Abstract
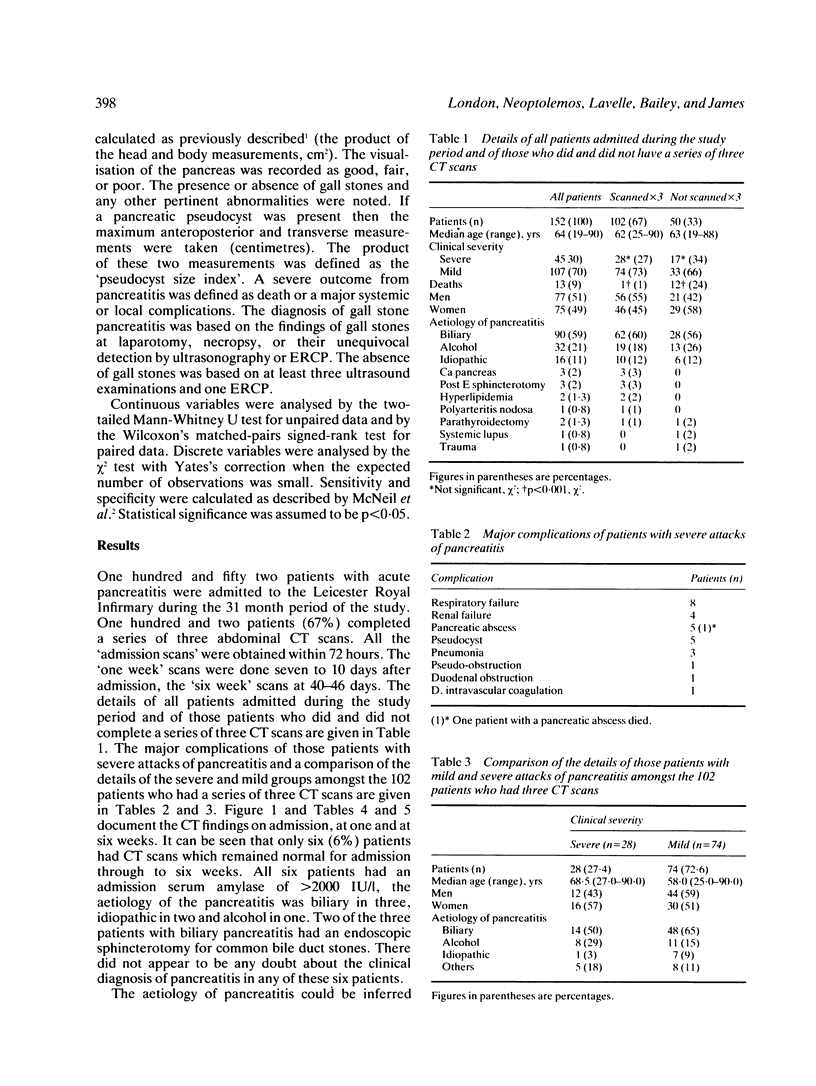
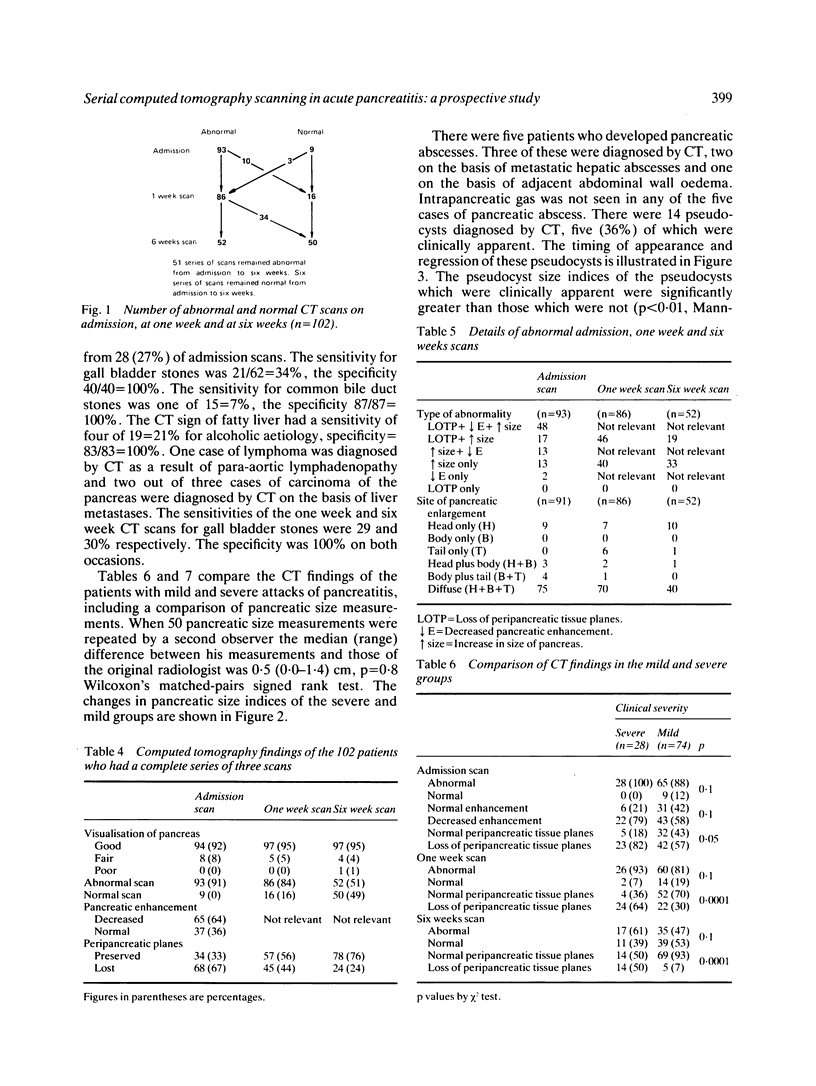
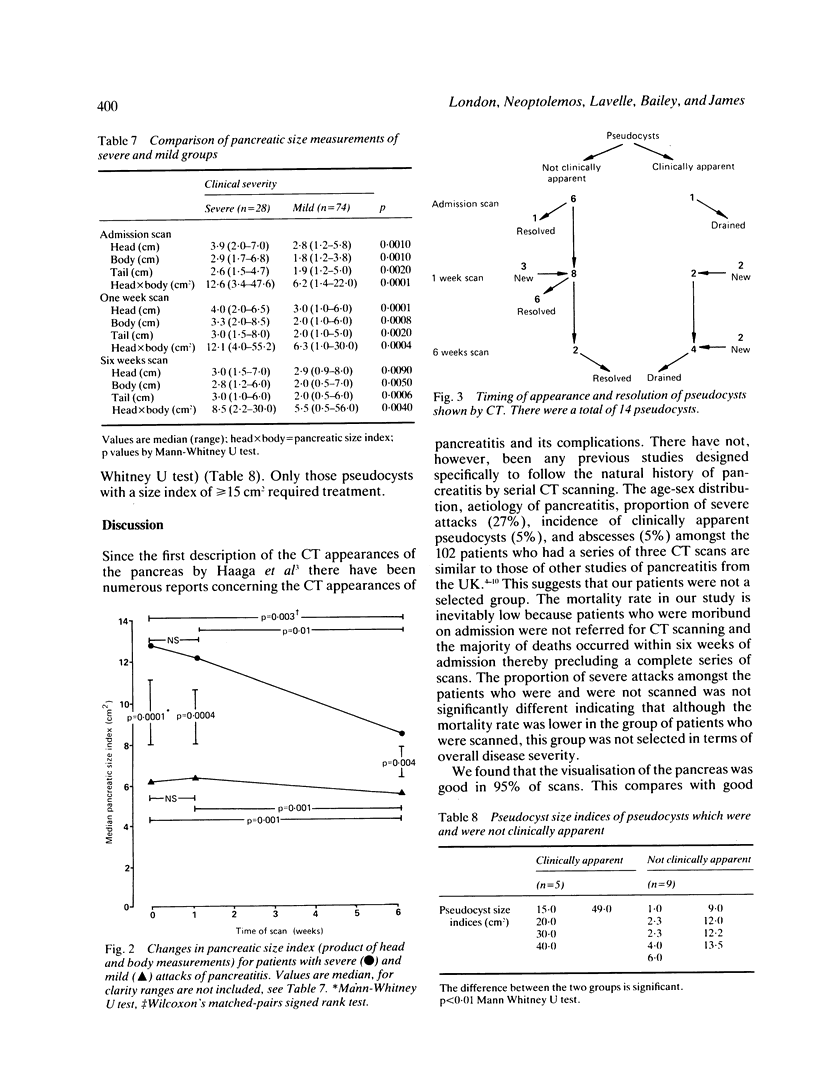
One hundred and two patients with acute pancreatitis had abdominal computed tomography (CT) scans within 72 hours of admission, at one week and at six weeks. Twenty eight attacks were clinically severe, 74 clinically mild. Ninety three (91%) admission scans, 85 (84%) one week scans, and 52 (51%) six week scans were abnormal. The aetiology of the pancreatitis could be inferred from 28 (27%) of admission scans, the CT sign of fatty liver having a sensitivity of 21% and specificity of 100% for alcoholic aetiology. The sensitivity of CT for gall stone aetiology was 34%, specificity 100%. The pancreatic size indices (max anteroposterior measurement of head x max anteroposterior measurement of body) of those patients with severe attacks were significantly greater than those with mild attacks on admission, at one week and at six weeks (p less than 0.004). Fourteen pseudocysts were detected by CT, five (36%) of which were clinically apparent. The pseudocyst size indices (max anteroposterior x max transverse measurement) of the pseudocysts which were clinically apparent were significantly greater than those which were not apparent (p less than 0.01) and only those pseudocysts with a size index greater than or equal to 15 cm2 required treatment.
Full text
PDF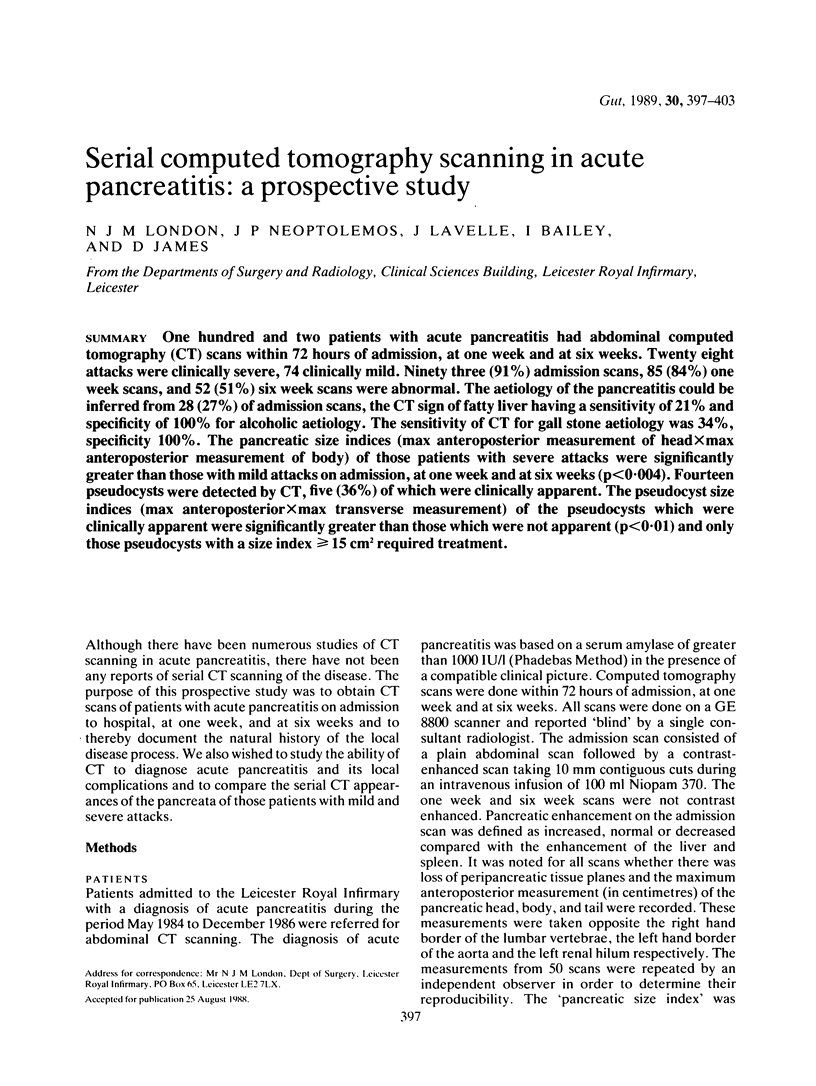



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander E. S., Clark R. A., Federle M. P. Pancreatic gas: indication of pancreatic fistula. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1982 Dec;139(6):1089–1093. doi: 10.2214/ajr.139.6.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. H., Morran C. G., Anderson J. R., Carter D. C. Acute pancreatitis and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Postgrad Med J. 1987 Feb;63(736):137–139. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.63.736.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balthazar E. J., Ranson J. H., Naidich D. P., Megibow A. J., Caccavale R., Cooper M. M. Acute pancreatitis: prognostic value of CT. Radiology. 1985 Sep;156(3):767–772. doi: 10.1148/radiology.156.3.4023241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker H., Gahbauer H., Horn J., Mechler T. Korrelation klinischer und computertomographischer Befunde für die Therapie und Prognose der akuten Pankreatitis. Chirurg. 1985 Jun;56(6):386–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blamey S. L., Imrie C. W., O'Neill J., Gilmour W. H., Carter D. C. Prognostic factors in acute pancreatitis. Gut. 1984 Dec;25(12):1340–1346. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.12.1340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block S., Maier W., Clausen C., Büchler M., Malfertheiner P., Beger H. G. Diagnostik der nekrotisierenden Pankreatitis. Vergleich von Kontrastmittel-CT und Ultraschall in einer klinischen Studie. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1985 May 24;110(21):826–832. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1068912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley E. L., Gonzalez A. C., Clements J. L., Jr Acute pancreatic pseudocysts: incidence and implications. Ann Surg. 1976 Dec;184(6):734–737. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197612000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzelaar R. M., Mulder G. L., Kuhler W. J., Buyink P. D., Davies G. Computer tomography in acute pancreatitis. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1978;19(3):417–422. doi: 10.1177/028418517801900303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavien P. A., Hauser H., Meyer P., Rohner A. Value of contrast-enhanced computerized tomography in the early diagnosis and prognosis of acute pancreatitis. A prospective study of 202 patients. Am J Surg. 1988 Mar;155(3):457–466. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(88)80113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. J., Williamson R. C., Pollock A. V. The role of peritoneal lavage in the prediction and treatment of severe acute pancreatitis. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1982 Nov;64(6):422–427. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crass R. A., Meyer A. A., Jeffrey R. B., Federle M. P., Grendell J. H., Wing V. W., Trunkey D. D. Pancreatic abscess: impact of computerized tomography on early diagnosis and surgery. Am J Surg. 1985 Jul;150(1):127–131. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuschieri A., Wood R. A., Cumming J. R., Meehan S. E., Mackie C. R. Treatment of acute pancreatitis with fresh frozen plasma. Br J Surg. 1983 Dec;70(12):710–712. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800701205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dardik H., Baier R. E., Mennaghan M., Natiella J., Weinberg S., Turner R., Sussman B., Kahn M., Ibrahim I. M., Dardik I. I. Morphologic and biophysical assessment of long term human umbilical cord vein implants used as vascular conduits. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1982 Jan;154(1):17–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bolla A. R., Obeid M. L. Mortality in acute pancreatitis. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1984 May;66(3):184–186. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dembner A. G., Jaffe C. C., Simeone J., Walsh J. A new computed tomographic sign of pancreatitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1979 Sep;133(3):477–479. doi: 10.2214/ajr.133.3.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frija J., Abanou A., Viandier A., Laval-Jeantet M. Tomodensitométrie des pancréatites aiguës graves. J Radiol. 1983 Aug-Sep;64(8-9):483–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman A. J., Neoptolemos J. P., Carr-Locke D. L., Finlay D. B., Fossard D. P. Detection of gall stones after acute pancreatitis. Gut. 1985 Feb;26(2):125–132. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.2.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabbe E., Dammann H. G., Heller M. Wert der Computertomographie für die Prognose der akuten Pankreatitis. Rofo. 1982 May;136(5):534–537. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1056096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. C., Barkin J., Isikoff M. B., Silverstein W., Kalser M. Acute pancreatitis: clinical vs. CT findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1982 Aug;139(2):263–269. doi: 10.2214/ajr.139.2.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtado Andrade H., Hernández Zazueta L. A., Zenteno Castellanos M. A., Barajas González E. R. Utilidad de la tomografía axial computada en el diagnóstico de pancreatitis aguda y sus complicaciones. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 1984 Jan-Mar;49(1):31–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imrie C. W., Benjamin I. S., Ferguson J. C., McKay A. J., Mackenzie I., O'Neill J., Blumgart L. H. A single-centre double-blind trial of Trasylol therapy in primary acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1978 May;65(5):337–341. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800650514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imrie C. W., Whyte A. S. A prospective study of acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1975 Jun;62(6):490–494. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800620615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalmar J. A., Matthews C. C., Bishop L. A. Computerized tomography in acute and chronic pancreatitis. South Med J. 1984 Nov;77(11):1393–1395. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198411000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivisaari L., Somer K., Standertskjöld-Nordenstam C. G., Schröder T., Kivilaakso E., Lempinen M. A new method for the diagnosis of acute hemorrhagic-necrotizing pancreatitis using contrast-enhanced CT. Gastrointest Radiol. 1984;9(1):27–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01887796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivisaari L., Somer K., Standertskjöld-Nordenstam C. G., Schröder T., Kivilaakso E., Lempinen M. Early detection of acute fulminant pancreatitis by contrast-enhanced computed tomography. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1983 Jan;18(1):39–41. doi: 10.3109/00365528309181556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivisaari L., Virtama P., Rantakokko V. Computerised tomography of the pancreas with acute pancreatitis. Ann Clin Res. 1979 Jun;11(3):90–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolmannskog F., Kolbenstvedt A., Aakhus T. Computed tomography in inflammatory mass lesions following acute pancreatitis. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1981 Apr;5(2):169–172. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198104000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kursawe R., Lüning M., Wolff H., Mai A. Ergebnisse der computertomographischen Diagnostik zur Differenzierung des Schweregrades der akuten Pankreatitis. Rofo. 1987 Jan;146(1):27–33. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1048436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leese T., Holliday M., Heath D., Hall A. W., Bell P. R. Multicentre clinical trial of low volume fresh frozen plasma therapy in acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1987 Oct;74(10):907–911. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800741012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine E. Carcinoma of the pancreas presenting as acute pancreatitis: CT diagnosis. Gastrointest Radiol. 1981 Jan 15;6(1):29–33. doi: 10.1007/BF01890217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay A. J., Imrie C. W., O'Neill J., Duncan J. G. Is an early ultrasound scan of value in acute pancreatitis? Br J Surg. 1982 Jul;69(7):369–372. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800690704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil B. J., Keller E., Adelstein S. J. Primer on certain elements of medical decision making. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jul 31;293(5):211–215. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197507312930501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez G., Jr, Isikoff M. B., Hill M. C. CT of acute pancreatitis: interim assessment. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1980 Sep;135(3):463–469. doi: 10.2214/ajr.135.3.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez G., Jr, Isikoff M. B. Significance of intrapancreatic gas demonstrated by CT: a review of nine cases. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1979 Jan;132(1):59–62. doi: 10.2214/ajr.132.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moossa A. R. Current concepts. Diagnostic tests and procedures in acute pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 1984 Sep 6;311(10):639–643. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198409063111005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neoptolemos J. P., Hall A. W., Finlay D. F., Berry J. M., Carr-Locke D. L., Fossard D. P. The urgent diagnosis of gallstones in acute pancreatitis: a prospective study of three methods. Br J Surg. 1984 Mar;71(3):230–233. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800710324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordestgaard A. G., Wilson S. E., Williams R. A. Early computerized tomography as a predictor of outcome in acute pancreatitis. Am J Surg. 1986 Jul;152(1):127–132. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(86)90162-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponette E., Pringot J., Baert A. L., Marchal G., Dardenne A. N., Coenen Y. Computerized tomography and ultrasonography in pancratitis. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 1976 Nov-Dec;39(11-12):402–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor H. J., Schwartz J. A., Rutledge R., Mauro M. A. Radiology and surgery in the treatment of the complications of acute pancreatitis. N C Med J. 1987 Apr;48(4):211–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranson J. H., Balthazar E., Caccavale R., Cooper M. Computed tomography and the prediction of pancreatic abscess in acute pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 1985 May;201(5):656–665. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198505000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert J. H., Meyer P., Rohner A. Can serum and peritoneal amylase and lipase determinations help in the early prognosis of acute pancreatitis? Ann Surg. 1986 Feb;203(2):163–168. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198602000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder T., Kivisaari L., Somer K., Standertskjöld-Nordenstam C. G., Kivilaakso E., Lempinen M. Significance of extrapancreatic findings in computed tomography (CT) of acute pancreatitis. Eur J Radiol. 1985 Nov;5(4):273–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder T., Kivisaari L., Standertskjöld-Nordenstam C. G., Somer K., Lehtola A., Puolakkainen P., Karonen S. L., Kivilaakso E., Lempinen M. Pancreatic blood flow and contrast enhancement in computed tomography during experimental pancreatitis. Eur Surg Res. 1985;17(5):286–291. doi: 10.1159/000128480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein W., Isikoff M. B., Hill M. C., Barkin J. Diagnostic imaging of acute pancreatitis: prospective study using CT and sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981 Sep;137(3):497–502. doi: 10.2214/ajr.137.3.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler S. J., Dalton J. W., Robbins A. H., Gerzof S. G., Stern J. S., Johnson W. C., Nabseth D. C., Schimmel E. M. Prevalence of normal serum amylase levels in patients with acute alcoholic pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1983 Oct;28(10):865–869. doi: 10.1007/BF01317034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada T., Yasuda H., Uchiyama K., Hasegawa H., Sitaka J., Nagai J. [CT findings and CT score in acute pancreatitis compared its with severity]. Nihon Igaku Hoshasen Gakkai Zasshi. 1986 Oct 25;46(10):1167–1173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres W. E., Clements J. L., Jr, Sones P. J., Knopf D. R. Gas in the pancreatic bed without abscess. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981 Dec;137(6):1131–1133. doi: 10.2214/ajr.137.6.1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapnell J. E., Duncan E. H. Patterns of incidence in acute pancreatitis. Br Med J. 1975 Apr 26;2(5964):179–183. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5964.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissberg D., Adam Y. G., Volk H., State D. Acute pancreatitis: a 10-year study. Am Surg. 1972 Oct;38(10):574–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



