Abstract
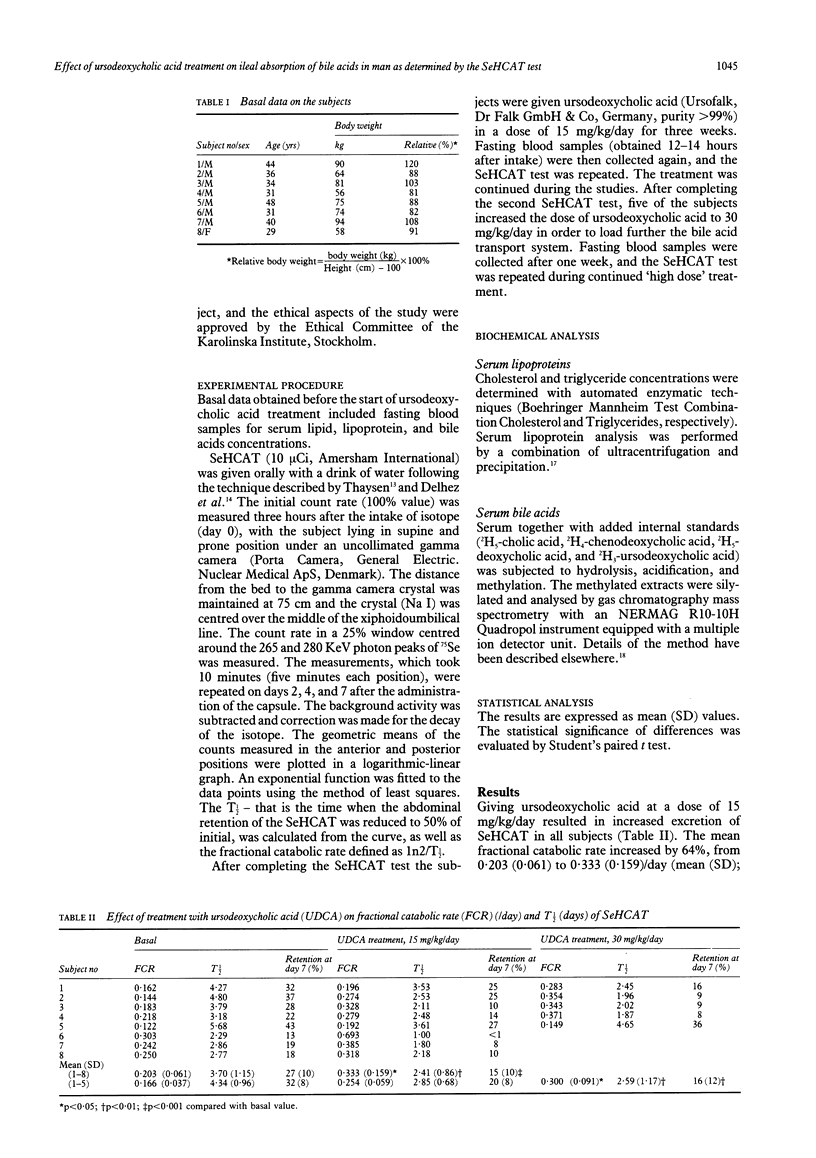
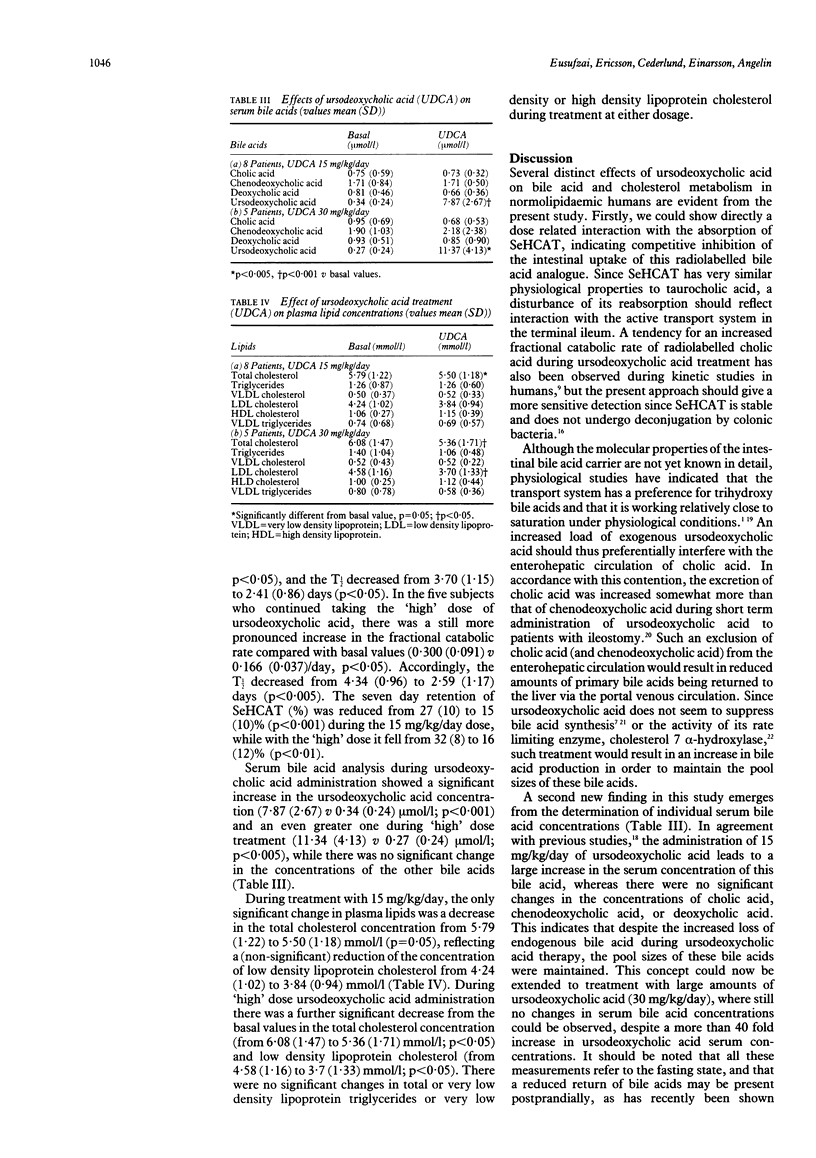
The effects of urodeoxycholic acid on ileal absorption of bile acids and on serum bile acid and lipoprotein concentrations were studied. Eight healthy subjects were investigated. The gamma emitting bile acid analogue, SeHCAT, was given orally and its fractional catabolic rate and seven day retention were assessed by repeated external counting over the upper abdomen during the next seven days. Ursodeoxycholic acid was then given orally at a dose of 15 mg/kg/day for three weeks and the study was repeated during treatment. The fractional catabolic rate increased by 64% (mean (SD), 0.333 (0.159) v 0.203 (0.061)/day; p less than 0.05) and seven day retention decreased by 44% (15(10) v 27(10)%, p less than 0.001), indicating bile acid malabsorption. Total serum cholesterol fell from 5.79 (1.22) to 5.50 (1.18) mmol/l (p = 0.05), while serum ursodeoxycholic acid increased 22 fold (7.87 (2.67) v 0.34 (0.24) mumol/l, p less than 0.001). Five of the subjects continued taking 30 mg/kg/day of ursodeoxycholic acid for one week and showed an increase in fractional catabolic rate of 81% (0.300 (0.091) v 0.166 (0.037)/day; p less than 0.05) and a fall in seven day retention of 50% (16 (12) v 32 (8)%, p less than 0.01). There were significant reductions in total cholesterol (5.36 (1.71) v 6.08 (1.47) mmol/l; p less than 0.05) and low density lipoprotein cholesterol (3.70 (1.33) v 4.58 (1.16) mmol/l; p less than 0.05). The results support the concept tht ursodeoxycholic acid treatment interferes with the absorption of endogenous bile acids, and emphasise the beneficial effects of this treatment of lipoprotein concentrations in man.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angelin B., Björkhem I., Einarsson K., Ewerth S. Cholestyramine treatment reduces postprandial but not fasting serum bile acid levels in humans. Gastroenterology. 1982 Nov;83(5):1097–1101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelin B., Einarsson K., Leijd B. Clofibrate treatment and bile cholesterol saturation: short-term and long-term effects and influence of combination with chenodeoxycholic acid. Eur J Clin Invest. 1981 Jun;11(3):185–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1981.tb01839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelin B., Nilsell K., Einarsson K. Ursodeoxycholic acid treatment in humans: effects on plasma and biliary lipid metabolism with special reference to very low density lipoprotein triglyceride and bile acid kinetics. Eur J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;16(2):169–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1986.tb01325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelin B., Reihnér E., Rudling M., Ewerth S., Björkhem I., Einarsson K. In vitro studies of lipid metabolism in human liver. Am Heart J. 1987 Feb;113(2 Pt 2):482–487. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(87)90618-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachrach W. H., Hofmann A. F. Ursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of cholesterol cholelithiasis. part I. Dig Dis Sci. 1982 Aug;27(8):737–761. doi: 10.1007/BF01393771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson K. Lipoprotein fractionation. J Clin Pathol Suppl (Assoc Clin Pathol) 1973;5:32–37. doi: 10.1136/jcp.s1-5.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carulli N., Ponz De Leon M., Zironi F., Pinetti A., Smerieri A., Iori R., Loria P. Hepatic cholesterol and bile acid metabolism in subjects with gallstones: comparative effects of short erm feeding of chenodeoxycholic and ursodeoxycholic acid. J Lipid Res. 1980 Jan;21(1):35–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delhez H., van den Berg J. W., van Blankenstein M., Meerwaldt J. H. New method for the determination of bile acid turnover using 75Se-homocholic acid taurine. Eur J Nucl Med. 1982;7(6):269–271. doi: 10.1007/BF00251479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarsson K., Björkhem I., Eklöf R., Ewerth S., Nilsell K., Blomstrand R. Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid treatment on intestinal absorption of triglycerides in man. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1984 Mar;19(2):283–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewerth S., Angelin B., Einarsson K., Nilsell K., Björkhem I. Serum concentrations of ursodeoxycholic acid in portal venous and systemic venous blood of fasting humans as determined by isotope dilution-mass spectrometry. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jan;88(1 Pt 1):126–133. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galatola G., Jazrawi R. P., Bridges C., Joseph A. E., Northfield T. C. Hepatic handling of a synthetic gamma-labeled bile acid (75SeHCAT). Gastroenterology. 1988 Mar;94(3):771–778. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardison W. G., Grundy S. M. Effect of ursodeoxycholate and its taurine conjugate on bile acid synthesis and cholesterol absorption. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jul;87(1):130–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jazrawi R. P., Ferraris R., Bridges C., Northfield T. C. Kinetics for the synthetic bile acid 75selenohomocholic acid-taurine in humans: comparison with [14C]taurocholate. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jul;95(1):164–169. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krag E., Phillips S. F. Active and passive bile acid absorption in man. Perfusion studies of the ileum and jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jun;53(6):1686–1694. doi: 10.1172/JCI107720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRusso N. F., Hoffman N. E., Hofmann A. F., Northfield T. C., Thistle J. L. Effect of primary bile acid ingestion on bile acid metabolism and biliary lipid secretion in gallstone patients. Gastroenterology. 1975 Dec;69(6):1301–1314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzini A., Northfield T. C. Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on biliary lipid coupling and on cholesterol absorption during fasting and eating in subjects with cholesterol gallstones. Gastroenterology. 1988 Aug;95(2):408–416. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90498-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick M. V., Eastwood M. A., Anderson J. R., Ross H. M. Enterohepatic circulation in man of a gamma-emitting bile-acid conjugate, 23-selena-25-homotaurocholic acid (SeHCAT). J Nucl Med. 1982 Feb;23(2):126–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsell K., Angelin B., Leijd B., Einarsson K. Comparative effects of ursodeoxycholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid on bile acid kinetics and biliary lipid secretion in humans. Evidence for different modes of action on bile acid synthesis. Gastroenterology. 1983 Dec;85(6):1248–1256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponz de Leon M., Carulli N., Loria P., Iori R., Zironi F. Cholesterol absorption during bile acid feeding. Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) administration. Gastroenterology. 1980 Feb;78(2):214–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poupon R., Chrétien Y., Poupon R. E., Ballet F., Calmus Y., Darnis F. Is ursodeoxycholic acid an effective treatment for primary biliary cirrhosis? Lancet. 1987 Apr 11;1(8537):834–836. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91610-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reihnér E., Björkhem I., Angelin B., Ewerth S., Einarsson K. Bile acid synthesis in humans: regulation of hepatic microsomal cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase activity. Gastroenterology. 1989 Dec;97(6):1498–1505. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90395-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehl A., Raedsch R., Rudolph G. Acute effects of ursodeoxycholic and chenodeoxycholic acid on the small intestinal absorption of bile acids. Gastroenterology. 1990 Feb;98(2):424–428. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90834-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thaysen E. H., Orholm M., Arnfred T., Carl J., Rødbro P. Assessment of ileal function by abdominal counting of the retention of a gamma emitting bile acid analogue. Gut. 1982 Oct;23(10):862–865. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.10.862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bergmann K., Epple-Gutsfeld M., Leiss O. Differences in the effects of chenodeoxycholic and ursodeoxycholic acid on biliary lipid secretion and bile acid synthesis in patients with gallstones. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jul;87(1):136–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


