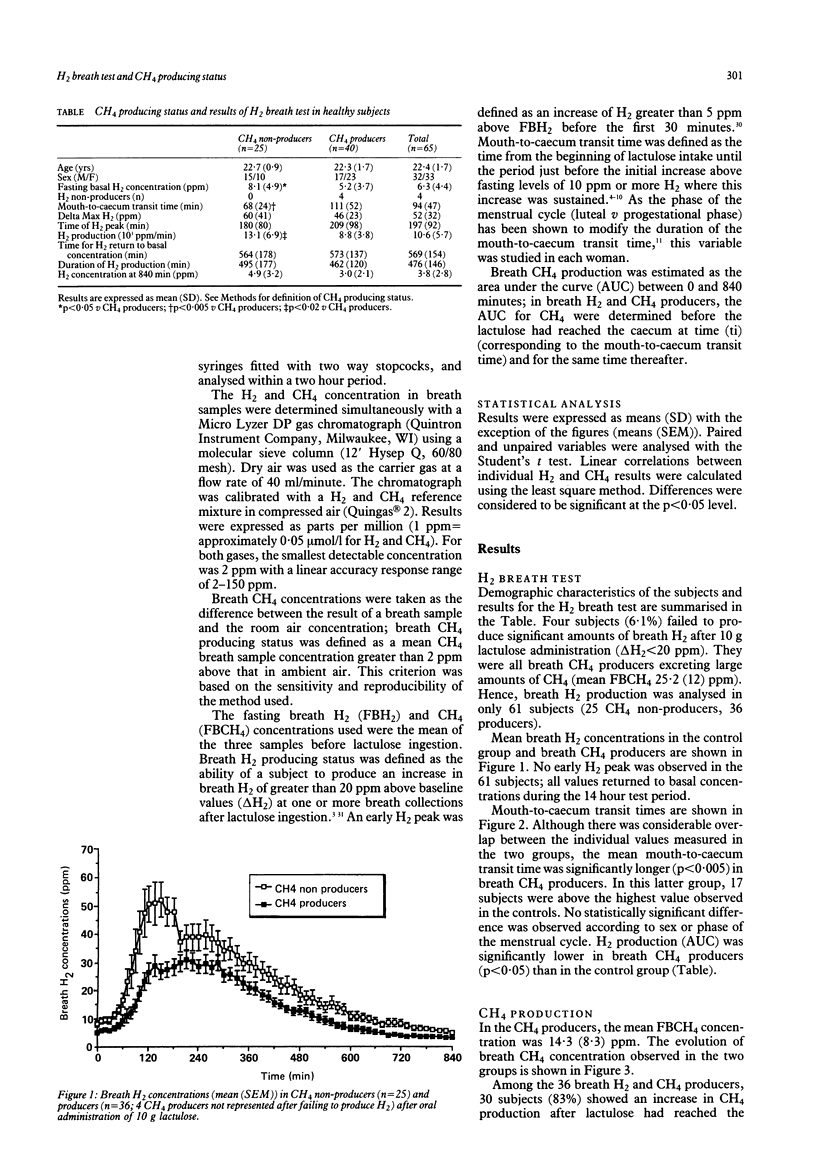
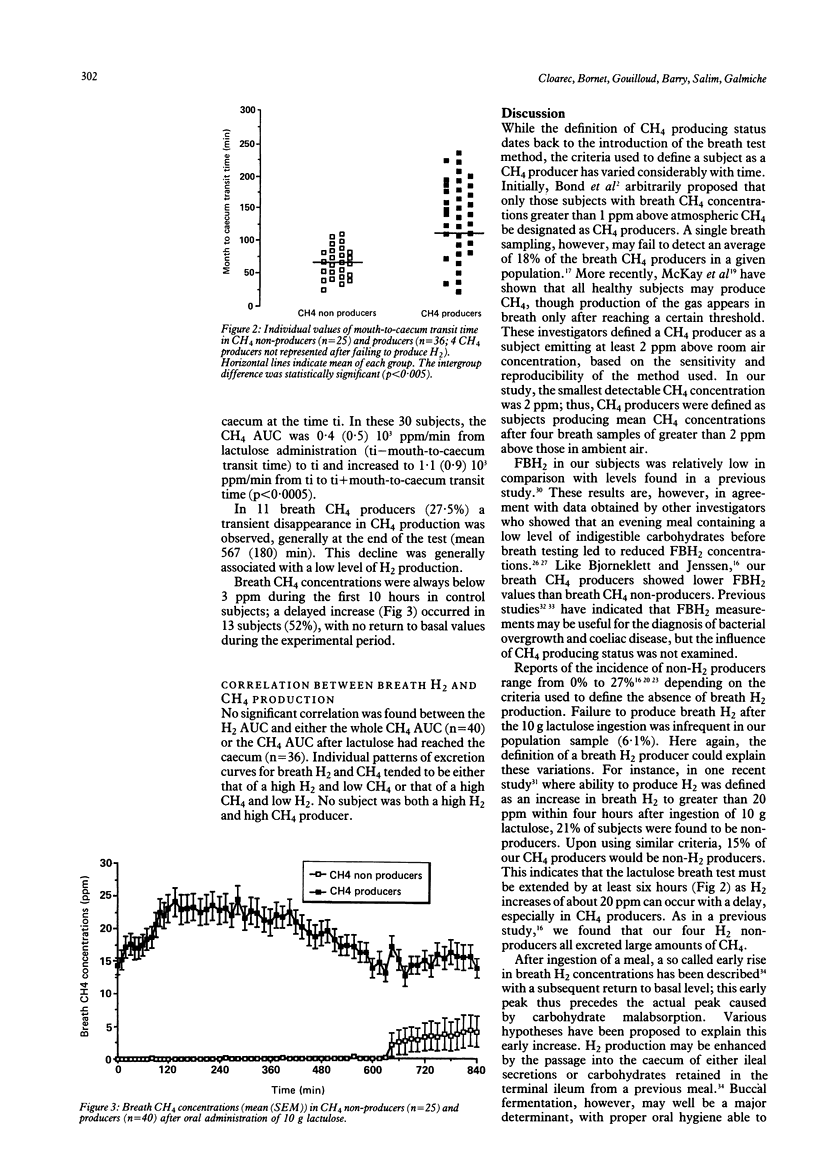
In order to assess the relationship between methane (CH4) producing status and the breath excretion of hydrogen (H2) in healthy subjects, breath CH4 and H2 were simultaneously measured for 14 hours after oral ingestion of 10 g lactulose in 65 young volunteers. Forty were breath CH4 producers and 25 were not. Statistically significant differences were observed between both groups, with lower values for CH4 producers recorded for the following parameters: fasting basal value of breath H2 (8.1 (4.9) v 5.2 (3.7) ppm, p less than 0.05), mouth-to-caecum transit time (68 (24) v 111 (52) min, p less than 0.005), and breath H2 production measured as area under the curve 13.1 (6.9) v 8.8 (3.8) 10(3) ppm/min, p less than 0.02). There was no significant correlation between individual production of breath H2 and CH4. These results indicate that the response to lactulose depends on breath CH4 producing status. In clinical practice, defining normal values of mouth-to-caecum transit time without knowledge of breath CH4 producing status may lead to misinterpretation of the H2 breath test.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basilisco G., Bozzani A., Camboni G., Recchia M., Quatrini M., Conte D., Penagini R., Bianchi P. A. Effect of loperamide and naloxone on mouth-to-caecum transit time evaluated by lactulose hydrogen breath test. Gut. 1985 Jul;26(7):700–703. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.7.700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjørneklett A., Jenssen E. Relationships between hydrogen (H2) and methane (CH4) production in man. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1982 Nov;17(8):985–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. H., Jr, Engel R. R., Levitt M. D. Factors influencing pulmonary methane excretion in man. An indirect method of studying the in situ metabolism of the methane-producing colonic bacteria. J Exp Med. 1971 Mar 1;133(3):572–588. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.3.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. H., Jr, Levitt M. D., Prentiss R. Investigation of small bowel transit time in man utilizing pulmonary hydrogen (H2) measurements. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Apr;85(4):546–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. H., Jr, Levitt M. D. Use of pulmonary hydrogen (H 2 ) measurements to quantitate carbohydrate absorption. Study of partially gastrectomized patients. J Clin Invest. 1972 May;51(5):1219–1225. doi: 10.1172/JCI106916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummer R. J., Armbrecht U., Bosaeus I., Dotevall G., Stockbruegger R. W. The hydrogen (H2) breath test. Sampling methods and the influence of dietary fibre on fasting level. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1985 Oct;20(8):1007–1013. doi: 10.3109/00365528509088863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calloway D. H. Respiratory hydrogen and methane as affected by consumption of gas-forming foods. Gastroenterology. 1966 Sep;51(3):383–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caride V. J., Prokop E. K., Troncale F. J., Buddoura W., Winchenbach K., McCallum R. W. Scintigraphic determination of small intestinal transit time: comparison with the hydrogen breath technique. Gastroenterology. 1984 Apr;86(4):714–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corazza G. R., Strocchi A., Gasbarrini G. Fasting breath hydrogen in celiac disease. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jul;93(1):53–58. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90313-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett C. L., Thomas S., Read N. W., Hobson N., Bergman I., Holdsworth C. D. Electrochemical detector for breath hydrogen determination: measurement of small bowel transit time in normal subjects and patients with the irritable bowel syndrome. Gut. 1981 Oct;22(10):836–840. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.10.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatz G., Czeizel A., Métneki J., Flatz S. D., Kühnau W., Jahn D. Pulmonary hydrogen and methane excretion following ingestion of an unabsorbable carbohydrate: a study of twins. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1985 Dec;4(6):936–941. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198512000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz M., Siebert G., Kasper H. Dose dependence of breath hydrogen and methane in healthy volunteers after ingestion of a commercial disaccharide mixture, Palatinit. Br J Nutr. 1985 Sep;54(2):389–400. doi: 10.1079/bjn19850124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilat T., Ben Hur H., Gelman-Malachi E., Terdiman R., Peled Y. Alterations of the colonic flora and their effect on the hydrogen breath test. Gut. 1978 Jul;19(7):602–605. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.7.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellow J. E., Borody T. J., Phillips S. F., Haddad A. C., Brown M. L. Sulfapyridine appearance in plasma after salicylazosulfapyridine. Another simple measure of intestinal transit. Gastroenterology. 1986 Aug;91(2):396–400. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90574-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotler D. P., Holt P. R., Rosensweig N. S. Modification of the breath hydrogen test: increased sensitivity for the detection of carbohydrate malabsorption. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Nov;100(5):798–805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Brooy S. J., Male P. J., Beavis A. K., Misiewicz J. J. Assessment of the reproducibility of the lactulose H2 breath test as a measure of mouth to caecum transit time. Gut. 1983 Oct;24(10):893–896. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.10.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M. D., Hirsh P., Fetzer C. A., Sheahan M., Levine A. S. H2 excretion after ingestion of complex carbohydrates. Gastroenterology. 1987 Feb;92(2):383–389. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90132-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastropaolo G., Rees W. D. Evaluation of the hydrogen breath test in man: definition and elimination of the early hydrogen peak. Gut. 1987 Jun;28(6):721–725. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.6.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. F., Eastwood M. A., Brydon W. G. Methane excretion in man--a study of breath, flatus, and faeces. Gut. 1985 Jan;26(1):69–74. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peled Y., Weinberg D., Hallak A., Gilat T. Factors affecting methane production in humans. Gastrointestinal diseases and alterations of colonic flora. Dig Dis Sci. 1987 Mar;32(3):267–271. doi: 10.1007/BF01297052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perman J. A., Modler S., Barr R. G., Rosenthal P. Fasting breath hydrogen concentration: normal values and clinical application. Gastroenterology. 1984 Dec;87(6):1358–1363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piqué J. M., Pallarés M., Cusó E., Vilar-Bonet J., Gassull M. A. Methane production and colon cancer. Gastroenterology. 1984 Sep;87(3):601–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt P., de Bruijn K. M., Beeching M. F., Goldberg E., Blendis L. M. Studies on breath methane: the effect of ethnic origins and lactulose. Gut. 1980 Nov;21(11):951–954. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.11.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read N. W., Al-Janabi M. N., Bates T. E., Holgate A. M., Cann P. A., Kinsman R. I., McFarlane A., Brown C. Interpretation of the breath hydrogen profile obtained after ingesting a solid meal containing unabsorbable carbohydrate. Gut. 1985 Aug;26(8):834–842. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.8.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltzberg D. M., Levine G. M., Lubar C. Impact of age, sex, race, and functional complaints on hydrogen (H2) production. Dig Dis Sci. 1988 Mar;33(3):308–313. doi: 10.1007/BF01535755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal I., Walker A. R., Lord S., Cummings J. H. Breath methane and large bowel cancer risk in contrasting African populations. Gut. 1988 May;29(5):608–613. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.5.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephen A. M., Wiggins H. S., Englyst H. N., Cole T. J., Wayman B. J., Cummings J. H. The effect of age, sex and level of intake of dietary fibre from wheat on large-bowel function in thirty healthy subjects. Br J Nutr. 1986 Sep;56(2):349–361. doi: 10.1079/bjn19860116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. G., Binfield P., De Belder A., O'Brien J., Warren S., Wilson M. Extra intestinal influences on exhaled breath hydrogen measurements during the investigation of gastrointestinal disease. Gut. 1985 Dec;26(12):1349–1352. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.12.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. G., O'Brien J. D., Hardie J. M. Influence of the oropharyngeal microflora on the measurement of exhaled breath hydrogen. Gastroenterology. 1986 Oct;91(4):853–860. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90686-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald A., Van Thiel D. H., Hoechstetter L., Gavaler J. S., Egler K. M., Verm R., Scott L., Lester R. Gastrointestinal transit: the effect of the menstrual cycle. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jun;80(6):1497–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



