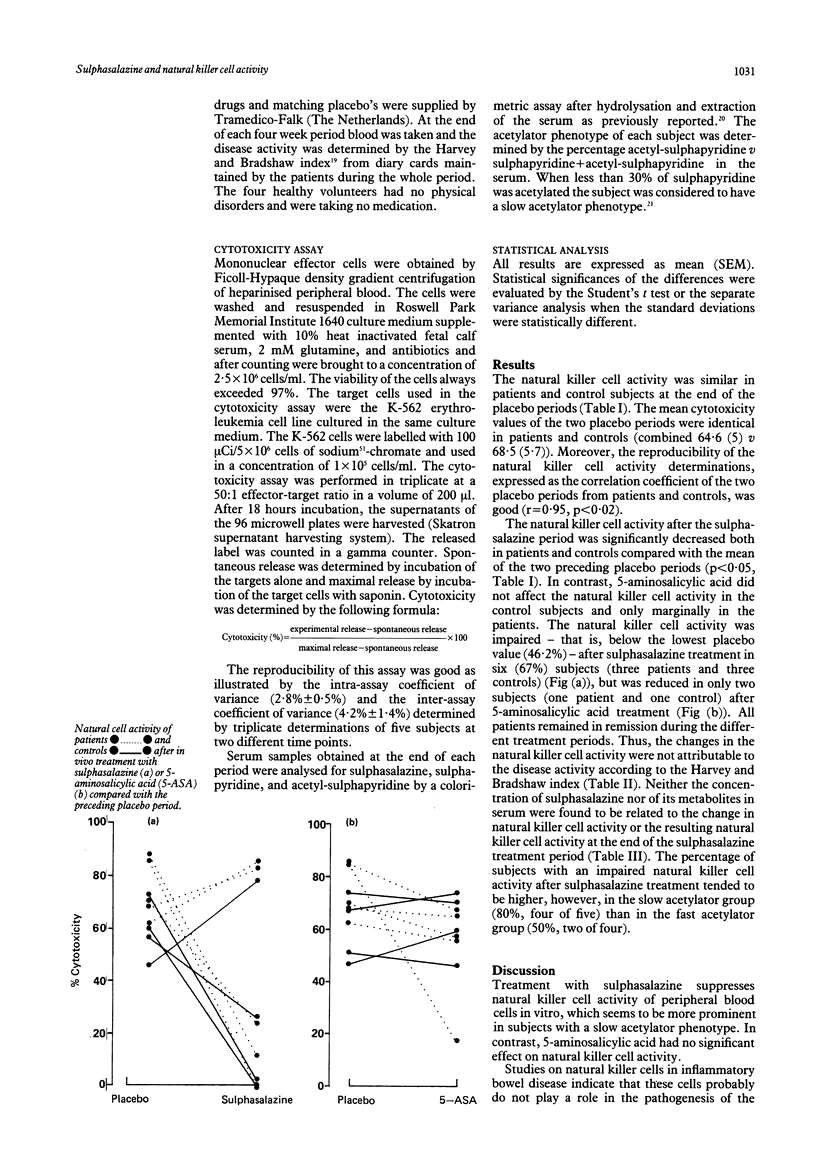
Abstract
Decreased cell mediated cytotoxicity occurs frequently in inflammatory bowel disease, particularly in patients with active disease. It is not clear, however, whether this decrease is caused by the disease or is a consequence of the medical treatment. In this study we evaluated the effect of in vivo treatment with 5-aminosalicylic acid and sulphasalazine on the in vitro natural killer cell activity in five patients with inflammatory bowel disease in remission and in four healthy control subjects in a double blind randomised crossover trial preceded and separated by four weeks of treatment with placebo. The natural killer cell activity was significantly impaired in 67% (six of nine subjects) after four weeks' sulphasalazine treatment and tended to be related to subjects with a slow acetylator phenotype. In contrast, 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment caused only a marginal reaction in the natural killer cell activity in 22% (two of nine subjects). The inhibitory effects were found to be reversible since the decreased natural killer cell activity was completely restored after placebo treatment in all subjects. In conclusion, in vivo treatment with sulphasalazine inhibits the in vitro natural killer cell activity and this seems to be mediated by the sulphapyridine moiety. This phenomenon may contribute to the low natural killer cell activity found in patients with active inflammatory bowel disease.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aparicio-Pagés M. N., Verspaget H. W., Peña A. S., Weterman I. T., Mieremet-Ooms M. A., van der Zon J. M., de Bruin P. A., Lamers C. B. Natural, lectin- and phorbol ester-induced cellular cytotoxicity in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1988 Nov;27(3):109–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aparició-Pagés M. N., Verspaget H. W., Peña A. S., Weterman I. T., de Bruin P. A., Mieremet-Ooms M. A., van der Zon J. M., van Tol E. A., Lamers C. B. In vitro cellular cytotoxicity in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis: relation with disease activity and treatment, and the effect of recombinant gamma-interferon. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1989 Jul;29(3):119–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auer I. O., Ziemer E., Sommer H. Immune status in Crohn's disease. V. Decreased in vitro natural killer cell activity in peripheral blood. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Oct;42(1):41–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachrach W. H. Sulfasalazine: I. An historical perspective. Am J Gastroenterol. 1988 May;83(5):487–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson P. R., Jewell D. P. Local immune mechanisms in inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal carcinoma. Natural killer cells and their activity. Gastroenterology. 1986 Jan;90(1):12–19. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson P. R., Jewell D. P. Sulphasalazine and derivatives, natural killer activity and ulcerative colitis. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Aug;69(2):177–184. doi: 10.1042/cs0690177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg C. H., Dambrauskas J. T., Ault K. A., Falchuk Z. M. Impaired natural killer cell activity in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: evidence for a qualitative defect. Gastroenterology. 1983 Oct;85(4):846–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson K. A., Sandberg M. Determination of sulphapyridine and its metabolites in biological materials after administration of salicylazosulphapyridine. Acta Pharm Suec. 1973 Mar;10(1):87–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. F., Bradshaw J. M. A simple index of Crohn's-disease activity. Lancet. 1980 Mar 8;1(8167):514–514. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92767-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdstock G., Chastenay B. F., Krawitt E. L. Increased suppressor cell activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1981 Dec;22(12):1025–1030. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.12.1025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott R. P., Bragdon M. J., Kodner I. J., Bertovich M. J. Deficient cell-mediated cytotoxicity and hyporesponsiveness to interferon and mitogenic lectin activation by inflammatory bowel disease peripheral blood and intestinal mononuclear cells. Gastroenterology. 1986 Jan;90(1):6–11. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott R. P., Kane M. G., Steele L. L., Stenson W. F. Inhibition of cytotoxicity by sulfasalazine. I. Sulfasalazine inhibits spontaneous cell-mediated cytotoxicity by peripheral blood and intestinal mononuclear cells from control and inflammatory bowel disease patients. Immunopharmacology. 1986 Apr;11(2):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(86)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason P. D., Weetman A. P., Sissons J. G., Borysiewicz L. K. Suppressive role of NK cells in pokeweed mitogen-induced immunoglobulin synthesis: effect of depletion/enrichment of Leu 11b+ cells. Immunology. 1988 Sep;65(1):113–118. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyachi Y., Yoshioka A., Imamura S., Niwa Y. Effect of sulphasalazine and its metabolites on the generation of reactive oxygen species. Gut. 1987 Feb;28(2):190–195. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.2.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen O. H., Verspaget H. W., Elmgreen J. Inhibition of intestinal macrophage chemotaxis to leukotriene B4 by sulphasalazine, olsalazine, and 5-aminosalicylic acid. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1988 Jun;2(3):203–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1988.tb00689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon P., Stenson W. F. Enhanced synthesis of leukotriene B4 by colonic mucosa in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1984 Mar;86(3):453–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svartz N. Sulfasalazine: II. Some notes on the discovery and development of salazopyrin. Am J Gastroenterol. 1988 May;83(5):497–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taggart A. J., Neumann V. C., Hill J., Astbury C., Le Gallez P., Dixon J. S. 5-Aminosalicylic acid or sulphapyridine. Which is the active moiety of sulphasalazine in rheumatoid arthritis? Drugs. 1986;32 (Suppl 1):27–34. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198600321-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


