Abstract
Studies in animals have suggested a neural reflex between the gall bladder and the sphincter of Oddi. The aim of this study was to investigate whether sphincter of Oddi motility is altered by distension of the gall bladder in humans. Sphincter of Oddi motility was recorded intraoperatively in 10 patients undergoing elective cholecystectomy for gall stones. The manometry was performed by a triple lumen constantly perfused catheter which was introduced through the cystic duct and positioned across the sphincter of Oddi to record sphincter basal pressure, wave amplitude, and frequency of contractions. In five patients a separate catheter was introduced into the gall bladder after ligation of the cystic duct. This catheter was used to distend the gall bladder. Sphincter of Oddi pressures were measured before, during, and after the distension. In a separate control group of patients (n = 5) basal sphincter of Oddi activity was recorded without distension of the gall bladder. Distension of the gall bladder decreased sphincter of Oddi basal pressure from (mean (SD] 22.8 (8.5) mmHg to 18.6 (6.5) mmHg (p = 0.01, paired t test) and frequency of sphincter of Oddi contractions decreased from 2.6 (1.6) to 1.1 (1.3) contractions/min (p = 0.003, paired t test). The results were significantly different from those of the control group (p less than 0.05, unpaired t test) during the same time period (four minutes). Pulse rate and blood pressure were not affected by the gall bladder distension. The results suggest a local reflex between the gall bladder and the sphincter of Oddi that might be important in the regulation of the pressure within the bile ducts and flow across the sphincter. This reflex is likely to be neurally mediated and injuries to it may be important in the aetiology of postcholecystectomy sphincter of Oddi dysfunction.
Full text
PDF
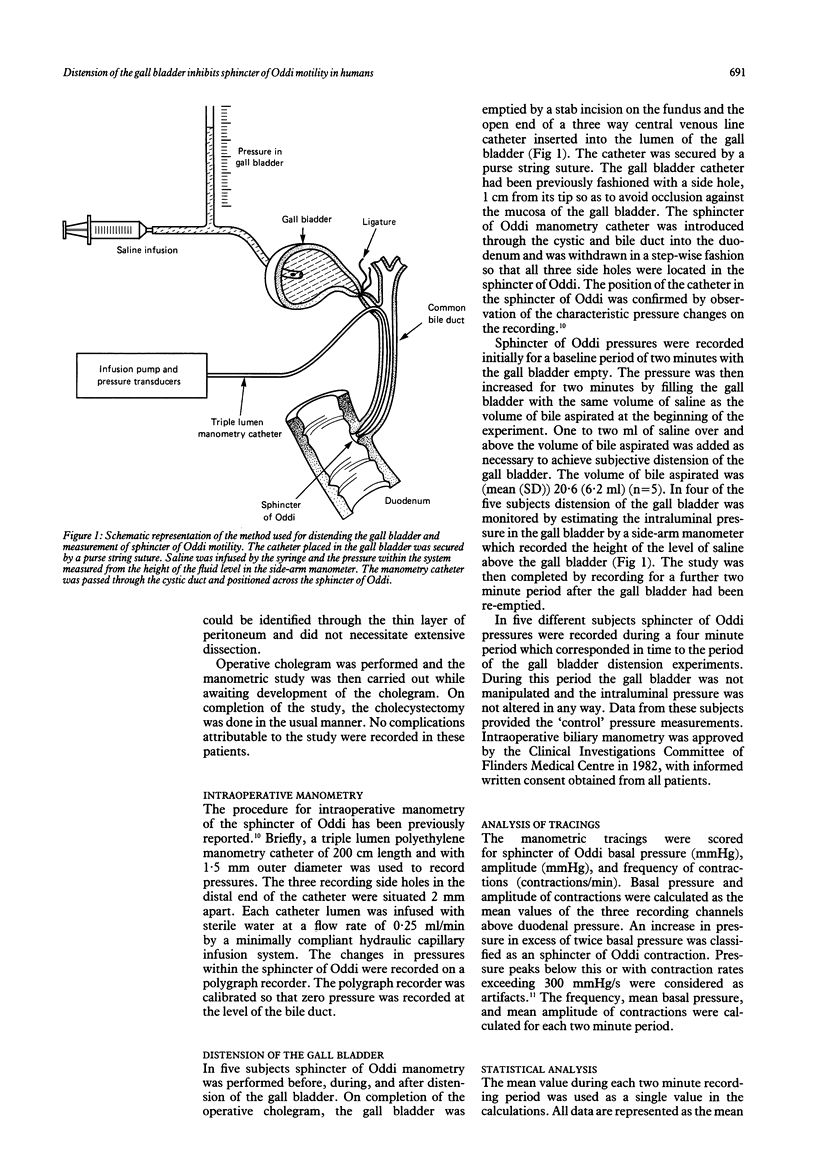
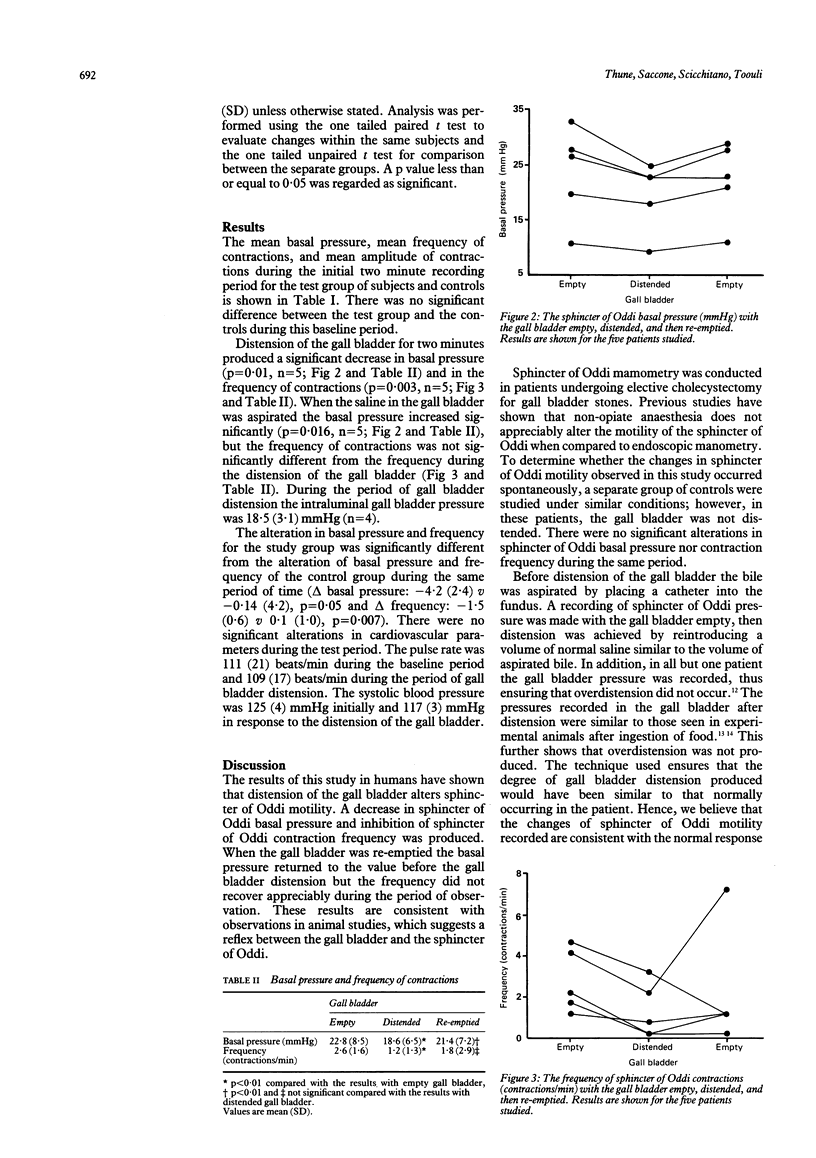

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behar J., Biancani P. Neural control of the sphincter of Oddi. Physiologic role of enkephalins on the regulation of basal sphincter of Oddi motor activity in the cat. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jan;86(1):134–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlstrand C., Dahlström A., Ahlman H. Adrenergic and VIP-ergic relaxatory mechanisms of the feline extrahepatic biliary tree. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1989 Mar;26(2):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(89)90157-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlstrand C., Edin R., Dahlström A., Ahlman H. An in vivo model for the simultaneous study of motility of the gallbladder, sphincter of Oddi and duodenal wall in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1985 Mar;123(3):355–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1985.tb07600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh Z., Takahashi I. Periodic contractions of the canine gallbladder during the interdigestive state. Am J Physiol. 1981 Feb;240(2):G183–G189. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1981.240.2.G183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mawe G. M., Gershon M. D. Structure, afferent innervation, and transmitter content of ganglia of the guinea pig gallbladder: relationship to the enteric nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 1989 May 15;283(3):374–390. doi: 10.1002/cne.902830306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller E. L., Lewinski M. A., Pitt H. A. The cholecysto-sphincter of Oddi reflex. J Surg Res. 1984 Apr;36(4):377–383. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(84)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson C. G. Dual effects on the sphincter of Oddi and gallbladder induced by stimulation of the right great splanchnic nerve. Acta Physiol Scand. 1973 Mar;87(3):334–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1973.tb05397.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi I., Kern M. K., Dodds W. J., Hogan W. J., Sarna S. K., Soergel K. H., Itoh Z. Contraction pattern of opossum gallbladder during fasting and after feeding. Am J Physiol. 1986 Feb;250(2 Pt 1):G227–G235. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.250.2.G227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thune A., Friman S., Conradi N., Svanvik J. Functional and morphological relationships between the feline main pancreatic and bile duct sphincters. Gastroenterology. 1990 Mar;98(3):758–765. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90299-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thune A., Thornell E., Svanvik J. Reflex regulation of flow resistance in the feline sphincter of Oddi by hydrostatic pressure in the biliary tract. Gastroenterology. 1986 Dec;91(6):1364–1369. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90188-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toouli J., Bushell M., Iannos J., Collinson T., Wearne J., Kitchen D. Peroperative sphincter of Oddi manometry: motility disorder in patients with cholelithiasis. Aust N Z J Surg. 1986 Aug;56(8):625–629. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1986.tb04517.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toouli J., Geenen J. E., Hogan W. J., Dodds W. J., Arndorfer R. C. Sphincter of Oddi motor activity: a comparison between patients with common bile duct stones and controls. Gastroenterology. 1982 Jan;82(1):111–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toouli J., Hogan W. J., Geenen J. E., Dodds W. J., Arndorfer R. C. Action of cholecystokinin-octapeptide on sphincter of Oddi basal pressure and phasic wave activity in humans. Surgery. 1982 Sep;92(3):497–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb T. H., Lillemoe K. D., Pitt H. A. Gastrosphincter of Oddi reflex. Am J Surg. 1988 Feb;155(2):193–198. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(88)80692-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worthley C. S., Baker R. A., Iannos J., Saccone G. T., Toouli J. Human fasting and postprandial sphincter of Oddi motility. Br J Surg. 1989 Jul;76(7):709–714. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800760720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt A. P. The relationship of the sphincter of Oddi to the stomach, duodenum and gall-bladder. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):225–243. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


