Abstract
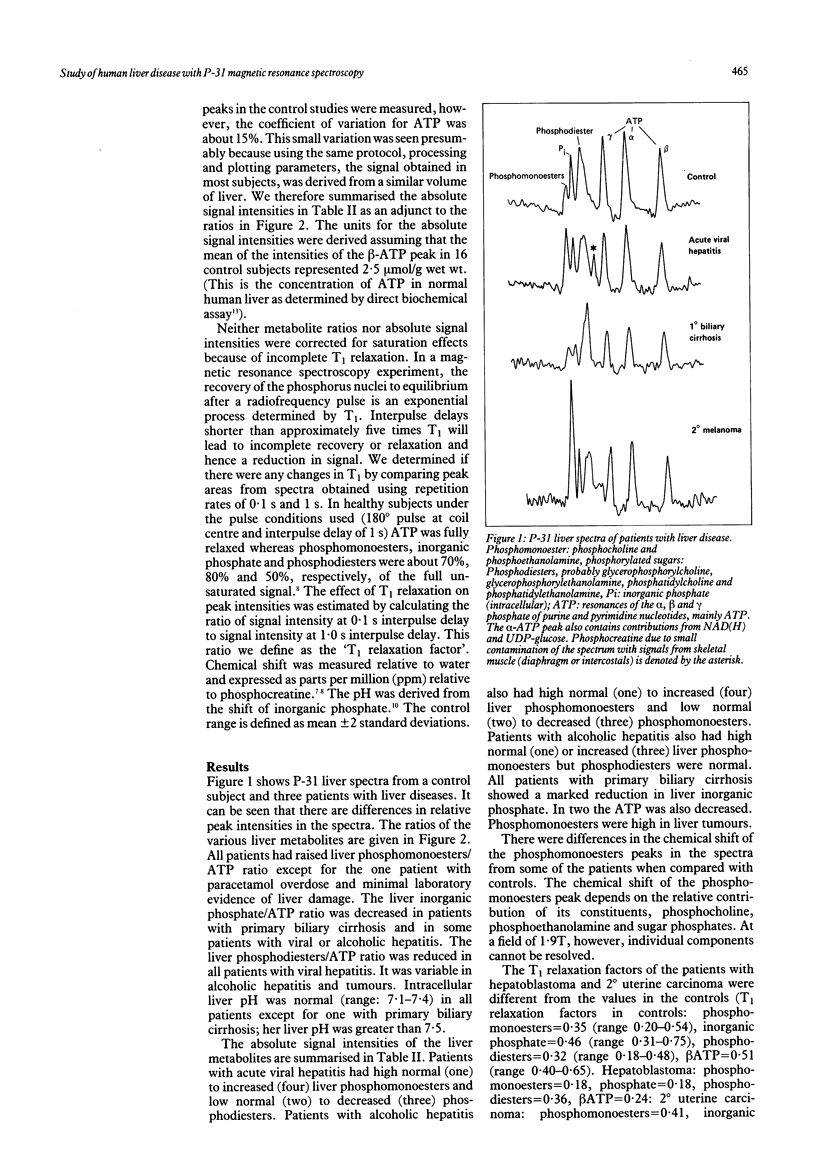
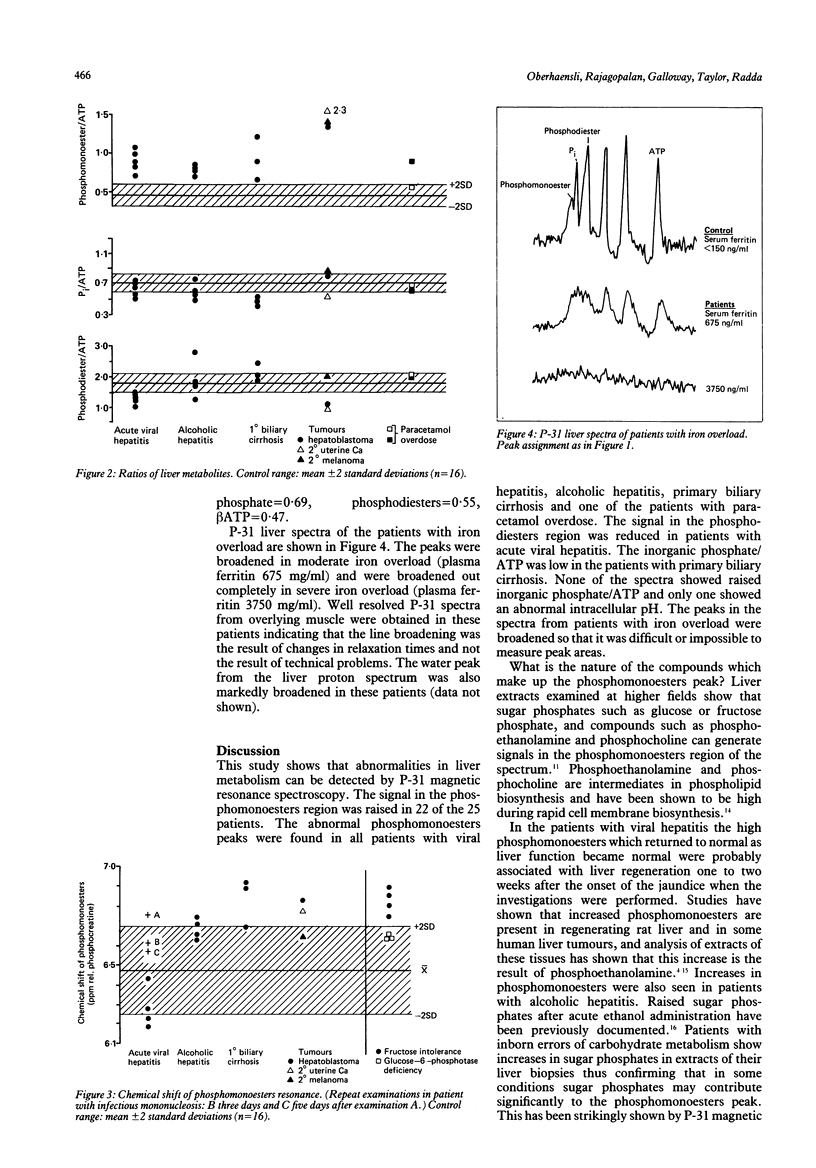
Liver metabolism and energetics of 24 patients with liver disease were studied using phosphorus-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Significant abnormalities were detected in the majority of these patients. A striking diversity in metabolic patterns was observed. Patients with acute viral hepatitis had low liver phosphodiesters and high phosphomonoesters, possibly phosphocholine and phosphoethanolamine. In alcoholic hepatitis phosphomonoesters were raised. Intracellular inorganic phosphate and inorganic phosphate/ATP ratios were decreased in primary biliary cirrhosis and in some patients with hepatitis. These spectroscopic results were evaluated in respect of the pattern of liver damage and cellular regeneration. Liver tumours had raised phosphomonoesters and also showed evidence for altered spin-lattice relaxation of the phosphorus nucleus in various metabolites. In iron overload the liver ATP resonances were broadened. The line broadening correlated with the degree of iron overload suggesting the potential use of P-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy for measuring liver iron.
Full text
PDF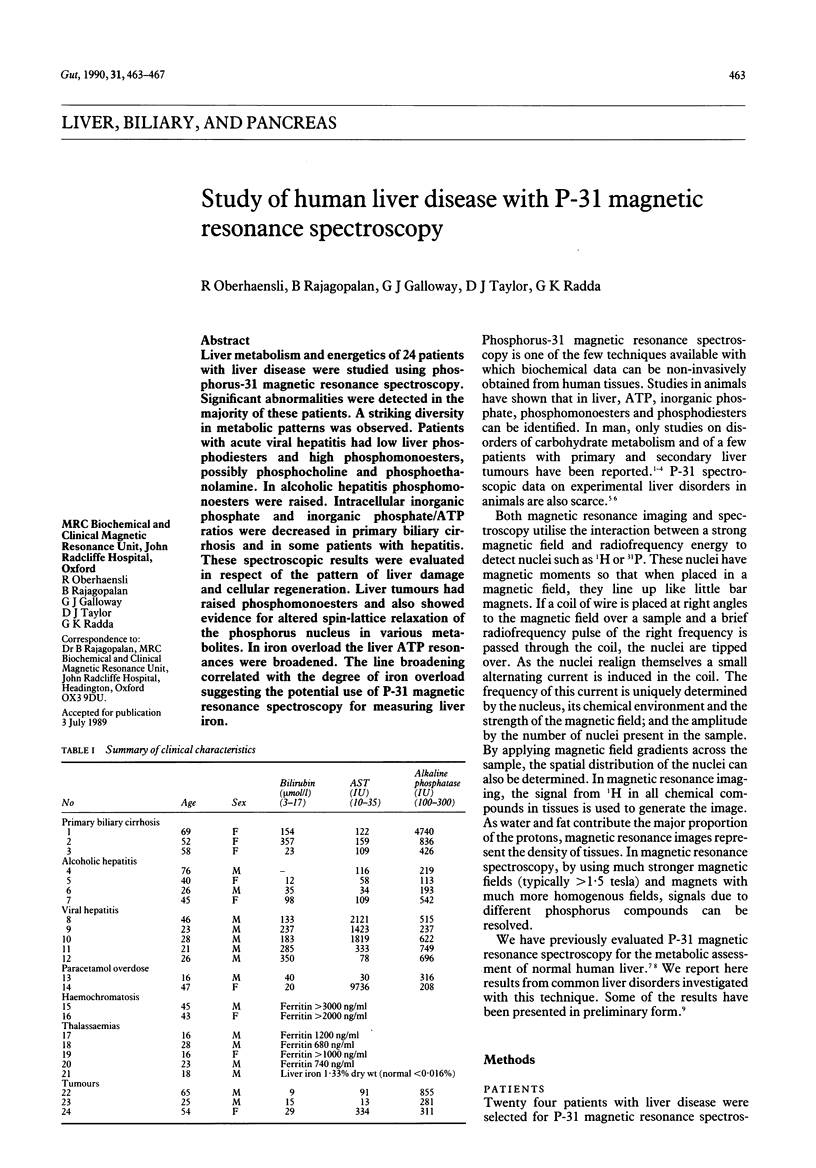


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bates T. E., Williams S. R., Busza A. L., Gadian D. G., Proctor E. A 31P nuclear magnetic resonance study in vivo of metabolic abnormalities in rats with acute liver failure. NMR Biomed. 1988 Apr;1(2):67–73. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1940010203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerdan S., Subramanian V. H., Hilberman M., Cone J., Egan J., Chance B., Williamson J. R. 31P NMR detection of mobile dog brain phospholipids. Magn Reson Med. 1986 Jun;3(3):432–439. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910030308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. M. Simultaneous 13C and 31P NMR studies of perfused rat liver. Effects of insulin and glucagon and a 13C NMR assay of free Mg2+. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14294–14308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmoulin F., Canioni P., Crotte C., Gérolami A., Cozzone P. J. Hepatic metabolism during acute ethanol administration: a phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance study on the perfused rat liver under normoxic or hypoxic conditions. Hepatology. 1987 Mar-Apr;7(2):315–323. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultman E., Nilsson L. H., Sahlin K. Adenine nucleotide content of human liver. Normal values and fructose-induced depletion. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1975 May;35(3):245–251. doi: 10.1080/00365517509095736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maris J. M., Evans A. E., McLaughlin A. C., D'Angio G. J., Bolinger L., Manos H., Chance B. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic investigation of human neuroblastoma in situ. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jun 6;312(23):1500–1505. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198506063122307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro H. N., Linder M. C. Ferritin: structure, biosynthesis, and role in iron metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1978 Apr;58(2):317–396. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1978.58.2.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhaensli R. D., Galloway G. J., Hilton-Jones D., Bore P. J., Styles P., Rajagopalan B., Taylor D. J., Radda G. K. The study of human organs by phosphorus-31 topical magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Br J Radiol. 1987 Apr;60(712):367–373. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-60-712-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhaensli R. D., Galloway G. J., Taylor D. J., Bore P. J., Radda G. K. Assessment of human liver metabolism by phosphorus-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Br J Radiol. 1986 Jul;59(703):695–699. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-59-703-695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhaensli R. D., Hilton-Jones D., Bore P. J., Hands L. J., Rampling R. P., Radda G. K. Biochemical investigation of human tumours in vivo with phosphorus-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Lancet. 1986 Jul 5;2(8497):8–11. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92558-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhaensli R. D., Rajagopalan B., Taylor D. J., Radda G. K., Collins J. E., Leonard J. V., Schwarz H., Herschkowitz N. Study of hereditary fructose intolerance by use of 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Lancet. 1987 Oct 24;2(8565):931–934. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91419-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhaensli R. D., Rajagopalan B., Taylor D. J., Radda G. K., Collins J. E., Leonard J. V. Study of liver metabolism in glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency (glycogen storage disease type 1A) by P-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Pediatr Res. 1988 Apr;23(4):375–380. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198804000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Vance D. E. Regulation of phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 25;779(2):217–251. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(84)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein J. D., Ebraheim N. A., Kellam J. F. Traumatic scapulothoracic dissociation. Radiology. 1985 Nov;157(2):297–298. doi: 10.1148/radiology.157.2.4048434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark D. D., Moseley M. E., Bacon B. R., Moss A. A., Goldberg H. I., Bass N. M., James T. L. Magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy of hepatic iron overload. Radiology. 1985 Jan;154(1):137–142. doi: 10.1148/radiology.154.1.3964933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. J., Bore P. J., Styles P., Gadian D. G., Radda G. K. Bioenergetics of intact human muscle. A 31P nuclear magnetic resonance study. Mol Biol Med. 1983 Jul;1(1):77–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wixom R. L., Prutkin L., Munro H. N. Hemosiderin: nature, formation, and significance. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1980;22:193–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


