Abstract
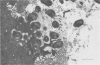
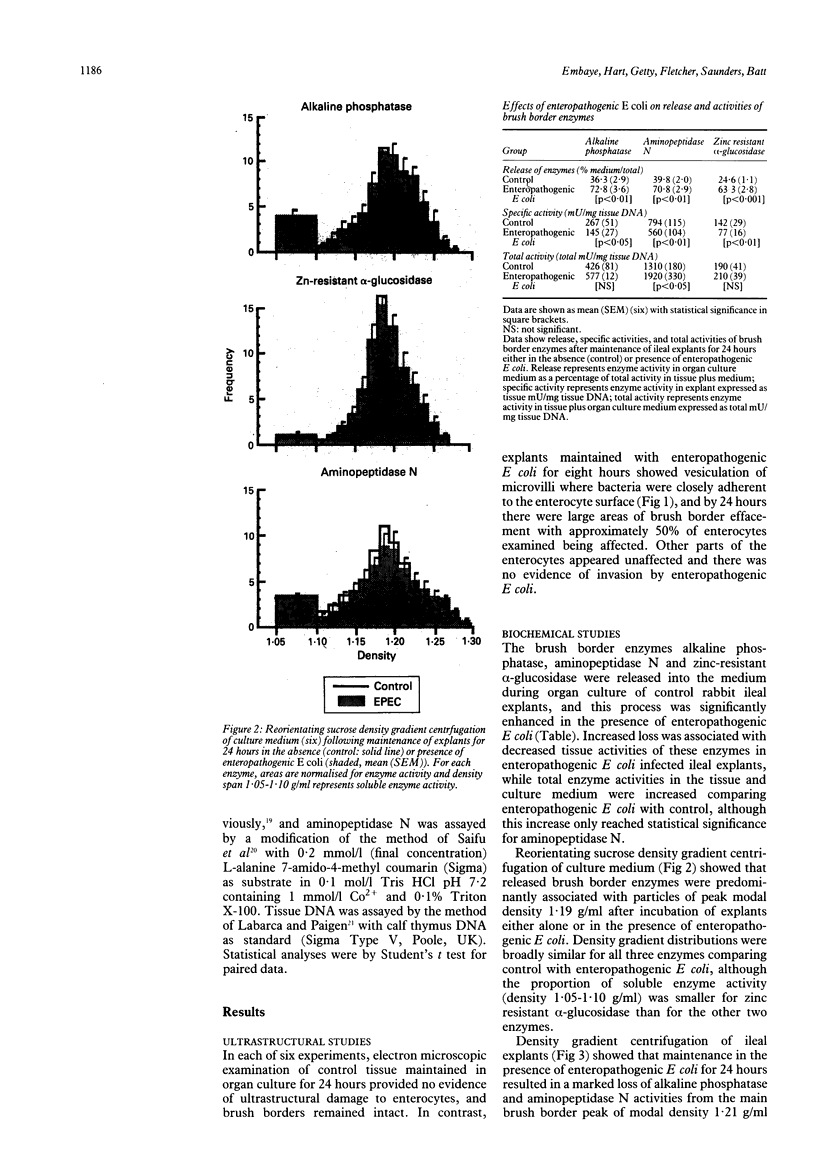
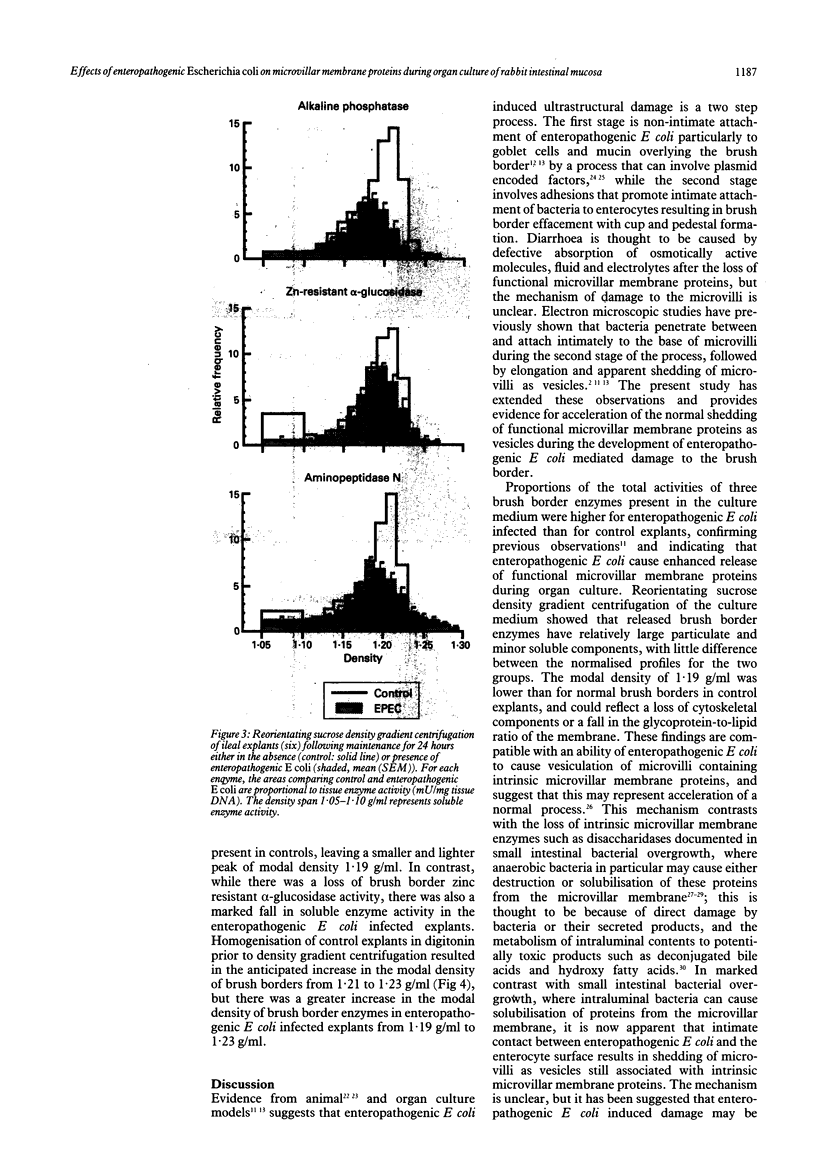
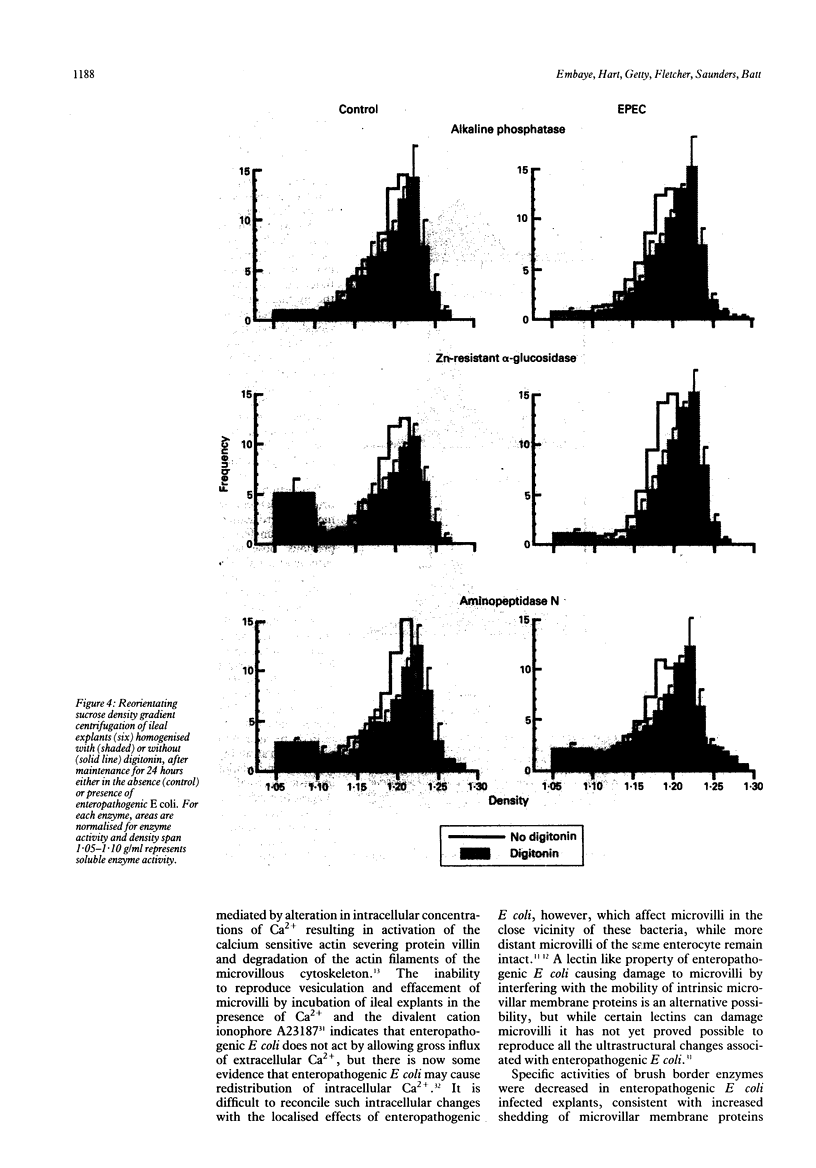
This study examines the effects of an enteropathogenic Escherichia coli on microvillar membrane proteins during organ culture of rabbit ileal explants. Explants maintained with enteropathogenic E coli showed brush border effacement affecting approximately 50% of enterocytes, and where enteropathogenic E coli were closely adherent to the enterocyte surface microvilli were apparently being shed as vesicles. The microvillar membrane enzymes alkaline phosphatase, aminopeptidase N and alpha-glucosidase were released into the culture medium during organ culture, and this process was significantly enhanced by enteropathogenic E coli. This increased loss of microvillar membrane enzymes into the culture medium was associated with decreased tissue activities of microvillar membrane enzymes in enteropathogenic E coli infected ileal explants compared with control. For aminopeptidase N in particular, however, total enzyme activities in the tissue plus culture medium were increased comparing enteropathogenic E coli with control, suggesting that there might be an increase in the rate of synthesis of certain microvillar membrane proteins. Reorientating sucrose density gradient centrifugation of culture medium showed that alkaline phosphatase, aminopeptidase N and alpha-glucosidase were predominantly associated with particles of peak modal density 1.19 g/ml in both groups, confirming that enteropathogenic E coli accelerate release of microvillar membrane enzymes as vesicles. Analytical fractionation of ileal explants showed that enteropathogenic E coli resulted in a loss of microvillar membrane enzyme activities from the main brush border peak of modal density 1.21 g/ml present in controls. The density of the remaining smaller and lighter peak increased from 1.19 g/ml to 1.23 g/ml after homogenisation in digitonin, confirming association of these proteins with cholesterol containing membranes and not endoplasmic reticulum. These findings suggest that enteropathogenic E. coli accelerate the normal shedding of microvillar membrane proteins as vesicles, and may stimulate a compensatory increase in microvillar membrane protein synthesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin T. J., Ward W., Aitken A., Knutton S., Williams P. H. Elevation of intracellular free calcium levels in HEp-2 cells infected with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1599–1604. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1599-1604.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batt R. M., Embaye H., Hunt J., Hart C. A. Ultrastructural damage to equine intestinal epithelium induced by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Equine Vet J. 1989 Sep;21(5):373–375. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1989.tb02695.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batt R. M., Hart C. A., McLean L., Saunders J. R. Organ culture of rabbit ileum as a model for the investigation of the mechanism of intestinal damage by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Gut. 1987 Oct;28(10):1283–1290. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.10.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batt R. M., McLean L., Carter M. W. Sequential morphologic and biochemical studies of naturally occurring wheat-sensitive enteropathy in Irish setter dogs. Dig Dis Sci. 1987 Feb;32(2):184–194. doi: 10.1007/BF01297107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batt R. M., Peters T. J. Subcellular fractionation studies on peroral jejunal biopsies from the dog. Res Vet Sci. 1978 Jul;25(1):94–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantey J. R., Lushbaugh W. B., Inman L. R. Attachment of bacteria to intestinal epithelial cells in diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli strain RDEC-1 in the rabbit: stages and role of capsule. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):219–230. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embaye H., Batt R. M., Saunders J. R., Getty B., Hart C. A. Interaction of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli 0111 with rabbit intestinal mucosa in vitro. Gastroenterology. 1989 Apr;96(4):1079–1086. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91626-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher J. N., Saunders J. R., Batt R. M., Embaye H., Getty B., Hart C. A. Attaching effacement of the rabbit enterocyte brush border is encoded on a single 96.5-kilobase-pair plasmid in an enteropathogenic Escherichia coli O111 strain. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1316–1322. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1316-1322.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall G. A., Reynolds D. J., Chanter N., Morgan J. H., Parsons K. R., Debney T. G., Bland A. P., Bridger J. C. Dysentery caused by Escherichia coli (S102-9) in calves: natural and experimental disease. Vet Pathol. 1985 Mar;22(2):156–163. doi: 10.1177/030098588502200210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart C. A., Batt R. M., Fletcher J., Embaye H., Saunders J. R. Interactions between enterocytes and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Biochem Soc Trans. 1989 Jun;17(3):466–469. doi: 10.1042/bst0170466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart C. A., Batt R. M., Saunders J. R., Getty B. Lectin-induced damage to the enterocyte brush border. An electron-microscopic study in rabbits. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1988 Dec;23(10):1153–1159. doi: 10.3109/00365528809090184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerse A. E., Yu J., Tall B. D., Kaper J. B. A genetic locus of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli necessary for the production of attaching and effacing lesions on tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7839–7843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas A., Flanagan P. R., Forstner G. G. Pathogenesis of mucosal injury in the blind loop syndrome. Brush border enzyme activity and glycoprotein degradation. J Clin Invest. 1977 Dec;60(6):1321–1330. doi: 10.1172/JCI108891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas A., Krishnan C., Forstner G. Pathogenesis of mucosal injury in the blind loop syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1978 Nov;75(5):791–795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. E., Toskes P. P. Small intestine bacterial overgrowth. Gastroenterology. 1979 May;76(5 Pt 1):1035–1055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Lloyd D. R., McNeish A. S. Adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to human intestinal enterocytes and cultured human intestinal mucosa. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):69–77. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.69-77.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton F., Poole B., Beaufay H., Baudhuin P., Coffey J. W., Fowler S., De Duve C. The large-scale separation of peroxisomes, mitochondria, and lysosomes from the livers of rats injected with triton WR-1339. Improved isolation procedures, automated analysis, biochemical and morphological properties of fractions. J Cell Biol. 1968 May;37(2):482–513. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.2.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Edelman R. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli of classic serotypes associated with infant diarrhea: epidemiology and pathogenesis. Epidemiol Rev. 1984;6:31–51. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea: enterotoxigenic, enteropathogenic, enteroinvasive, enterohemorrhagic, and enteroadherent. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):377–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters J. E., Charlier G. J., Halen P. H. Pathogenicity of attaching effacing enteropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from diarrheic suckling and weanling rabbits for newborn rabbits. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):690–696. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.690-696.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pospischil A., Mainil J. G., Baljer G., Moon H. W. Attaching and effacing bacteria in the intestines of calves and cats with diarrhea. Vet Pathol. 1987 Jul;24(4):330–334. doi: 10.1177/030098588702400407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riepe S. P., Goldstein J., Alpers D. H. Effect of secreted Bacteroides proteases on human intestinal brush border hydrolases. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):314–322. doi: 10.1172/JCI109859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbaum R., McAdams A. J., Giannella R., Partin J. C. A clinicopathologic study of enterocyte-adherent Escherichia coli: a cause of protracted diarrhea in infants. Gastroenterology. 1982 Aug;83(2):441–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saifuku K., Sekine T., Namihisa T., Takahashi T., Kanaoka Y. A novel fluorometric ultramicro determination of serum leucine aminopeptidase using a coumarine derivative. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 Mar 1;84(1-2):85–91. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90479-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Peters T. J. Protection of epithelial function in human jejunum cultured with hydrocortisone. Am J Physiol. 1983 May;244(5):G532–G540. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.244.5.G532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. M., Boedeker E. C. Pilus-mediated interactions of the Escherichia coli strain RDEC-1 with mucosal glycoproteins in the small intestine of rabbits. Gastroenterology. 1987 Oct;93(4):734–743. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90435-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. J., Hart A., Batt R. M., McDougall C., McLean L. Ultrastructural and biochemical changes in human jejunal mucosa associated with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (0111) infection. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1986 Jan;5(1):70–73. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198601000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Robins-Browne R. M., Gonis G., Hayes J., Withers M., McCartney E. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli enteritis: evaluation of the gnotobiotic piglet as a model of human infection. Gut. 1985 Jun;26(6):570–578. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.6.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulshen M. H., Rollo J. L. Pathogenesis of escherichia coli gastroenteritis in man--another mechanism. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 10;302(2):99–101. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001103020207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M. K., Andrews G. P., Fritz D. L., Sjogren R. W., Jr, Boedeker E. C. Characterization of the plasmid from Escherichia coli RDEC-1 that mediates expression of adhesin AF/R1 and evidence that AF/R1 pili promote but are not essential for enteropathogenic disease. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1846–1857. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1846-1857.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]