Abstract
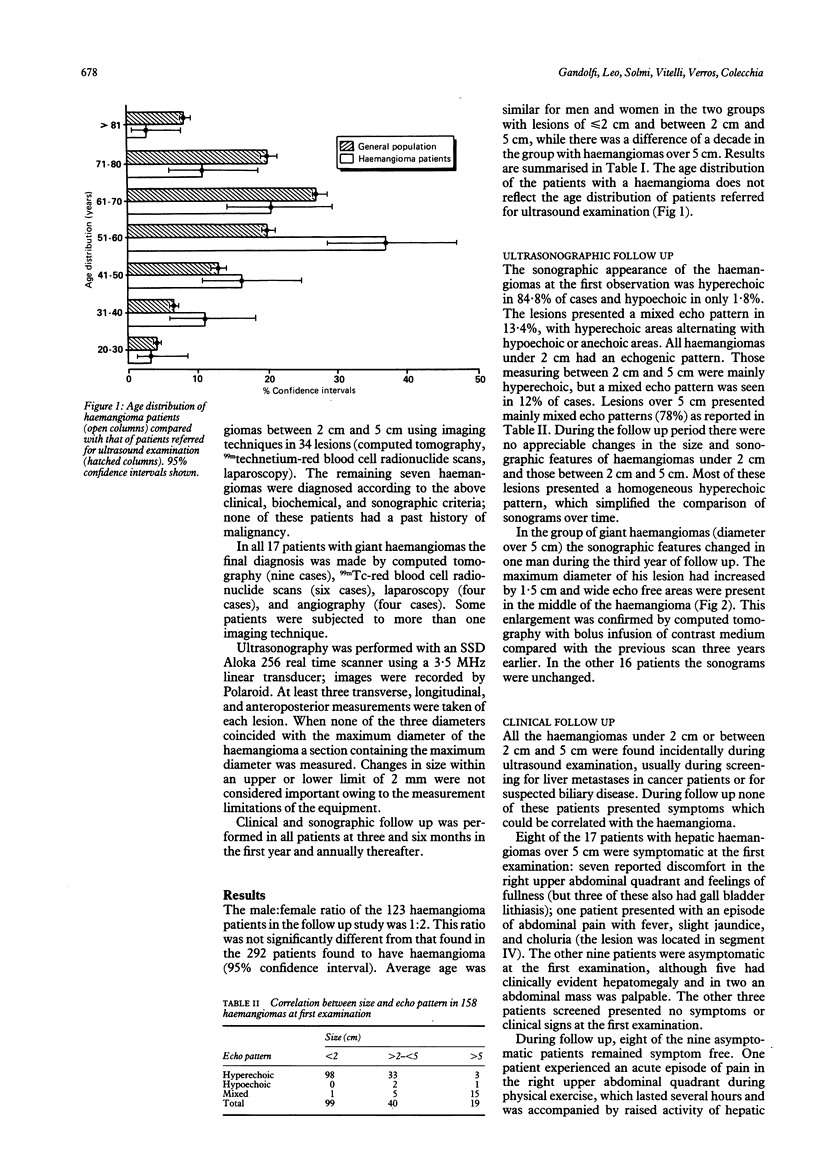
Hepatic haemangiomas are the most common benign tumours of the liver and commonly present as incidental findings on sonographic examination of the abdomen. Since little is known of the natural course of these tumours, we performed a clinical and sonographic follow up of 123 haemangioma patients. Our prospective study investigated clinical and sonographic findings in 158 haemangiomas for periods of 12 to 60 months. Ninety nine haemangiomas measured less than 2 cm and had an echogenic pattern; 40 were between 2 cm and 5 cm with a mainly echogenic structure; 19 measured greater than 5 cm and showed a mixed echo pattern. At the first examination only eight patients, all with giant haemangiomas, presented symptoms which could be attributed to the tumour. During follow up only one haemangioma changed in shape and size. One patient who was symptom free at the first examination experienced right upper abdominal quadrant pain during follow up. No deterioration occurred in any of the patients with symptoms at the first examination, and all had a satisfactory quality of life. No complications arose during the follow up period. This study shows that in adults haemangiomas remain stable in size and echo patterns rarely change. Only haemangiomas greater than 5 cm may cause symptoms. Prolonged clinical and sonographic follow up of small and medium sized haemangiomas is not warranted.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam Y. G., Huvos A. G., Fortner J. G. Giant hemangiomas of the liver. Ann Surg. 1970 Aug;172(2):239–245. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197008000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adson M. A. Diagnosis and surgical treatment of primary and secondary solid hepatic tumors in the adult. Surg Clin North Am. 1981 Feb;61(1):181–196. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)42342-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornman P. C., Terblanche J., Blumgart R. L., Jones E. P., Pickard H., Kalvaria I. Giant hepatic hemangiomas: diagnostic and therapeutic dilemmas. Surgery. 1987 Apr;101(4):445–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bree R. L., Schwab R. E., Neiman H. L. Solitary echogenic spot in the liver: is it diagnostic of a hemangioma? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1983 Jan;140(1):41–45. doi: 10.2214/ajr.140.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOCKERTY M. B., GRAY H. K., HENSON S. W., Jr Benign tumors of the liver. II. Hemangiomas. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1956 Sep;103(3):327–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDMAN M. Hemangioma of the liver; special reference to its association with cysts of the liver and pancreas. Am J Clin Pathol. 1958 Feb;29(2):160–162. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/29.2.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeny P. C., Marks W. M. Patterns of contrast enhancement of benign and malignant hepatic neoplasms during bolus dynamic and delayed CT. Radiology. 1986 Sep;160(3):613–618. doi: 10.1148/radiology.160.3.3016794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeny P. C., Vimont T. R., Barnett D. C. Cavernous hemangioma of the liver: ultrasonography, arteriography, and computed tomography. Radiology. 1979 Jul;132(1):143–148. doi: 10.1148/132.1.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandolfi L., Solmi L., Bolondi L., Rossi A., Casanova P., Leo P. The value of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of hepatic haemangiomas. Eur J Radiol. 1983 Aug;3(3):222–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibney R. G., Hendin A. P., Cooperberg P. L. Sonographically detected hepatic hemangiomas: absence of change over time. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987 Nov;149(5):953–957. doi: 10.2214/ajr.149.5.953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grieco M. B., Miscall B. G. Giant hemangiomas of the liver. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1978 Nov;147(5):783–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishak K. G., Rabin L. Benign tumors of the liver. Med Clin North Am. 1975 Jul;59(4):995–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31998-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issa P. Cavernous haemangioma of the liver: the role of radiotherapy. Br J Radiol. 1968 Jan;41(481):26–32. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-41-481-26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itai Y., Ohtomo K., Furui S., Yamauchi T., Minami M., Yashiro N. Noninvasive diagnosis of small cavernous hemangioma of the liver: advantage of MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1985 Dec;145(6):1195–1199. doi: 10.2214/ajr.145.6.1195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato M., Sugawara I., Okada A., Kuwata K., Satani M. Hemangioma of the liver. Diagnosis with combined use of laparoscopy and hepatic arteriography. Am J Surg. 1975 Jun;129(6):698–703. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(75)90350-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawarada Y., Mizumoto R. Surgical treatment of giant hemangioma of the liver. Am J Surg. 1984 Aug;148(2):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(84)90239-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVITT L. M., COLEMAN M., YARVIS J. Multiple large hemangiomas of the liver. N Engl J Med. 1955 May 19;252(20):854–855. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195505192522004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B., Roche A., Radice L., Aguilar K., Kraiem C. L'embolisation artérielle a-t-elle une place dans le traitement des hémangiomes caverneux du foie de l'adulte? Presse Med. 1986 Jun 7;15(23):1073–1076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McArdle C. R. Ultrasonic appearances of a hepatic hemangioma. J Clin Ultrasound. 1978 Apr;6(2):124–124. doi: 10.1002/jcu.1870060217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley J. E., Myers J. B., Sack F. S., Kalk F., Epstein E. E., Lannon J. Enlargement of cavernous haemangioma associated with exogenous administration of oestrogens. S Afr Med J. 1974 Apr 6;48(16):695–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OCHSNER J. L., HALPERT B. Cavernous hemangioma of the liver. Surgery. 1958 Apr;43(4):577–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEWELL J. H., WEISS K. Spontaneous rupture of hemangioma of the liver. A review of the literature and presentation of illustrative case. Arch Surg. 1961 Nov;83:729–733. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1961.01300170085016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scatarige J. C., Kenny J. M., Fishman E. K., Herlong F. H., Siegelman S. S. CT of giant cavernous hemangioma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987 Jul;149(1):83–85. doi: 10.2214/ajr.149.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Koep L. J., Weil R., 3rd, Fennell R. H., Iwatsuki S., Kano T., Johnson M. L. Excisional treatment of cavernous hemangioma of the liver. Ann Surg. 1980 Jul;192(1):25–27. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198007000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stayman J. W., Jr, Polsky H. S., Blaum L. Case report. Ruptured cavernous hemangioma of the liver. Pa Med. 1976 Mar;79(3):62–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. R., Taylor K. J. An incidental hemangioma of the liver: the dilemma of patient management. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1981 Mar;3(1):93–97. doi: 10.1097/00004836-198103000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trastek V. F., van Heerden J. A., Sheedy P. F., 2nd, Adson M. A. Cavernous hemangiomas of the liver: resect or observe? Am J Surg. 1983 Jan;145(1):49–53. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(83)90165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



