Abstract
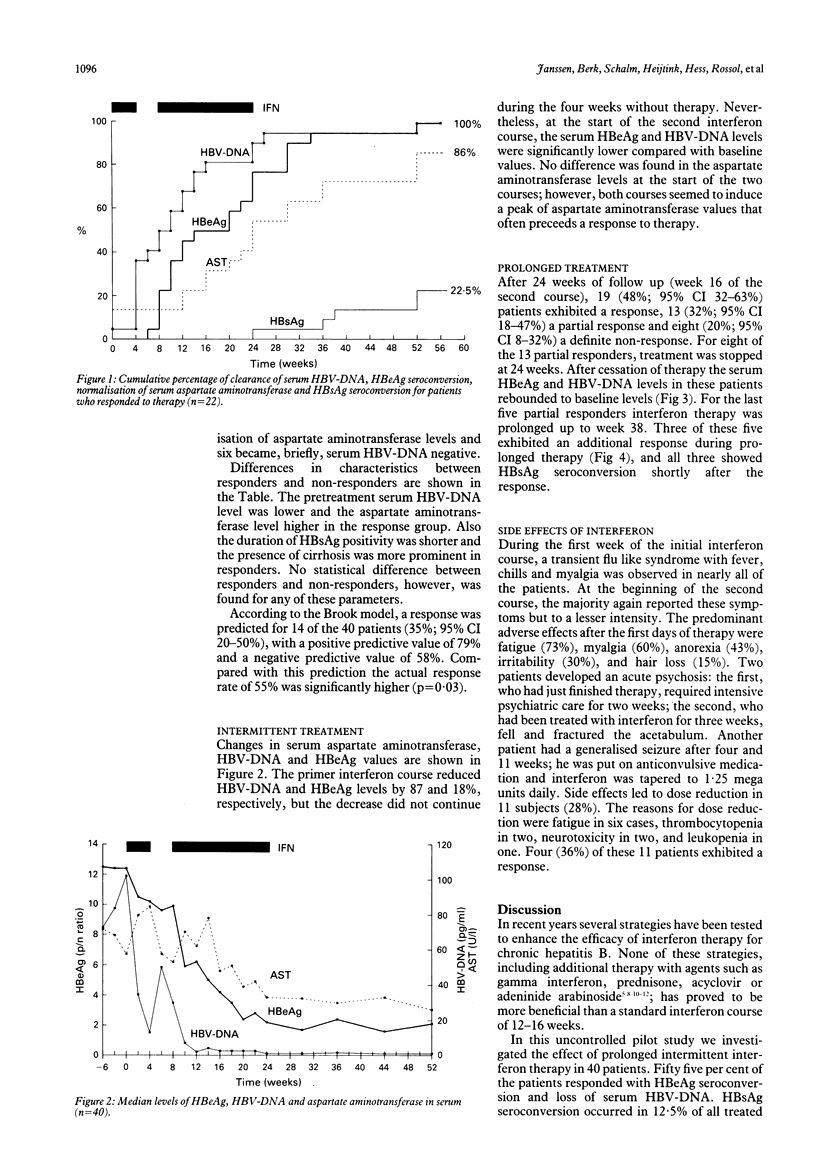
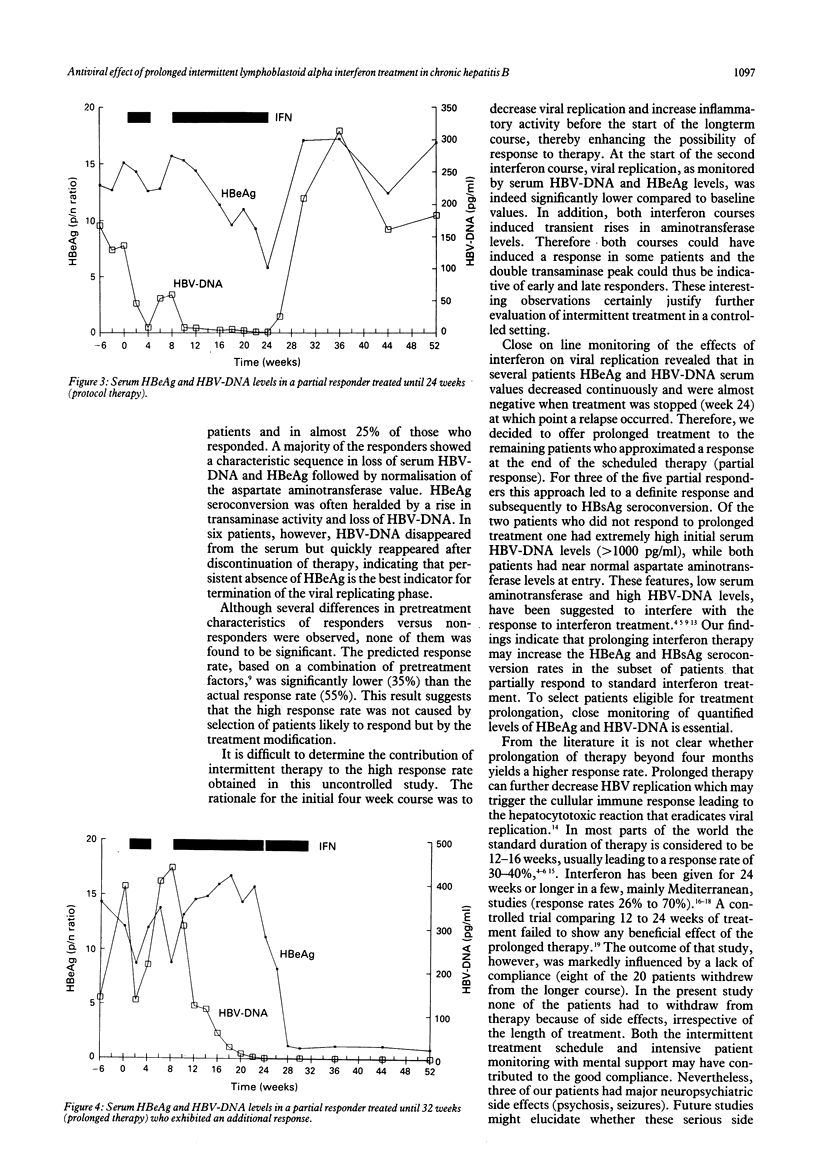
In a European multicentre study 40 patients with HBeAg positive chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection were treated with 5 mega units of lymphoblastoid alpha-interferon daily according to the following regimen: a four week primer course, four weeks of rest and a second course lasting 16 to 30 weeks. After 52 weeks of follow up, a response (HBeAg seroconversion and HBV-DNA negativity) was observed in 22 patients (55%). HBsAg seroconversion occurred in five patients (12.5%). One patient exhibited a relapse for serum HBeAg and HBV-DNA after cessation of treatment. According to a response prediction model, the observed response rate was not related to the selection of patients likely to respond. The initial interferon course induced a reduction of the serum HBV-DNA and HBeAg levels of 87% and 18%, respectively, leading to a significantly lower level of viral replication activity at the start of the second longterm course compared with baseline. After 24 weeks of follow up (week 16 of the second course), 19 (48%) patients exhibited a response, 13 (32%) a partial response (HBeAg < 50% of initial level or HBV-DNA negative) and 8 (20%) no response. For eight of the 13 partial responders treatment was stopped at week 24 and viral replication rebounded to pretreatment values. In the last five partial responders prolongation of therapy up to week 38 led to a definite response and HBsAg seroconversion in three of the five patients. The results of this study suggest that a short primer course and prolongation of therapy may help to enhance the response rate of alpha-interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis type B.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander G. J., Brahm J., Fagan E. A., Smith H. M., Daniels H. M., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Loss of HBsAg with interferon therapy in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet. 1987 Jul 11;2(8550):66–69. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92735-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk L., Schalm S. W., de Man R. A., Heytink R. A., Berthelot P., Brechot C., Boboc B., Degos F., Marcellin P., Benhamou J. P. Failure of acyclovir to enhance the antiviral effect of alpha lymphoblastoid interferon on HBe-seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B. A multi-centre randomized controlled trial. J Hepatol. 1992 Mar;14(2-3):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(92)90175-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook M. G., Chan G., Yap I., Karayiannis P., Lever A. M., Jacyna M., Main J., Thomas H. C. Randomised controlled trial of lymphoblastoid interferon alfa in Europid men with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. BMJ. 1989 Sep 9;299(6700):652–656. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6700.652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook M. G., Karayiannis P., Thomas H. C. Which patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection will respond to alpha-interferon therapy? A statistical analysis of predictive factors. Hepatology. 1989 Nov;10(5):761–763. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carreño V., Porres J. C., Mora I., Bartolomé J., Bas C., Gutiez J., Cortés J., Hernández Guio C. Prolonged (6 months) treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection with recombinant leukocyte A interferon. Liver. 1987 Dec;7(6):325–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1987.tb00363.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Bisceglie A. M., Rustgi V. K., Kassianides C., Lisker-Melman M., Park Y., Waggoner J. G., Hoofnagle J. H. Therapy of chronic hepatitis B with recombinant human alpha and gamma interferon. Hepatology. 1990 Feb;11(2):266–270. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840110217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fattovich G., Brollo L., Boscaro S., Pontisso P., Giustina G., Criscuolo D., Maladorno D., Alberti A., Realdi G., Ruol A. Long-term effect of low dose recombinant interferon therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 1989 Nov;9(3):331–337. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(89)90142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fattovich G., Rugge M., Brollo L., Pontisso P., Noventa F., Guido M., Alberti A., Realdi G. Clinical, virologic and histologic outcome following seroconversion from HBeAg to anti-HBe in chronic hepatitis type B. Hepatology. 1986 Mar-Apr;6(2):167–172. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia G., Smith C. I., Weissberg J. I., Eisenberg M., Bissett J., Nair P. V., Mastre B., Rosno S., Roskamp D., Waterman K. Adenine arabinoside monophosphate (vidarabine phosphate) in combination with human leukocyte interferon in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Sep;107(3):278–285. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-2-278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H. Alpha-interferon therapy of chronic hepatitis B. Current status and recommendations. J Hepatol. 1990;11 (Suppl 1):S100–S107. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(90)90173-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H., Dusheiko G. M., Seeff L. B., Jones E. A., Waggoner J. G., Bales Z. B. Seroconversion from hepatitis B e antigen to antibody in chronic type B hepatitis. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jun;94(6):744–748. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-6-744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H., Peters M., Mullen K. D., Jones D. B., Rustgi V., Di Bisceglie A., Hallahan C., Park Y., Meschievitz C., Jones E. A. Randomized, controlled trial of recombinant human alpha-interferon in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 1988 Nov;95(5):1318–1325. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90367-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lok A. S., Lai C. L., Wu P. C., Leung E. K. Long-term follow-up in a randomised controlled trial of recombinant alpha 2-interferon in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. Lancet. 1988 Aug 6;2(8606):298–302. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrillo R. P., Schiff E. R., Davis G. L., Bodenheimer H. C., Jr, Lindsay K., Payne J., Dienstag J. L., O'Brien C., Tamburro C., Jacobson I. M. A randomized, controlled trial of interferon alfa-2b alone and after prednisone withdrawal for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. The Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group. N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 2;323(5):295–301. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008023230503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Realdi G., Alberti A., Rugge M., Bortolotti F., Rigoli A. M., Tremolada F., Ruol A. Seroconversion from hepatitis B e antigen to anti-HBe in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Gastroenterology. 1980 Aug;79(2):195–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saracco G., Mazzella G., Rosina F., Cancellieri C., Lattore V., Raise E., Rocca G., Giorda L., Verme G., Gasbarrini G. A controlled trial of human lymphoblastoid interferon in chronic hepatitis B in Italy. Hepatology. 1989 Sep;10(3):336–341. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalm S. W., Heytink R. A., van Buuren H. R., de Man R. A. Acyclovir enhances the antiviral effect of interferon in chronic hepatitis B. Lancet. 1985 Aug 17;2(8451):358–360. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92498-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scully L. J., Shein R., Karayiannis P., McDonald J. A., Thomas H. C. Lymphoblastoid interferon therapy of chronic HBV infection. A comparison of 12 vs. 24 weeks of thrice weekly treatment. J Hepatol. 1987 Aug;5(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(87)80061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas H. C. The hepatitis B virus and the host response. J Hepatol. 1990;11 (Suppl 1):S83–S89. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(90)90170-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


