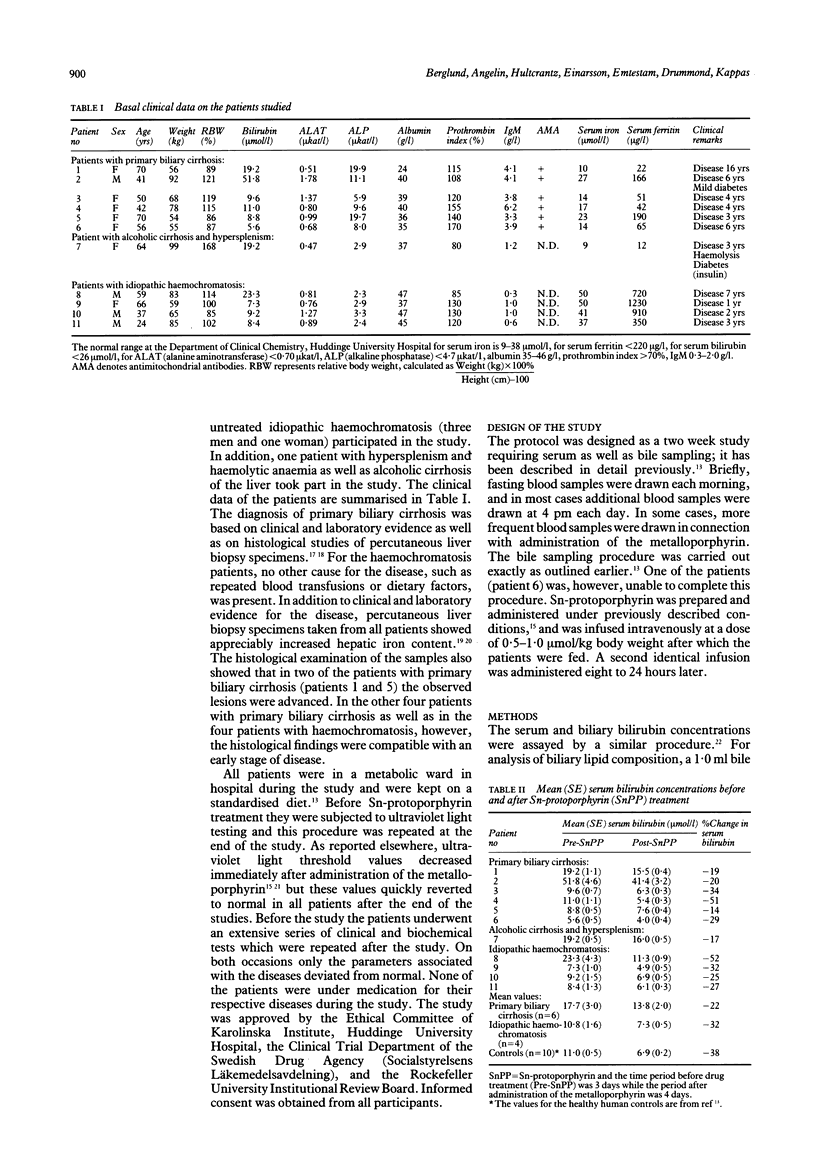
Abstract
Sn(tin4+)-protoporphyrin, a potent competitive inhibitor of haeme oxygenase, the rate limiting enzyme in the degradation of haeme to bile pigments, was given intravenously to six patients with primary biliary cirrhosis and to four patients with idiopathic haemochromatosis. Serum bilirubin concentrations decreased in all patients after administration of 1-2 mumol/kg body weight of the metalloporphyrin, given in two doses eight to 24 hours apart. This reduction lasted approximately four to five days after injection of the compound. Excretion of endogenous haeme in bile increased (mean increase approximately two to threefold) in parallel with the decrease in serum bilirubin concentrations in both patient groups, and the highest biliary haeme concentrations were found during the first 48 hours after treatment. Sn-protoporphyrin was cleared rapidly from plasma with a half-life of 3.4 hours. Biliary bilirubin concentrations decreased (mean decrease, 49%) in the haemochromatosis patients after Sn-protoporphyrin administration. No decrease in biliary bilirubin concentrations could be detected in the primary biliary cirrhosis patients under the same conditions. Thus, Sn-protoporphyrin treatment resulted in a decrease in serum bilirubin concentrations and an increase in biliary haeme excretion in patients with haemochromatosis and primary biliary cirrhosis, as has previously been shown in normal subjects. The results indicate that the synthetic haeme analogue inhibits haeme oxidation activity in the two patient groups studied, as it does in normal people and in experimental animals. The lack of effect of Sn-protoporphyrin on biliary bilirubin excretion in primary biliary cirrhosis may be related to a differently affected hepatic clearance system or to a different distribution of tissue bilirubin pools in this condition.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. E., Simionatto C. S., Drummond G. S., Kappas A. Disposition of tin-protoporphyrin and suppression of hyperbilirubinemia in humans. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1986 May;39(5):510–520. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1986.88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berglund L., Angelin B., Blomstrand R., Drummond G., Kappas A. Sn-protoporphyrin lowers serum bilirubin levels, decreases biliary bilirubin output, enhances biliary heme excretion and potently inhibits hepatic heme oxygenase activity in normal human subjects. Hepatology. 1988 May-Jun;8(3):625–631. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brink B., Disler P., Lynch S., Jacobs P., Charlton R., Bothwell T. Patterns of iron storage in dietary iron overload and idiopathic hemochromatosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Nov;88(5):725–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelius C. E., Rodgers P. A., Bruss M. L., Ahlfors C. E. Characterization of Gilbert-like syndrome in squirrel monkeys (Saimiri sciureus). J Med Primatol. 1985;14(2):59–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelius C. E., Rodgers P. A. Prevention of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia in rhesus monkeys by tin-protoporphyrin. Pediatr Res. 1984 Aug;18(8):728–730. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198408000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond G. S., Kappas A. An experimental model of postnatal jaundice in the suckling rat. Suppression of induced hyperbilirubinemia by Sn-protoporphyrin. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):142–149. doi: 10.1172/JCI111394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond G. S., Kappas A. Chemoprevention of neonatal jaundice: potency of tin-protoporphyrin in an animal model. Science. 1982 Sep 24;217(4566):1250–1252. doi: 10.1126/science.6896768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond G. S., Kappas A. Prevention of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia by tin protoporphyrin IX, a potent competitive inhibitor of heme oxidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6466–6470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond G. S., Kappas A. Sn-protoporphyrin inhibition of fetal and neonatal brain heme oxygenase. Transplacental passage of the metalloporphyrin and prenatal suppression of hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn animal. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):971–976. doi: 10.1172/JCI112398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond G. S., Kappas A. Suppression of hyperbilirubinemia in the rat neonate by chromium-protoporphyrin. Interactions of metalloporphyrins with microsomal heme oxygenase of human spleen. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1878–1883. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emtestam L., Berglund L., Angelin B., Drummond G. S., Kappas A. Tin-protoporphyrin and long wave length ultraviolet light in treatment of psoriasis. Lancet. 1989 Jun 3;1(8649):1231–1233. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92331-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fausa O., Skålhegg B. A. Quantitative determination of bile acids and their conjugates using thin-layer chromatography and a purified 3alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1974;9(3):249–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultcrantz R., Angelin B., Björn-Rasmussen E., Ewerth S., Einarsson K. Biliary excretion of iron and ferritin in idiopathic hemochromatosis. Gastroenterology. 1989 Jun;96(6):1539–1545. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90524-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. M. Primary biliary cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 26;316(9):521–528. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702263160907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappas A., Drummond G. S. Control of heme metabolism with synthetic metalloporphyrins. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):335–339. doi: 10.1172/JCI112309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappas A., Drummond G. S., Manola T., Petmezaki S., Valaes T. Sn-protoporphyrin use in the management of hyperbilirubinemia in term newborns with direct Coombs-positive ABO incompatibility. Pediatrics. 1988 Apr;81(4):485–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappas A., Simionatto C. S., Drummond G. S., Sassa S., Anderson K. E. The liver excretes large amounts of heme into bile when heme oxygenase is inhibited competitively by Sn-protoporphyrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):896–900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roda A., Festi D., Sama C., Mazzella G., Alini R., Roda E., Barbara L. Enzymatic determination of cholesterol in bile. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 Nov 3;64(3):337–341. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90364-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Fkeischer S., Yamamoto A. Two dimensional then layer chromatographic separation of polar lipids and determination of phospholipids by phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids. 1970 May;5(5):494–496. doi: 10.1007/BF02531316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassa S., Drummond G. S., Bernstein S. E., Kappas A. Tin-protoporphyrin suppression of hyperbilirubinemia in mutant mice with severe hemolytic anemia. Blood. 1983 May;61(5):1011–1013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock S., Scheuer P. J. The presentation and diagnosis of 100 patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Sep 27;289(13):674–678. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197309272891306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenhunen R., Marver H. S., Schmid R. Microsomal heme oxygenase. Characterization of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1969 Dec 10;244(23):6388–6394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valberg L. S., Ghent C. N. Diagnosis and management of hereditary hemochromatosis. Annu Rev Med. 1985;36:27–37. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.36.020185.000331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga T., Sassa S., Kappas A. Purification and properties of bovine spleen heme oxygenase. Amino acid composition and sites of action of inhibitors of heme oxidation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7778–7785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


