Abstract
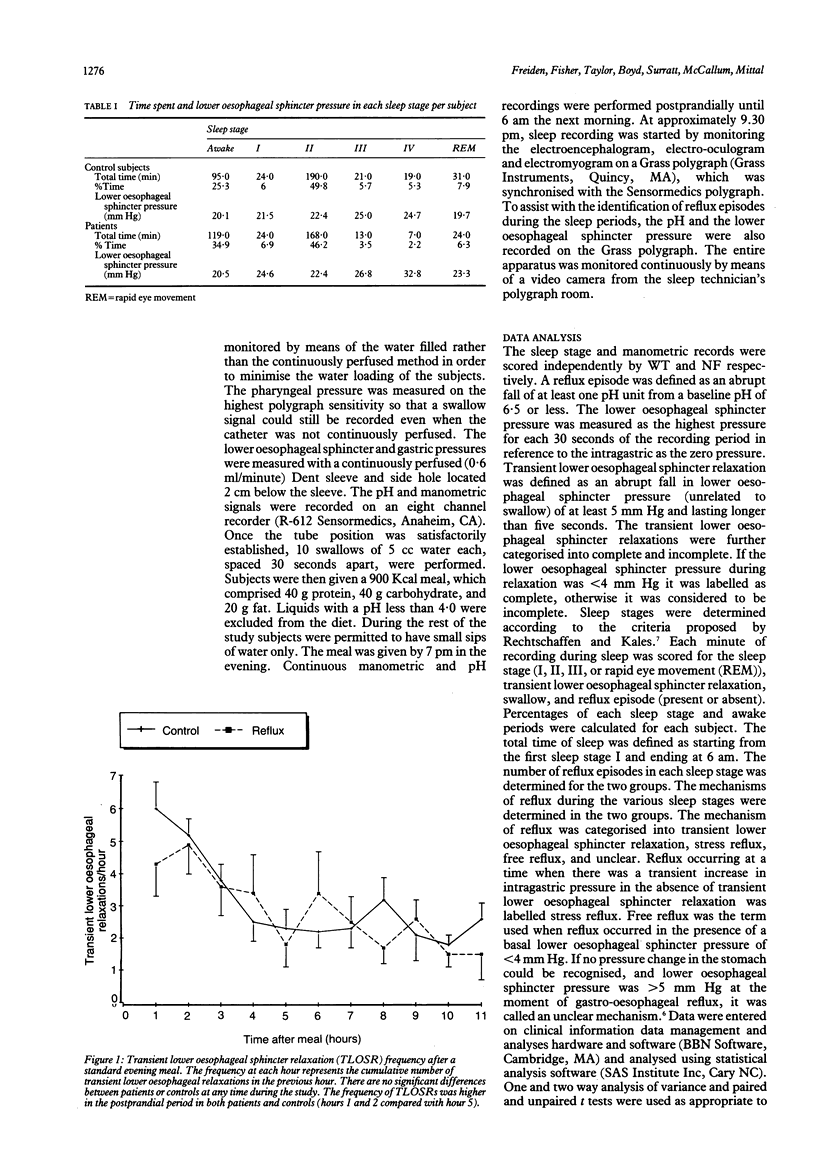
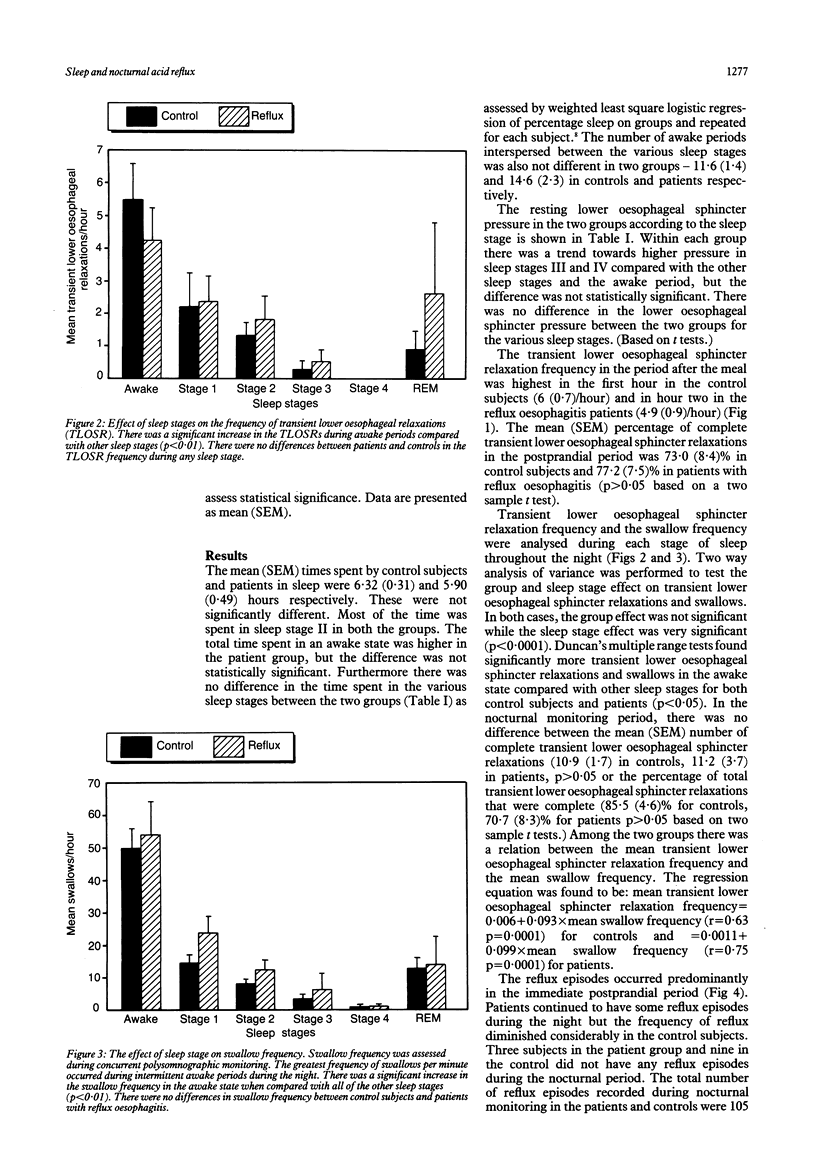
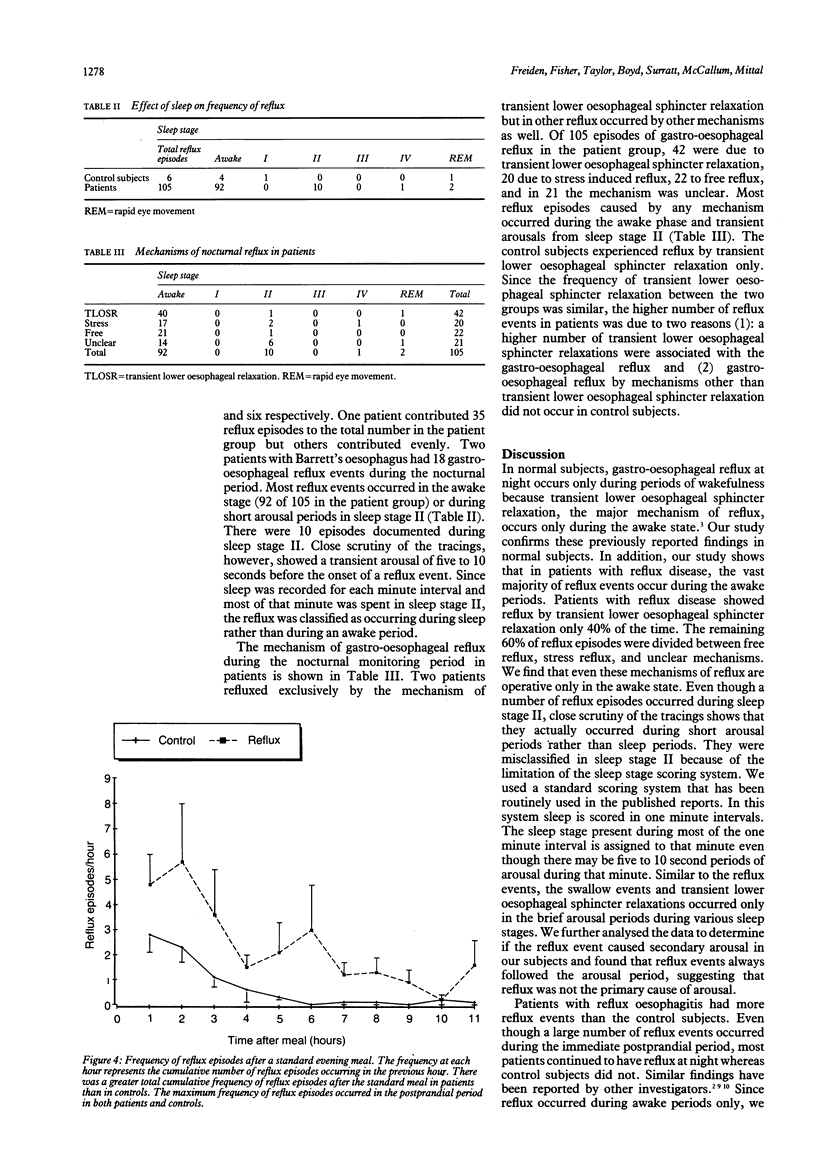
Nocturnal gastro-oesophageal reflux may be important in the pathogenesis of reflux oesophagitis. This study aimed to determine whether: (1) gastro-oesophageal reflux occurs during sleep in patients with reflux oesophagitis and, if so, to explore the mechanism, and (2) the sleep pattern of patients with oesophagitis is different from that of control subjects. After a standard evening meal, simultaneous manometric, oesophageal pH, and polysomnographic recordings were obtained in 11 patients with endoscopic oesophagitis and 11 control subjects. Patients with gastrooesophageal reflux disease had significantly more total reflux episodes throughout the nocturnal monitoring period than control subjects (105 v 6). Ninety two of 105 episodes of gastro-oesophageal reflux in patients occurred during the awake state and 10 during sleep stage II. A number of reflux episodes occurred during brief periods of arousal from the various sleep stages. Of the 105 reflux events recorded in patients, 42 were induced by transient lower oesophageal sphincter relaxation, 20 by stress reflux, 22 by free reflux mechanisms, and in 21 the mechanism was unclear. The sleep pattern and the time spent in each sleep stage was not different between the two groups. It is concluded that the awake state is crucial for the occurrence of nocturnal reflux episodes in normal subjects as well as in patients with reflux oesophagitis and that the difference between the frequency of gastro-oesophageal reflux between normal subjects and patients cannot be explained by different sleep patterns.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnew H. W., Jr, Webb W. B., Williams R. L. The first night effect: an EEG study of sleep. Psychophysiology. 1966 Jan;2(3):263–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1966.tb02650.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldi F., Ferrarini F., Balestra R., Borioni D., Longanesi A., Miglioli M., Barbara L. Oesophageal motor events at the occurrence of acid reflux and during endogenous acid exposure in healthy subjects and in patients with oesophagitis. Gut. 1985 Apr;26(4):336–341. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.4.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coble P., McPartland R. J., Silva W. J., Kupfer D. J. Is there a first night effect? (a revisit). Biol Psychiatry. 1974 Oct;9(2):215–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demeester T. R., Johnson L. F., Joseph G. J., Toscano M. S., Hall A. W., Skinner D. B. Patterns of gastroesophageal reflux in health and disease. Ann Surg. 1976 Oct;184(4):459–470. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197610000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J., Dodds W. J., Friedman R. H., Sekiguchi T., Hogan W. J., Arndorfer R. C., Petrie D. J. Mechanism of gastroesophageal reflux in recumbent asymptomatic human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):256–267. doi: 10.1172/JCI109667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodds W. J., Dent J., Hogan W. J., Helm J. F., Hauser R., Patel G. K., Egide M. S. Mechanisms of gastroesophageal reflux in patients with reflux esophagitis. N Engl J Med. 1982 Dec 16;307(25):1547–1552. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198212163072503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodds W. J., Hogan W. J., Helm J. F., Dent J. Pathogenesis of reflux esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1981 Aug;81(2):376–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink S. M., McCallum R. W. The role of prolonged esophageal pH monitoring in the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux. JAMA. 1984 Sep 7;252(9):1160–1164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F., Demeester T. R. Twenty-four-hour pH monitoring of the distal esophagus. A quantitative measure of gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Gastroenterol. 1974 Oct;62(4):325–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C. J., Patrikios J., Dent J. Abolition of gas reflux and transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation by vagal blockade in the dog. Gastroenterology. 1986 Oct;91(4):890–896. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90691-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCallum R. W., Berkowitz D. M., Lerner E. Gastric emptying in patients with gastroesophageal reflux. Gastroenterology. 1981 Feb;80(2):285–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal R. K., Lange R. C., McCallum R. W. Identification and mechanism of delayed esophageal acid clearance in subjects with hiatus hernia. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jan;92(1):130–135. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90849-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal R. K., McCallum R. W. Characteristics and frequency of transient relaxations of the lower esophageal sphincter in patients with reflux esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1988 Sep;95(3):593–599. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(88)80003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal R. K., McCallum R. W. Characteristics of transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation in humans. Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 1):G636–G641. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.252.5.G636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr W. C., Johnson L. F., Robinson M. G. Effect of sleep on swallowing, esophageal peristalsis, and acid clearance. Gastroenterology. 1984 May;86(5 Pt 1):814–819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson W. G., Rattan S., Goyal R. K. Experimental induction of isolated lower esophageal sphincter relaxation in anesthetized opossums. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1187–1193. doi: 10.1172/JCI112420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds R. P., el-Sharkawy T. Y., Diamant N. E. Oesophageal peristalsis in the cat: the role of central innervation assessed by transient vagal blockade. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;63(2):122–130. doi: 10.1139/y85-022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



