Abstract
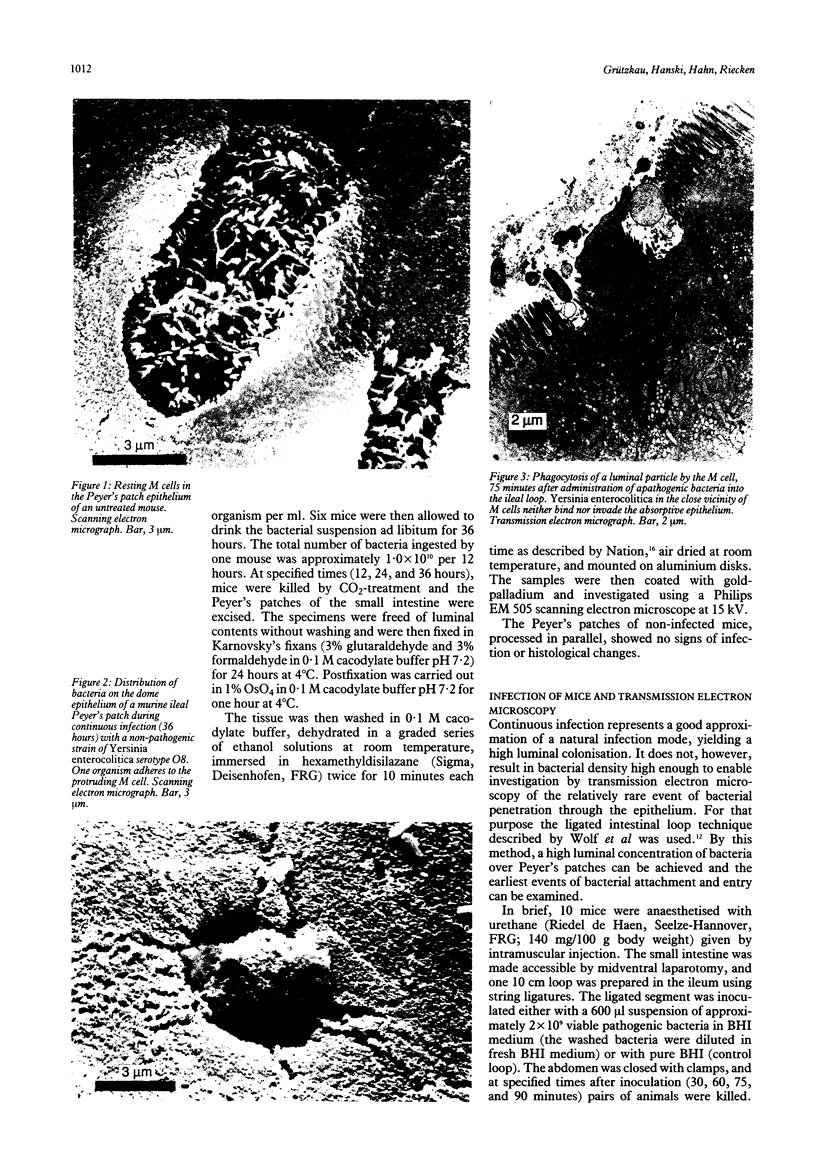
Recent evidence indicates that ileal Peyer's patches represent the main infection route for Yersinia enterocolitica. In this study transmission and scanning electron microscopy have shown that only a small fraction of bacteria present in the lumen adhere to the follicle-associated murine epithelium with no discernible preference for either M or absorptive cells. Yersiniae attached to M cells are phagocytosed and transported from the lumen into the lamina propria. No invasion of columnar absorptive cells was observed. These data, in combination with recently published reports, indicate that the involvement of M cells is a common step in bacterial invasion of Peyer's patches.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakour R., Balligand G., Laroche Y., Cornelis G., Wauters G. A simple adult-mouse test for tissue invasiveness in Yersinia enterocolitica strains of low experimental virulence. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Apr;19(2):237–246. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-2-237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockemühl J. Die enteralen Yersiniosen: Pathogenese, klinischer Verlauf, Epidemiologie und Diagnose. Immun Infekt. 1982 Sep;10(5):180–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. B. Pathogenecity of Yersinia enterocolitica for mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):164–170. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.164-170.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanski C., Kutschka U., Schmoranzer H. P., Naumann M., Stallmach A., Hahn H., Menge H., Riecken E. O. Immunohistochemical and electron microscopic study of interaction of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O8 with intestinal mucosa during experimental enteritis. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):673–678. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.673-678.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman L. R., Cantey J. R. Specific adherence of Escherichia coli (strain RDEC-1) to membranous (M) cells of the Peyer's patch in Escherichia coli diarrhea in the rabbit. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jan;71(1):1–8. doi: 10.1172/JCI110737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Voorhis D. L., Falkow S. Identification of invasin: a protein that allows enteric bacteria to penetrate cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):769–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohbata S., Yokoyama H., Yabuuchi E. Cytopathogenic effect of Salmonella typhi GIFU 10007 on M cells of murine ileal Peyer's patches in ligated ileal loops: an ultrastructural study. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(12):1225–1237. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb03055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian C. J., Hwang W. S., Kelly J. K., Pai C. H. Invasiveness of Yersinia enterocolitica lacking the virulence plasmid: an in-vivo study. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Nov;24(3):219–226. doi: 10.1099/00222615-24-3-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee Z. A., Gorby G. L., Wyrick P. B., Hodinka R., Hoffman L. H. Parasite-directed endocytosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S311–S316. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Falkow S. Evidence for two genetic loci in Yersinia enterocolitica that can promote invasion of epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1242–1248. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1242-1248.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Hill W. E., Falkow S. The ail locus is found uniquely in Yersinia enterocolitica serotypes commonly associated with disease. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):121–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.121-131.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nation J. L. A new method using hexamethyldisilazane for preparation of soft insect tissues for scanning electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 1983 Nov;58(6):347–351. doi: 10.3109/10520298309066811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. L., Pierce N. F., Apple R. T., Cray W. C., Jr M cell transport of Vibrio cholerae from the intestinal lumen into Peyer's patches: a mechanism for antigen sampling and for microbial transepithelial migration. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jun;153(6):1108–1118. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.6.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. L. Sequential uptake of horseradish peroxidase by lymphoid follicle epithelium of Peyer's patches in the normal unobstructed mouse intestine: an ultrastructural study. Gastroenterology. 1977 Mar;72(3):440–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., DeStephano L. Serum resistance associated with virulence in Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):605–611. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.605-611.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Tzipori S., Gonis G., Hayes J., Withers M., Prpic J. K. The pathogenesis of Yersinia enterocolitica infection in gnotobiotic piglets. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Jun;19(3):297–308. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-3-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosqvist R., Skurnik M., Wolf-Watz H. Increased virulence of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis by two independent mutations. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):522–524. doi: 10.1038/334522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneller M. C., Strober W. M cells and host defense. J Infect Dis. 1986 Nov;154(5):737–741. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.5.737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. I., Schmauder-Chock E. A., Parker J. L., Burr D. Selective association and transport of Campylobacter jejuni through M cells of rabbit Peyer's patches. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Oct;34(10):1142–1147. doi: 10.1139/m88-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassef J. S., Keren D. F., Mailloux J. L. Role of M cells in initial antigen uptake and in ulcer formation in the rabbit intestinal loop model of shigellosis. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):858–863. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.858-863.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf J. L., Bye W. A. The membranous epithelial (M) cell and the mucosal immune system. Annu Rev Med. 1984;35:95–112. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.35.020184.000523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf J. L., Rubin D. H., Finberg R., Kauffman R. S., Sharpe A. H., Trier J. S., Fields B. N. Intestinal M cells: a pathway for entry of reovirus into the host. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):471–472. doi: 10.1126/science.6259737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









