Abstract
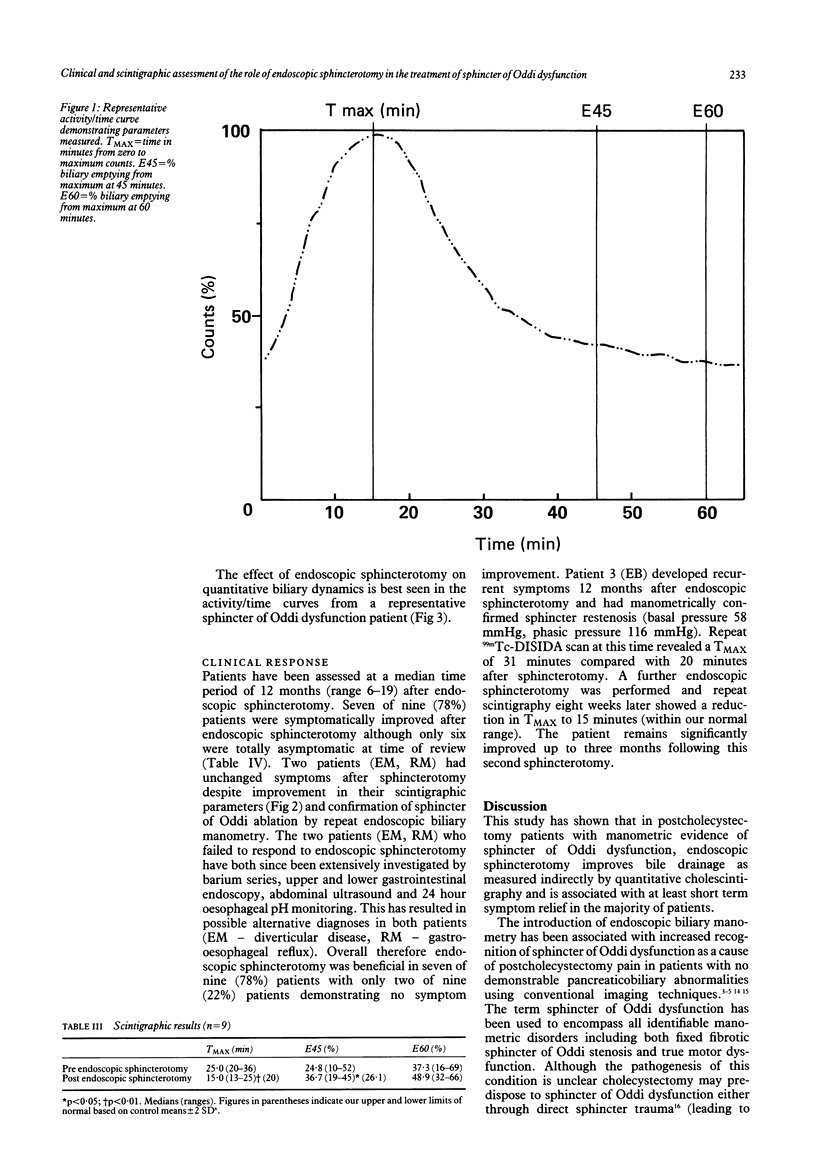
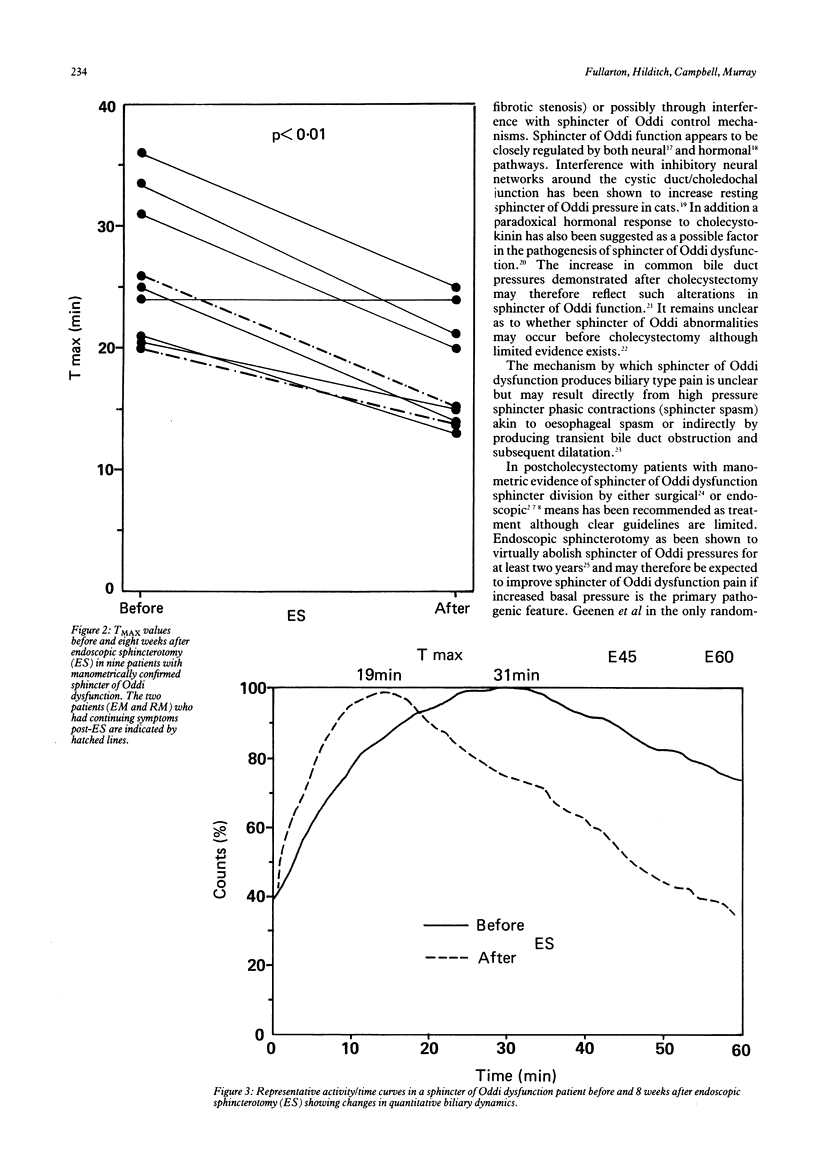
Postcholecystectomy pain caused by sphincter of Oddi dysfunction remains a difficult condition to treat. Endoscopic sphincterotomy has been recommended for those patients with confirmed sphincter of Oddi motor abnormalities. We have studied sphincter of Oddi dysfunction patients to evaluate the effects of endoscopic sphincterotomy on both clinical symptoms and previously reported scintigraphic parameters to determine the efficacy of this method of treatment. Nine postcholecystectomy patients (seven women: two men, median age 59 years) with clinical and manometric evidence of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction underwent endoscopic sphincterotomy for persisting biliary type pain. Each patient had scintigraphy before and eight weeks after endoscopic sphincterotomy. The patients symptomatic response was assessed independently at three monthly intervals after endoscopic sphincterotomy. Scintigraphic analysis showed that the TMAX (time in minutes to maximum counts) was significantly reduced from 25.0 (20-36) (median [range]) before endoscopic sphincterotomy to 15.0 (13-25) after endoscopic sphincterotomy (p less than 0.01). Seven of nine (78%) sphincter of Oddi dysfunction patients had significant improvement in their symptoms after a mean follow up period of 12 months (range 6-19) although only six of nine were totally pain free. These results suggest that endoscopic sphincterotomy in manometrically confirmed sphincter of Oddi dysfunction improves bile drainage as measured by quantitative cholescintigraphy and is associated with at least short term symptom relief in the majority of patients.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar-Meir S., Geenen J. E., Hogan W. J., Dodds W. J., Stewart E. T., Arndorfer R. C. Biliary and pancreatic duct pressures measured by ERCP manometry in patients with suspected papillary stenosis. Dig Dis Sci. 1979 Mar;24(3):209–213. doi: 10.1007/BF01308431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Meir S., Halpern Z., Bardan E., Gilat T. Frequency of papillary dysfunction among cholecystectomized patients. Hepatology. 1984 Mar-Apr;4(2):328–330. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behar J., Biancani P. Neural control of the sphincter of Oddi. A physiological role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the regulation of basal sphincter of Oddi motor activity in the cat. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):551–559. doi: 10.1172/JCI111003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortolotti M., Caletti G. C., Brocchi E., Bersani G., Caletti T., Guizzardi G., Labò G. Endoscopic manometry in the diagnosis of the postcholecystectomy pain syndrome. Digestion. 1983;28(3):153–157. doi: 10.1159/000198979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr-Locke D. L., Cotton P. B. Biliary tract and pancreas. Br Med Bull. 1986 Jul;42(3):257–264. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darweesh R. M., Dodds W. J., Hogan W. J., Geenen J. E., Collier B. D., Shaker R., Kishk S. M., Stewart E. T., Lawson T. L., Hassanein E. H. Efficacy of quantitative hepatobiliary scintigraphy and fatty-meal sonography for evaluating patients with suspected partial common duct obstruction. Gastroenterology. 1988 Mar;94(3):779–786. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90254-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Masi E., Corazziari E., Habib F. I., Fontana B., Gatti V., Fegiz G. F., Torsoli A. Manometric study of the sphincter of Oddi in patients with and without common bile duct stones. Gut. 1984 Mar;25(3):275–278. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.3.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullarton G. M., Allan A., Hilditch T., Murray W. R. Quantitative 99mTc-DISIDA scanning and endoscopic biliary manometry in sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Gut. 1988 Oct;29(10):1397–1401. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.10.1397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funch-Jensen P., Kruse A., Csendes A., Oster M. J., Amdrup E. Biliary manometry in patients with post-cholecystectomy syndrome. Acta Chir Scand. 1982;148(3):267–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geenen J. E., Hogan W. J., Dodds W. J., Toouli J., Venu R. P. The efficacy of endoscopic sphincterotomy after cholecystectomy in patients with sphincter-of-Oddi dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jan 12;320(2):82–87. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198901123200203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geenen J. E., Toouli J., Hogan W. J., Dodds W. J., Stewart E. T., Mavrelis P., Riedel D., Venu R. Endoscopic sphincterotomy: follow-up evaluation of effects on the sphincter of Oddi. Gastroenterology. 1984 Oct;87(4):754–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasson A., Fork F. T., Trägårdh B., Zederfeldt B. The postcholecystectomy syndrome: bile ducts as pain trigger zone. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1988 Apr;23(3):265–271. doi: 10.3109/00365528809093863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody F. G., Becker J. M., Potts J. R. Transduodenal sphincteroplasty and transampullary septectomy for postcholecystectomy pain. Ann Surg. 1983 May;197(5):627–636. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198305000-00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neoptolemos J. P., Bailey I. S., Carr-Locke D. L. Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction: results of treatment by endoscopic sphincterotomy. Br J Surg. 1988 May;75(5):454–459. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800750518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts-Thomson I. C., Toouli J., Blanchett W., Lichtenstein M., Andrews J. T. Assessment of bile flow by radioscintigraphy in patients with biliary-type pain after cholecystectomy. Aust N Z J Med. 1986 Dec;16(6):788–793. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1986.tb00038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts-Thomson I. C., Toouli J. Is endoscopic sphincterotomy for disabling biliary-type pain after cholecystectomy effective? Gastrointest Endosc. 1985 Dec;31(6):370–373. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(85)72250-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolny P., Arlebäck A., Funch-Jensen P., Kruse A., Ravnsbaeck J., Järnerot G. Paradoxical response of sphincter of Oddi to intravenous injection of cholecystokinin or ceruletide. Manometric findings and results of treatment in biliary dyskinesia. Gut. 1986 Dec;27(12):1507–1511. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.12.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarles J. C. Hormonal control of sphincter of Oddi. Dig Dis Sci. 1986 Feb;31(2):208–212. doi: 10.1007/BF01300710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer E. A., Hershfield N. B., Logan K., Kloiber R. Cholescintigraphic detection of functional obstruction of the sphincter of Oddi. Effect of papillotomy. Gastroenterology. 1986 Mar;90(3):728–733. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)91130-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Ikeda S., Matsumoto S., Yoshimoto H., Nakayama F. Manometric diagnosis of sphincter of Oddi spasm as a cause of postcholecystectomy pain and the treatment by endoscopic sphincterotomy. Ann Surg. 1985 Dec;202(6):712–719. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198512000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Ikeda S., Nakayama F. Change in bile duct pressure responses after cholecystectomy: loss of gallbladder as a pressure reservoir. Gastroenterology. 1984 Nov;87(5):1154–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thune A., Thornell E., Svanvik J. Reflex regulation of flow resistance in the feline sphincter of Oddi by hydrostatic pressure in the biliary tract. Gastroenterology. 1986 Dec;91(6):1364–1369. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90188-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toouli J., Geenen J. E., Hogan W. J., Dodds W. J., Arndorfer R. C. Sphincter of Oddi motor activity: a comparison between patients with common bile duct stones and controls. Gastroenterology. 1982 Jan;82(1):111–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toouli J., Roberts-Thomson I. C., Dent J., Lee J. Manometric disorders in patients with suspected sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Gastroenterology. 1985 May;88(5 Pt 1):1243–1250. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


