Abstract
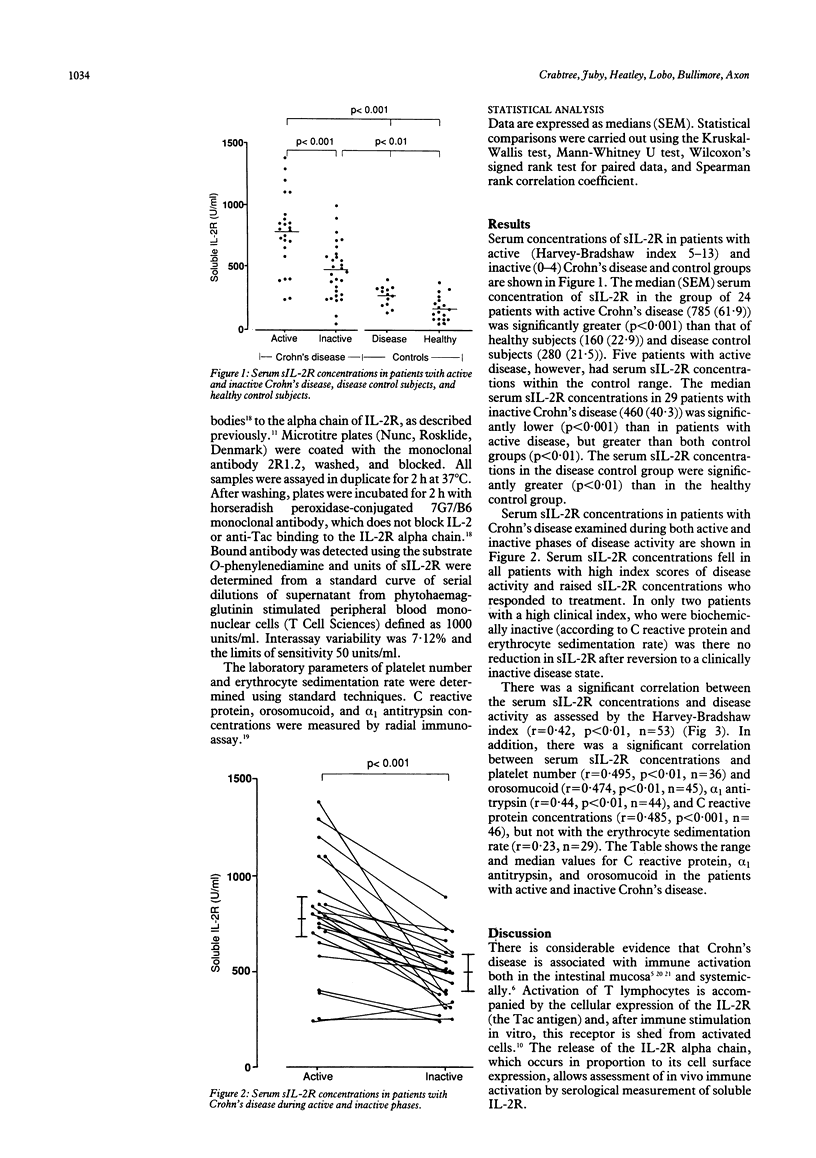
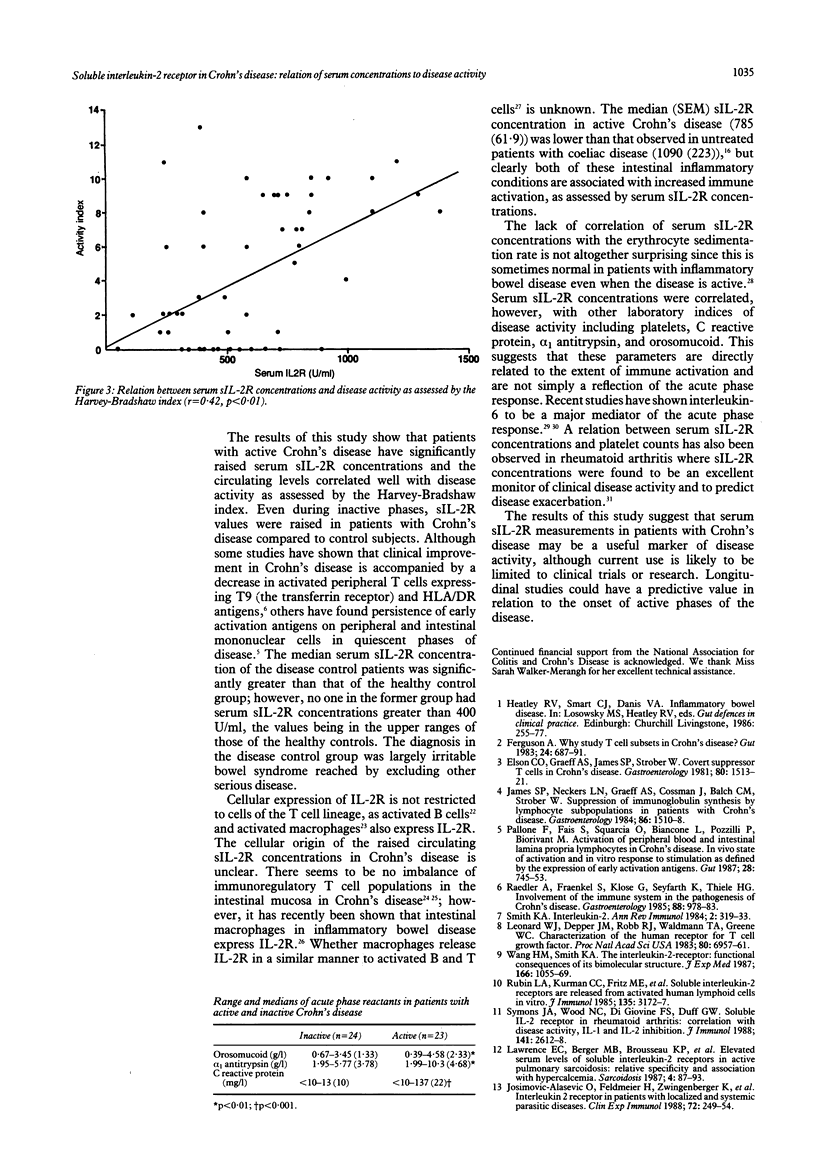
Serum concentrations of soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R) were measured as a marker of immune activation in a group of 30 patients with Crohn's disease. sIL-2R concentrations were determined by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay during periods of active and inactive disease and correlated with standard parameters of disease activity. Serum concentrations of sIL-2R were significantly raised in patients with active Crohn's disease compared with patients with inactive disease (p less than 0.001) and control subjects. There was a significant correlation between serum sIL-2R concentrations and disease activity as assessed by the Harvey-Bradshaw index (r = 0.42, p less than 0.01), platelet numbers (r = 0.49, p less than 0.01), and orosomucoid (r = 0.47, p less than 0.01), alpha 1 antitrypsin (r = 0.44, p less than 0.01), and C reactive protein concentrations (r = 0.48, p less than 0.001) but not with the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Measurement of serum sIL-2R concentration is a simple and useful laboratory means of assessing disease activity. Raised concentrations in patients with active Crohn's disease is further evidence for in vivo immune activation occurring in this disease.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. H., Wang L., Hubscher S. G., Elias E., Neuberger J. M. Soluble interleukin-2 receptors in serum and bile of liver transplant recipients. Lancet. 1989 Mar 4;1(8636):469–471. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91368-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andus T., Geiger T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Heinrich P. C. Action of recombinant human interleukin 6, interleukin 1 beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha on the mRNA induction of acute-phase proteins. Eur J Immunol. 1988 May;18(5):739–746. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colver G. B., Symons J. A., Duff G. W. Soluble interleukin 2 receptor in atopic eczema. BMJ. 1989 May 27;298(6685):1426–1428. doi: 10.1136/bmj.298.6685.1426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree J. E., Heatley R. V., Juby L. D., Howdle P. D., Losowsky M. S. Serum interleukin-2-receptor in coeliac disease: response to treatment and gluten challenge. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Sep;77(3):345–348. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Graeff A. S., James S. P., Strober W. Covert suppressor T cells in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jun;80(6):1513–1521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A. Why study T cell subsets in Crohn's disease? Gut. 1983 Aug;24(8):687–691. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.8.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock W. W., Muller W. A., Cotran R. S. Interleukin 2 receptors are expressed by alveolar macrophages during pulmonary sarcoidosis and are inducible by lymphokine treatment of normal human lung macrophages, blood monocytes, and monocyte cell lines. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 1;138(1):185–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. F., Bradshaw J. M. A simple index of Crohn's-disease activity. Lancet. 1980 Mar 8;1(8167):514–514. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92767-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. P., Fiocchi C., Graeff A. S., Strober W. Phenotypic analysis of lamina propria lymphocytes. Predominance of helper-inducer and cytolytic T-cell phenotypes and deficiency of suppressor-inducer phenotypes in Crohn's disease and control patients. Gastroenterology. 1986 Dec;91(6):1483–1489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. P., Neckers L. M., Graeff A. S., Cossman J., Balch C. M., Strober W. Suppression of immunoglobulin synthesis by lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jun;86(6):1510–1518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josimovic-Alasevic O., Feldmeier H., Zwingenberger K., Harms G., Hahn H., Shrisuphanunt M., Diamantstein T. Interleukin 2 receptor in patients with localized and systemic parasitic diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 May;72(2):249–254. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence E. C., Berger M. B., Brousseau K. P., Rodriguez T. M., Siegel S. J., Kurman C. C., Nelson D. L. Elevated serum levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptors in active pulmonary sarcoidosis: relative specificity and association with hypercalcemia. Sarcoidosis. 1987 Sep;4(2):87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Robb R. J., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Characterization of the human receptor for T-cell growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6957–6961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahida Y. R., Patel S., Gionchetti P., Vaux D., Jewell D. P. Macrophage subpopulations in lamina propria of normal and inflamed colon and terminal ileum. Gut. 1989 Jun;30(6):826–834. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.6.826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahida Y. R., Patel S., Wu K., Jewell D. P. Interleukin 2 receptor expression by macrophages in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Dec;74(3):382–386. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahida Y. R., Wu K., Jewell D. P. Enhanced production of interleukin 1-beta by mononuclear cells isolated from mucosa with active ulcerative colitis of Crohn's disease. Gut. 1989 Jun;30(6):835–838. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.6.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. L., Rubin L. A., Kurman C. C., Fritz M. E., Boutin B. An analysis of the cellular requirements for the production of soluble interleukin-2 receptors in vitro. J Clin Immunol. 1986 Mar;6(2):114–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00918743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallone F., Fais S., Squarcia O., Biancone L., Pozzilli P., Boirivant M. Activation of peripheral blood and intestinal lamina propria lymphocytes in Crohn's disease. In vivo state of activation and in vitro response to stimulation as defined by the expression of early activation antigens. Gut. 1987 Jun;28(6):745–753. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.6.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raedler A., Fraenkel S., Klose G., Seyfarth K., Thiele H. G. Involvement of the immune system in the pathogenesis of Crohn's disease. Expression of the T9 antigen on peripheral immunocytes correlates with the severity of the disease. Gastroenterology. 1985 Apr;88(4):978–983. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramadori G., Van Damme J., Rieder H., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. Interleukin 6, the third mediator of acute-phase reaction, modulates hepatic protein synthesis in human and mouse. Comparison with interleukin 1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Aug;18(8):1259–1264. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. A., Kurman C. C., Biddison W. E., Goldman N. D., Nelson D. L. A monoclonal antibody 7G7/B6, binds to an epitope on the human interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptor that is distinct from that recognized by IL-2 or anti-Tac. Hybridoma. 1985 Summer;4(2):91–102. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1985.4.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. A., Kurman C. C., Fritz M. E., Biddison W. E., Boutin B., Yarchoan R., Nelson D. L. Soluble interleukin 2 receptors are released from activated human lymphoid cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3172–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby W. S., Janossy G., Bofill M., Jewell D. P. Intestinal lymphocyte subpopulations in inflammatory bowel disease: an analysis by immunohistological and cell isolation techniques. Gut. 1984 Jan;25(1):32–40. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. Interleukin 2. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:319–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons J. A., Wood N. C., Di Giovine F. S., Duff G. W. Soluble IL-2 receptor in rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation with disease activity, IL-1 and IL-2 inhibition. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 15;141(8):2612–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Goldman C. K., Robb R. J., Depper J. M., Leonard W. J., Sharrow S. O., Bongiovanni K. F., Korsmeyer S. J., Greene W. C. Expression of interleukin 2 receptors on activated human B cells. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1450–1466. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. M., Smith K. A. The interleukin 2 receptor. Functional consequences of its bimolecular structure. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):1055–1069. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood N. C., Symons J. A., Duff G. W. Serum interleukin-2-receptor in rheumatoid arthritis: a prognostic indicator of disease activity? J Autoimmun. 1988 Aug;1(4):353–361. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



