Abstract
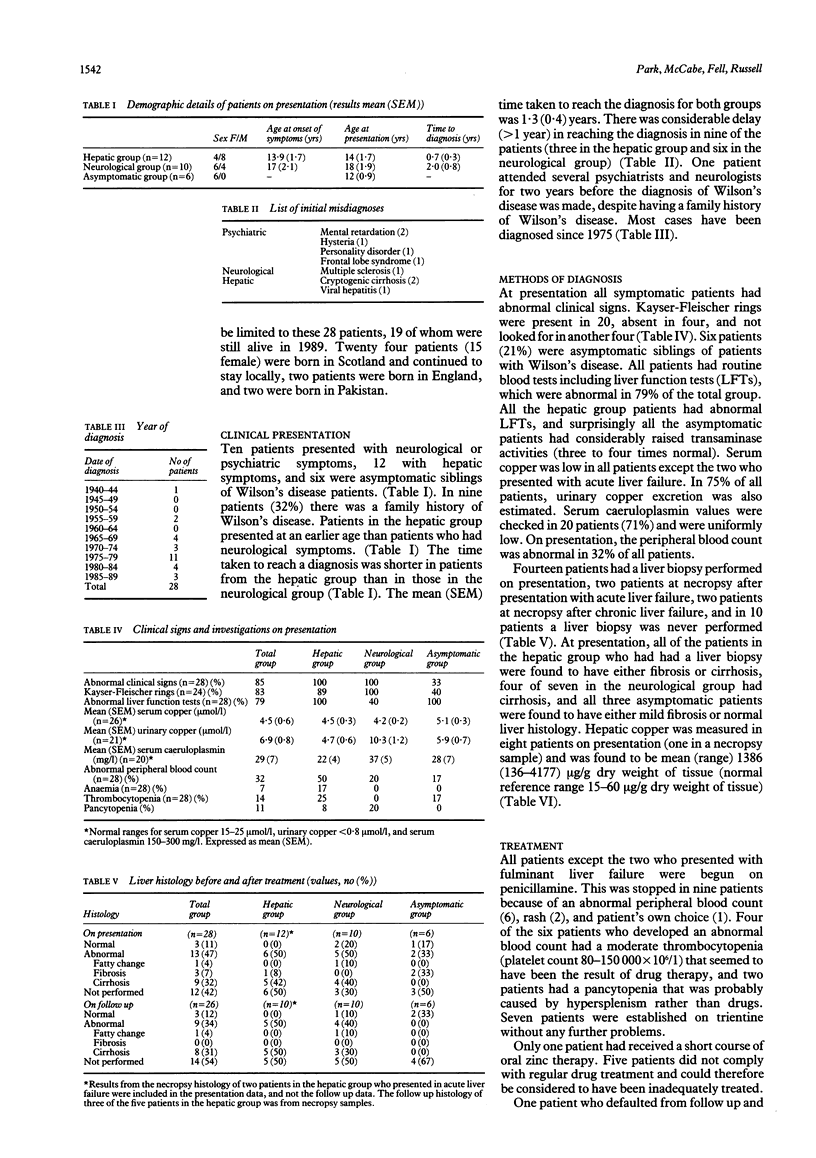
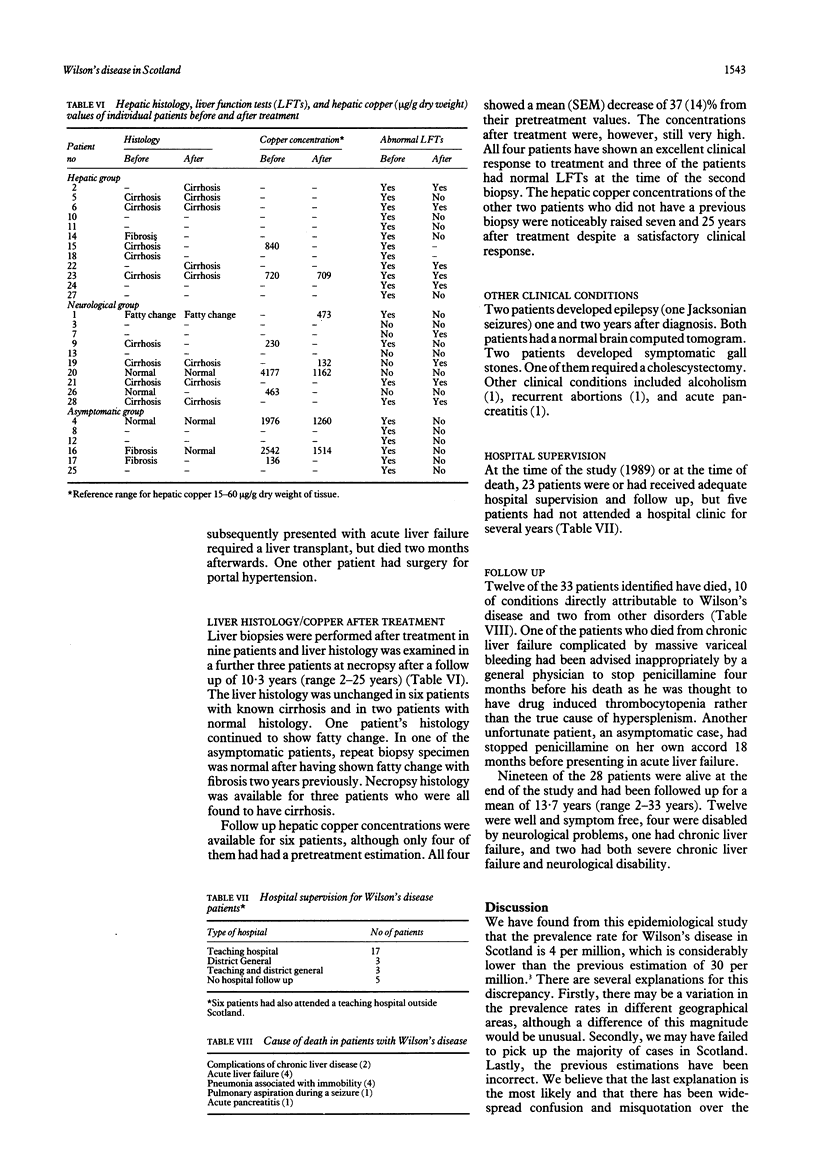
The prevalence and clinical features of Wilson's disease in Scotland were investigated. Thirty three cases were identified but adequate information was available on only 28. In 1989, the prevalence rate was 4 per million. Ten patients with a mean (SEM) age of 18 (1.9) years presented with neurological symptoms, 12 patients aged 14 (1.7) years presented with hepatic symptoms, and six patients aged 12 (0.9) years were asymptomatic siblings of patients with Wilson's disease. Nine (56%) of the 16 patients who underwent liver biopsy on presentation were found to have cirrhosis. Penicillamine treatment was stopped in nine patients because of: abnormal peripheral blood count (6), rash (2), and patient's own choice (1). Nineteen patients were alive in 1989 -12 were well, one had chronic liver failure, four chronic neurological disabilities, and two had both chronic liver failure and neurological disabilities. Twelve patients died from: complications of chronic liver failure (2), acute liver failure (4), pneumonia associated with immobility (4), and other causes (2). Several patients who died had received incomplete medical supervision.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEARN A. G. A genetical analysis of thirty families with Wilson's disease (hepatolenticular degeneration). Ann Hum Genet. 1960 Apr;24:33–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1959.tb01713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEARN A. G. Genetic and biochemical aspects of Wilson's disease. Am J Med. 1953 Oct;15(4):442–449. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(53)90134-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann H., Lössner J., Gruss B., Ruchholtz U. Die Epidemiologie der Wilson schen Erkrankung in der DDR und die derzeitige Problematik einer populationsgenetischen Bearbeitung. Psychiatr Neurol Med Psychol (Leipz) 1979 Jul;31(7):393–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breen E., Tolan M., Meaney J., Lucey C., McCarthy C., O'Gorman T. Wilson's disease: varied manifestations and consequences of non-compliance with treatment. Ir Med J. 1987 Dec;80(12):424–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. W., Fraser F. C., Sass-Kortsak A. A genetic study of Wilson's disease: evidence for heterogeneity. Am J Hum Genet. 1972 Nov;24(6 Pt 1):646–666. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dastur D. K., Manghani D. K., Wadia N. H. Wilson's disease in India. I. Geographic, genetic, and clinical aspects in 16 families. Neurology. 1968 Jan;18(1 Pt 1):21–31. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.1_part_1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downie A. W. Wilson's disease. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Jun 23;288(6434):1915–1915. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6434.1915-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmes M. E., Jasani B. Metallothionein and copper in liver disease. Lancet. 1987 Oct 10;2(8563):866–866. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91065-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giagheddu A., Demelia L., Puggioni G., Nurchi A. M., Contu L., Pirari G., Deplano A., Rachele M. G. Epidemiologic study of hepatolenticular degeneration (Wilson's disease) in Sardinia (1902-1983). Acta Neurol Scand. 1985 Jul;72(1):43–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1985.tb01546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudmundsson K. R. Prevalence and occurrence of some rare neurological diseases in Iceland. Acta Neurol Scand. 1969;45(1):114–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1969.tb01225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURLAND L. T. Descriptive epidemiology of selected neurologic and myopathic disorders with particular reference to a survey in Rochester, Minnesota. J Chronic Dis. 1958 Oct;8(4):378–418. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(58)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau J. Y., Lai C. L., Wu P. C., Pan H. Y., Lin H. J., Todd D. Wilson's disease: 35 years' experience. Q J Med. 1990 Jun;75(278):597–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D. Wilson's disease. Q J Med. 1987 Dec;65(248):959–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J., McQuaid A., Pheiffer H. Can Wilson's disease patients be decoppered? Lancet. 1989 Jun 24;1(8652):1455–1455. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCullough A. J., Fleming C. R., Thistle J. L., Baldus W. P., Ludwig J., McCall J. T., Dickson E. R. Diagnosis of Wilson's disease presenting as fulminant hepatic failure. Gastroenterology. 1983 Jan;84(1):161–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazer H., Ede R. J., Mowat A. P., Williams R. Wilson's disease: clinical presentation and use of prognostic index. Gut. 1986 Nov;27(11):1377–1381. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.11.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell J. G., Watson I. D., Fell G. S., Allison M. E., Russell R. I., Mills P. R. Wilson's disease presenting as acute fulminant hepatic failure. Scott Med J. 1990 Aug;35(4):118–119. doi: 10.1177/003693309003500410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkes D. Wilson's disease. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Apr 21;288(6425):1180–1181. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6425.1180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche-Sicot J., Benhamou J. P. Acute intravascular hemolysis and acute liver failure associated as a first manifestation of Wilson's disease. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Mar;86(3):301–303. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-3-301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito T. An assessment of efficiency in potential screening for Wilson's disease. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1981 Dec;35(4):274–280. doi: 10.1136/jech.35.4.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinberg I. H., Jaffe M. E., Sternlieb I. The use of trientine in preventing the effects of interrupting penicillamine therapy in Wilson's disease. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 23;317(4):209–213. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707233170405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinberg I. H., Sternlieb I., Schilsky M., Stockert R. J. Penicillamine may detoxify copper in Wilson's disease. Lancet. 1987 Jul 11;2(8550):95–95. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92753-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Gollan J. L., Samourian S., Sherlock S. Wilson's disease, presenting as chronic active hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1978 Apr;74(4):645–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starosta-Rubinstein S., Young A. B., Kluin K., Hill G., Aisen A. M., Gabrielsen T., Brewer G. J. Clinical assessment of 31 patients with Wilson's disease. Correlations with structural changes on magnetic resonance imaging. Arch Neurol. 1987 Apr;44(4):365–370. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1987.00520160007005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternlieb I. Perspectives on Wilson's disease. Hepatology. 1990 Nov;12(5):1234–1239. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternlieb I., Scheinberg I. H. Prevention of Wilson's disease in asymptomatic patients. N Engl J Med. 1968 Feb 15;278(7):352–359. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196802152780702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walshe J. M. Diagnosis and treatment of presymptomatic Wilson's disease. Lancet. 1988 Aug 20;2(8608):435–437. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90423-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walshe J. M., Dixon A. K. Dangers of non-compliance in Wilson's disease. Lancet. 1986 Apr 12;1(8485):845–847. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90949-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson's disease. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Jun 2;288(6431):1689–1689. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6431.1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


