Abstract
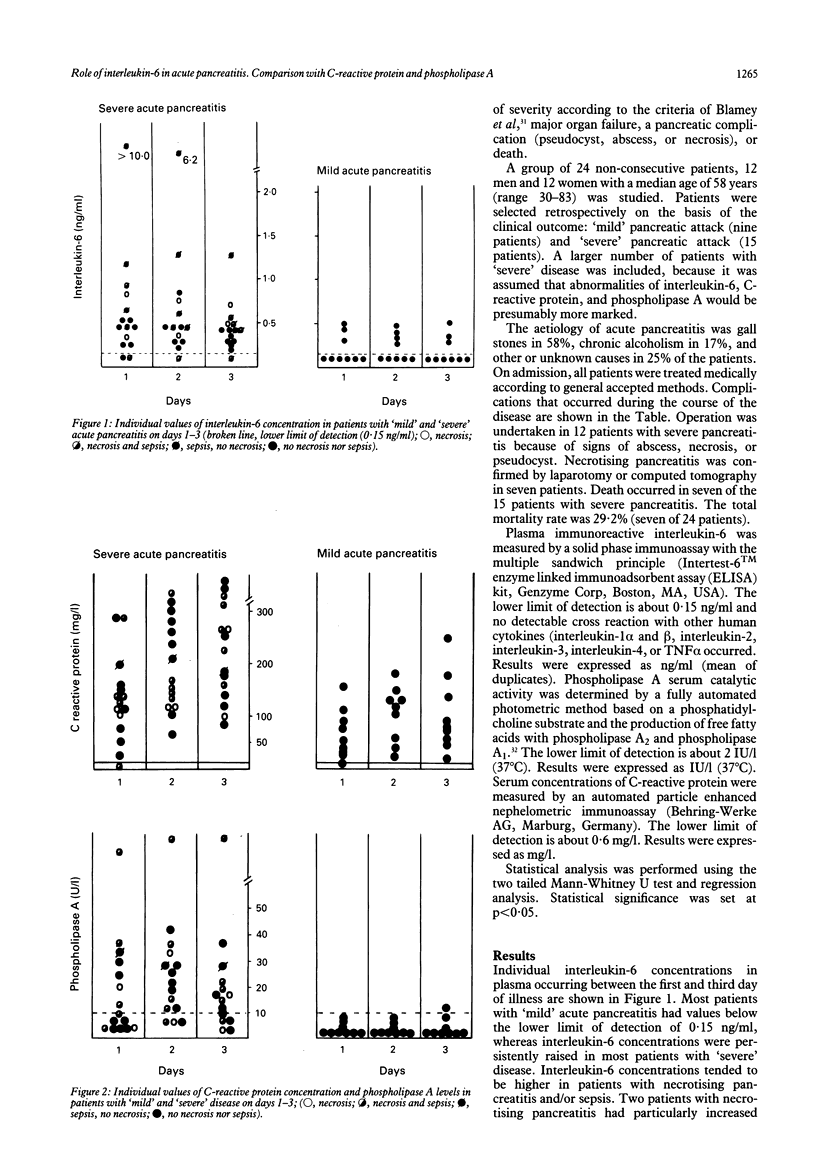
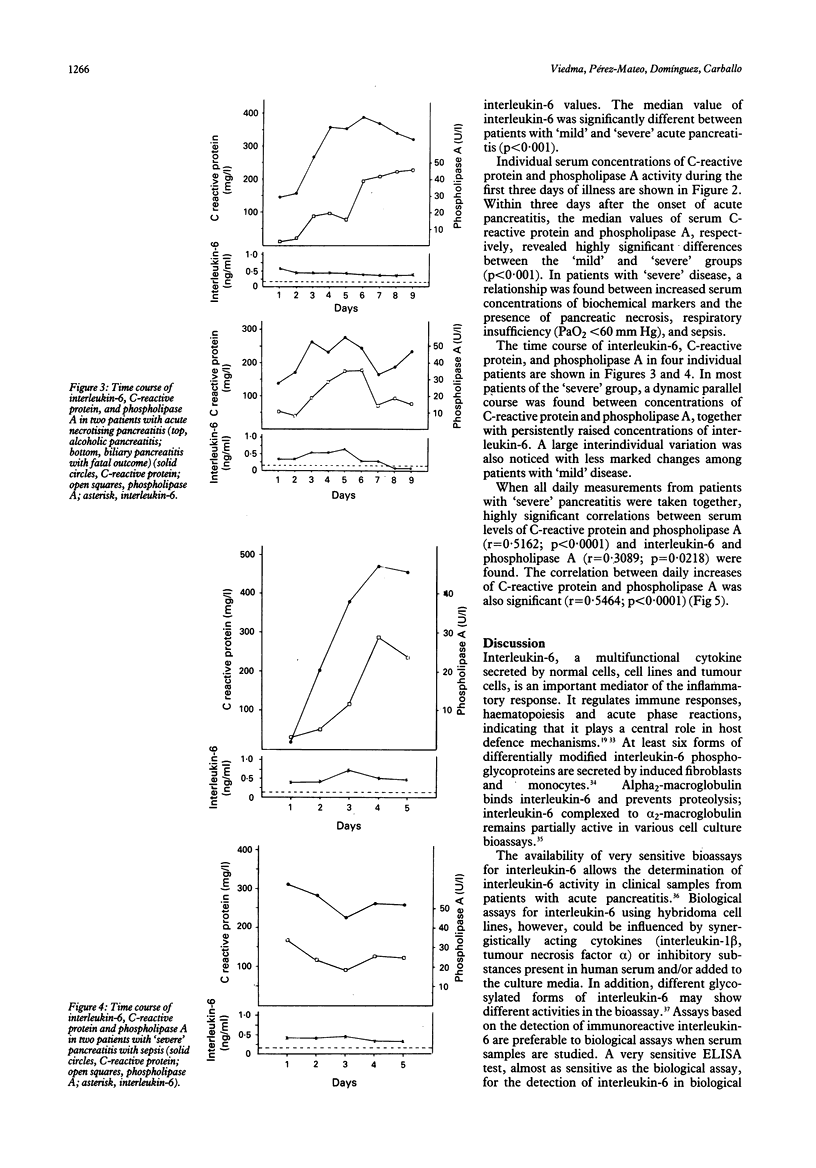
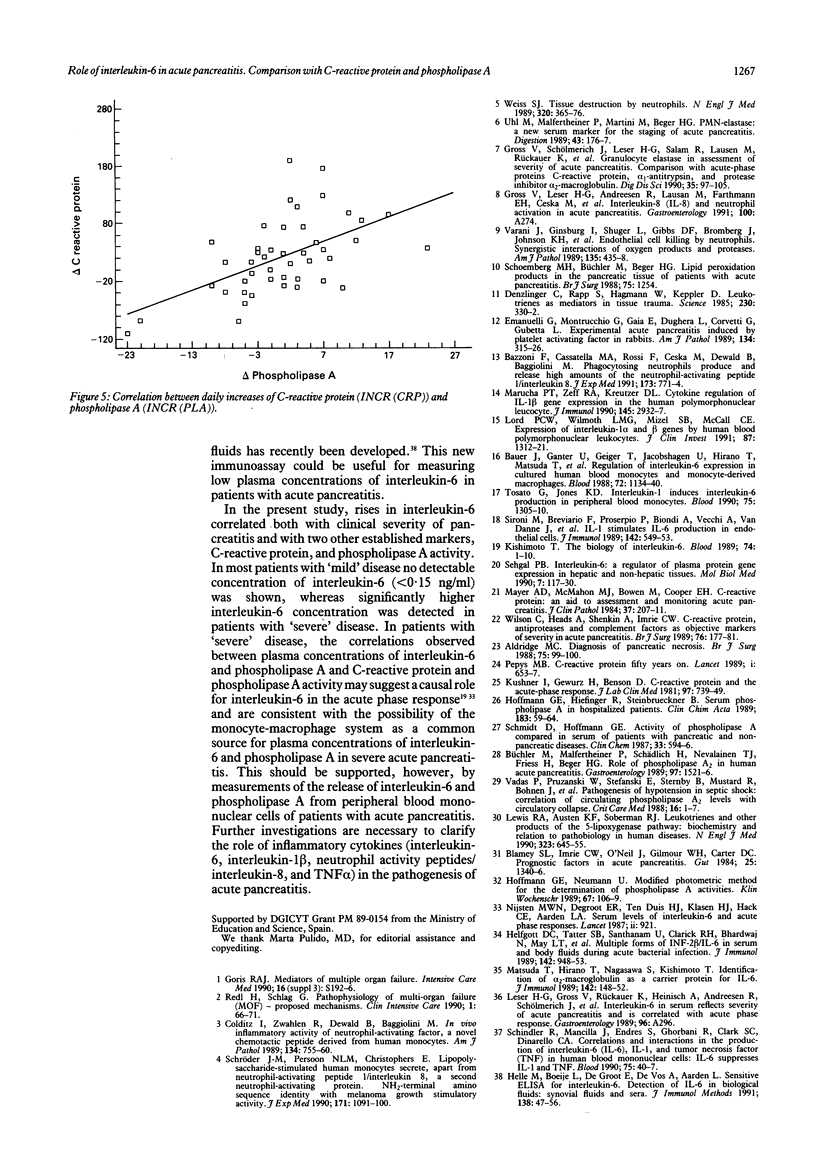
Plasma values of immunoreactive interleukin-6, C-reactive protein and phospholipase A have been determined in serial samples from 24 patients with acute pancreatitis ('mild' pancreatitis nine, 'severe' pancreatitis 15). Median plasma concentrations of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and phospholipase A activity were significantly higher in patients with 'severe' illness (p < 0.001) than those with 'mild' illness. A particularly marked increase in interleukin-6 was found in two patients with necrotising pancreatitis and fatal outcome. Significant correlations between plasma concentrations of interleukin-6 and phospholipase A (p = 0.0218) and C-reactive protein and phospholipase A activity (p < 0.0001) were found in patients with 'severe' disease. These findings in a limited number of patients with acute pancreatitis are promising in that raised interleukin-6 correlated with clinical severity and with two other established markers, C-reactive protein, and phospholipase A activity.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akinyanju O. O., Anionwu E. N. Training of counsellors on sickle-cell disorders in Africa. Lancet. 1989 Mar 25;1(8639):653–654. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldridge M. C. Diagnosis of pancreatic necrosis. Br J Surg. 1988 Feb;75(2):99–100. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800750203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer J., Ganter U., Geiger T., Jacobshagen U., Hirano T., Matsuda T., Kishimoto T., Andus T., Acs G., Gerok W. Regulation of interleukin-6 expression in cultured human blood monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages. Blood. 1988 Oct;72(4):1134–1140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazzoni F., Cassatella M. A., Rossi F., Ceska M., Dewald B., Baggiolini M. Phagocytosing neutrophils produce and release high amounts of the neutrophil-activating peptide 1/interleukin 8. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):771–774. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blamey S. L., Imrie C. W., O'Neill J., Gilmour W. H., Carter D. C. Prognostic factors in acute pancreatitis. Gut. 1984 Dec;25(12):1340–1346. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.12.1340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büchler M., Malfertheiner P., Schädlich H., Nevalainen T. J., Friess H., Beger H. G. Role of phospholipase A2 in human acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 1989 Dec;97(6):1521–1526. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90398-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colditz I., Zwahlen R., Dewald B., Baggiolini M. In vivo inflammatory activity of neutrophil-activating factor, a novel chemotactic peptide derived from human monocytes. Am J Pathol. 1989 Apr;134(4):755–760. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denzlinger C., Rapp S., Hagmann W., Keppler D. Leukotrienes as mediators in tissue trauma. Science. 1985 Oct 18;230(4723):330–332. doi: 10.1126/science.4048937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuelli G., Montrucchio G., Gaia E., Dughera L., Corvetti G., Gubetta L. Experimental acute pancreatitis induced by platelet activating factor in rabbits. Am J Pathol. 1989 Feb;134(2):315–326. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross V., Schölmerich J., Leser H. G., Salm R., Lausen M., Rückauer K., Schöffel U., Lay L., Heinisch A., Farthmann E. H. Granulocyte elastase in assessment of severity of acute pancreatitis. Comparison with acute-phase proteins C-reactive protein, alpha 1-antitrypsin, and protease inhibitor alpha 2-macroglobulin. Dig Dis Sci. 1990 Jan;35(1):97–105. doi: 10.1007/BF01537230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfgott D. C., Tatter S. B., Santhanam U., Clarick R. H., Bhardwaj N., May L. T., Sehgal P. B. Multiple forms of IFN-beta 2/IL-6 in serum and body fluids during acute bacterial infection. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):948–953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helle M., Boeije L., de Groot E., de Vos A., Aarden L. Sensitive ELISA for interleukin-6. Detection of IL-6 in biological fluids: synovial fluids and sera. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Apr 8;138(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90063-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann G. E., Hiefinger R., Steinbrueckner B. Serum phospholipase A in hospitalized patients. Clin Chim Acta. 1989 Jul 31;183(1):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(89)90272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann G. E., Neumann U. Modified photometric method for the determination of phospholipase A activities. Klin Wochenschr. 1989 Feb 1;67(3):106–109. doi: 10.1007/BF01711332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. The biology of interleukin-6. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner I., Gewurz H., Benson M. D. C-reactive protein and the acute-phase response. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Jun;97(6):739–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Austen K. F., Soberman R. J. Leukotrienes and other products of the 5-lipoxygenase pathway. Biochemistry and relation to pathobiology in human diseases. N Engl J Med. 1990 Sep 6;323(10):645–655. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199009063231006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord P. C., Wilmoth L. M., Mizel S. B., McCall C. E. Expression of interleukin-1 alpha and beta genes by human blood polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1312–1321. doi: 10.1172/JCI115134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marucha P. T., Zeff R. A., Kreutzer D. L. Cytokine regulation of IL-1 beta gene expression in the human polymorphonuclear leukocyte. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):2932–2937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda T., Hirano T., Nagasawa S., Kishimoto T. Identification of alpha 2-macroglobulin as a carrier protein for IL-6. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):148–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer A. D., McMahon M. J., Bowen M., Cooper E. H. C reactive protein: an aid to assessment and monitoring of acute pancreatitis. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Feb;37(2):207–211. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijsten M. W., de Groot E. R., ten Duis H. J., Klasen H. J., Hack C. E., Aarden L. A. Serum levels of interleukin-6 and acute phase responses. Lancet. 1987 Oct 17;2(8564):921–921. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91413-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler R., Mancilla J., Endres S., Ghorbani R., Clark S. C., Dinarello C. A. Correlations and interactions in the production of interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-1, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in human blood mononuclear cells: IL-6 suppresses IL-1 and TNF. Blood. 1990 Jan 1;75(1):40–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt D., Hoffmann G. E. Activity of phospholipase A compared in serum of patients with pancreatic and nonpancreatic diseases. Clin Chem. 1987 Apr;33(4):594–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. M., Persoon N. L., Christophers E. Lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes secrete, apart from neutrophil-activating peptide 1/interleukin 8, a second neutrophil-activating protein. NH2-terminal amino acid sequence identity with melanoma growth stimulatory activity. J Exp Med. 1990 Apr 1;171(4):1091–1100. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.4.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B. Interleukin-6: a regulator of plasma protein gene expression in hepatic and non-hepatic tissues. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Apr;7(2):117–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sironi M., Breviario F., Proserpio P., Biondi A., Vecchi A., Van Damme J., Dejana E., Mantovani A. IL-1 stimulates IL-6 production in endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):549–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosato G., Jones K. D. Interleukin-1 induces interleukin-6 production in peripheral blood monocytes. Blood. 1990 Mar 15;75(6):1305–1310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Pruzanski W., Stefanski E., Sternby B., Mustard R., Bohnen J., Fraser I., Farewell V., Bombardier C. Pathogenesis of hypotension in septic shock: correlation of circulating phospholipase A2 levels with circulatory collapse. Crit Care Med. 1988 Jan;16(1):1–7. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198801000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varani J., Ginsburg I., Schuger L., Gibbs D. F., Bromberg J., Johnson K. J., Ryan U. S., Ward P. A. Endothelial cell killing by neutrophils. Synergistic interaction of oxygen products and proteases. Am J Pathol. 1989 Sep;135(3):435–438. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J. Tissue destruction by neutrophils. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 9;320(6):365–376. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902093200606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C., Heads A., Shenkin A., Imrie C. W. C-reactive protein, antiproteases and complement factors as objective markers of severity in acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1989 Feb;76(2):177–181. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800760224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


