Abstract
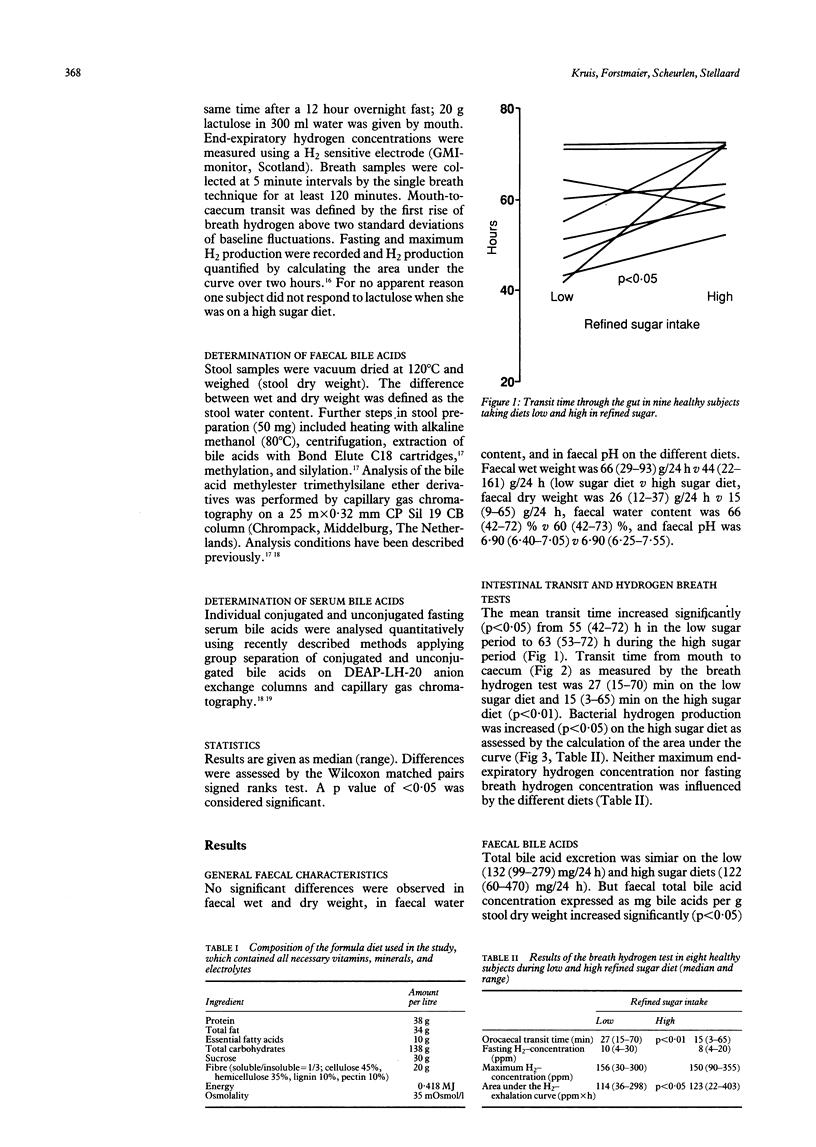
Increasing consumption of refined sugar has been implicated in many gastrointestinal disorders on epidemiological grounds. Nine volunteers agreed to participate in a study comparing the effects of a diet containing 165 g refined sugar/day with a diet of only 60 g/day on gut transit, bile acid metabolism, and fermentative activity of the intestinal flora. The wet and dry weight, pH, and water content of the stools were similar on the two diets. On the high sugar diet mouth-to-anus transit time was significantly prolonged, despite a shortened mouth-to-caecum transit time. The faecal concentration of total bile acids and the faecal concentration of secondary bile acids increased significantly. Diet affected neither the serum bile acid pattern nor the concentration. Breath hydrogen tests showed significantly enhanced H2 production on the high sugar diet. We conclude that the quantity of refined sugar in the diet can significantly influence gut function and the composition of bowel contents.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong B., Doll R. Environmental factors and cancer incidence and mortality in different countries, with special reference to dietary practices. Int J Cancer. 1975 Apr 15;15(4):617–631. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird I. M., Walters R. L., Davies P. S., Hill M. J., Drasar B. S., Southgate D. A. The effects of two dietary fiber supplements on gastrointestinal transit, stool weight and frequency, and bacterial flora, and fecal bile acids in normal subjects. Metabolism. 1977 Feb;26(2):117–128. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(77)90047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristol J. B., Emmett P. M., Heaton K. W., Williamson R. C. Sugar, fat, and the risk of colorectal cancer. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Nov 23;291(6507):1467–1470. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6507.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkitt D. P. Epidemiology of cancer of the colon and rectum. Cancer. 1971 Jul;28(1):3–13. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197107)28:1<3::aid-cncr2820280104>3.0.co;2-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. H., Jenkins D. J., Wiggins H. S. Measurement of the mean transit time of dietary residue through the human gut. Gut. 1976 Mar;17(3):210–218. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.3.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. H., Wiggins H. S. Transit through the gut measured by analysis of a single stool. Gut. 1976 Mar;17(3):219–223. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.3.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastwood M. A., Kirkpatrick J. R., Mitchell W. D., Bone A., Hamilton T. Effects of dietary supplements of wheat bran and cellulose on faeces and bowel function. Br Med J. 1973 Nov 17;4(5889):392–394. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5889.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman G. D., Kannel W. B., Dawber T. R. The epidemiology of gallbladder disease: observations in the Framingham Study. J Chronic Dis. 1966 Mar;19(3):273–292. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(66)90132-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbutt J. T., Wilkins R. M., Lack L., Tyor M. P. Bacterial modification of taurocholate during enterohepatic recirculation in normal man and patients with small intestinal disease. Gastroenterology. 1970 Oct;59(4):553–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel L. Overweight and cancer. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Dec;103(6 ):1034–1036. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-6-1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepner G. W. Effect of decreased gallbladder stimulation on enterohepatic cycling and kinetics of bile acids. Gastroenterology. 1975 Jun;68(6):1574–1581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martini G. A., Brandes J. W. Increased consumption of refined carbohydrates in patients with Crohn's disease. Klin Wochenschr. 1976 Apr 15;54(8):367–371. doi: 10.1007/BF01469792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf A. M., Phillips S. F., Zinsmeister A. R., MacCarty R. L., Beart R. W., Wolff B. G. Simplified assessment of segmental colonic transit. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jan;92(1):40–47. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90837-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. B., Anderson J. T., Taylor H. L., Keys A., Frantz I. D., Jr Effect of dietary fat on the fecal excretion of cholesterol and its degradation products in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jul;47(7):1517–1534. doi: 10.1172/JCI105845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter N. S., Burkitt D. P. Diverticular disease of the colon: a deficiency disease of Western civilization. Br Med J. 1971 May 22;2(5759):450–454. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5759.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perman J. A., Modler S., Barr R. G., Rosenthal P. Fasting breath hydrogen concentration: normal values and clinical application. Gastroenterology. 1984 Dec;87(6):1358–1363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachar D. B., Auslander M. O., Walfish J. S. Aetiological theories of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol. 1980 May;9(2):231–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindlbeck N. E., Heinrich C., Stellaard F., Paumgartner G., Müller-Lissner S. A. Healthy controls have as much bile reflux as gastric ulcer patients. Gut. 1987 Dec;28(12):1577–1583. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.12.1577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scragg R. K., McMichael A. J., Baghurst P. A. Diet, alcohol, and relative weight in gall stone disease: a case-control study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Apr 14;288(6424):1113–1119. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6424.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate D. A., Bingham S., Robertson J. Dietary fibre in the British diet. Nature. 1978 Jul 6;274(5666):51–52. doi: 10.1038/274051a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellaard F., Sackmann M., Sauerbruch T., Paumgartner G. Simultaneous determination of cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid pool sizes and fractional turnover rates in human serum using 13C-labeled bile acids. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 1;25(12):1313–1319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellaard F., Sauerbruch T., Luderschmidt C. H., Leisner B., Paumgartner G. Intestinal involvement in progressive systemic sclerosis detected by increased unconjugated serum bile acids. Gut. 1987 Apr;28(4):446–450. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.4.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. G. The irritable bowel. Gut. 1984 Mar;25(3):305–320. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.3.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner D., Emmett P. M., Heaton K. W. Effects of dietary sucrose on factors influencing cholesterol gall stone formation. Gut. 1984 Mar;25(3):269–274. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.3.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winitz M., Adams R. F., Seedman D. A., Davis P. N., Jayko L. G., Hamilton J. A. Studies in metabolic nutrition employing chemically defined diets. II. Effects on gut microflora populations. Am J Clin Nutr. 1970 May;23(5):546–559. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/23.5.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



