Abstract
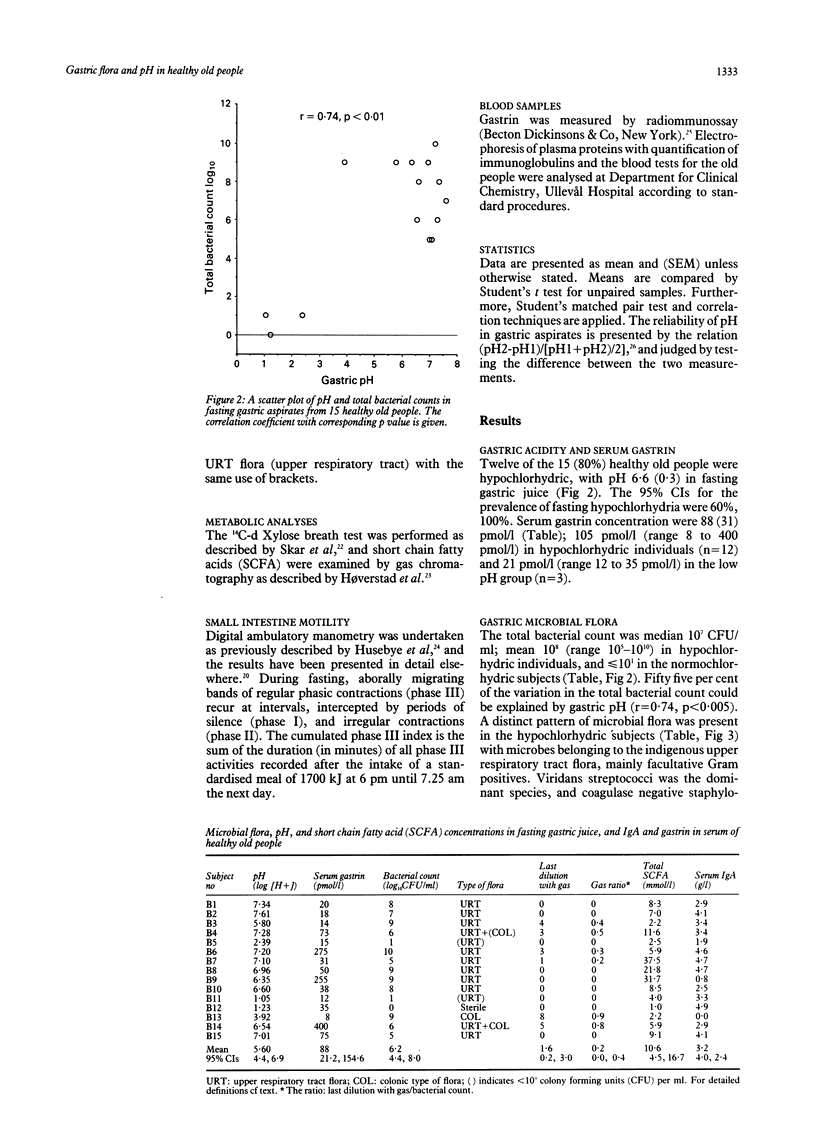
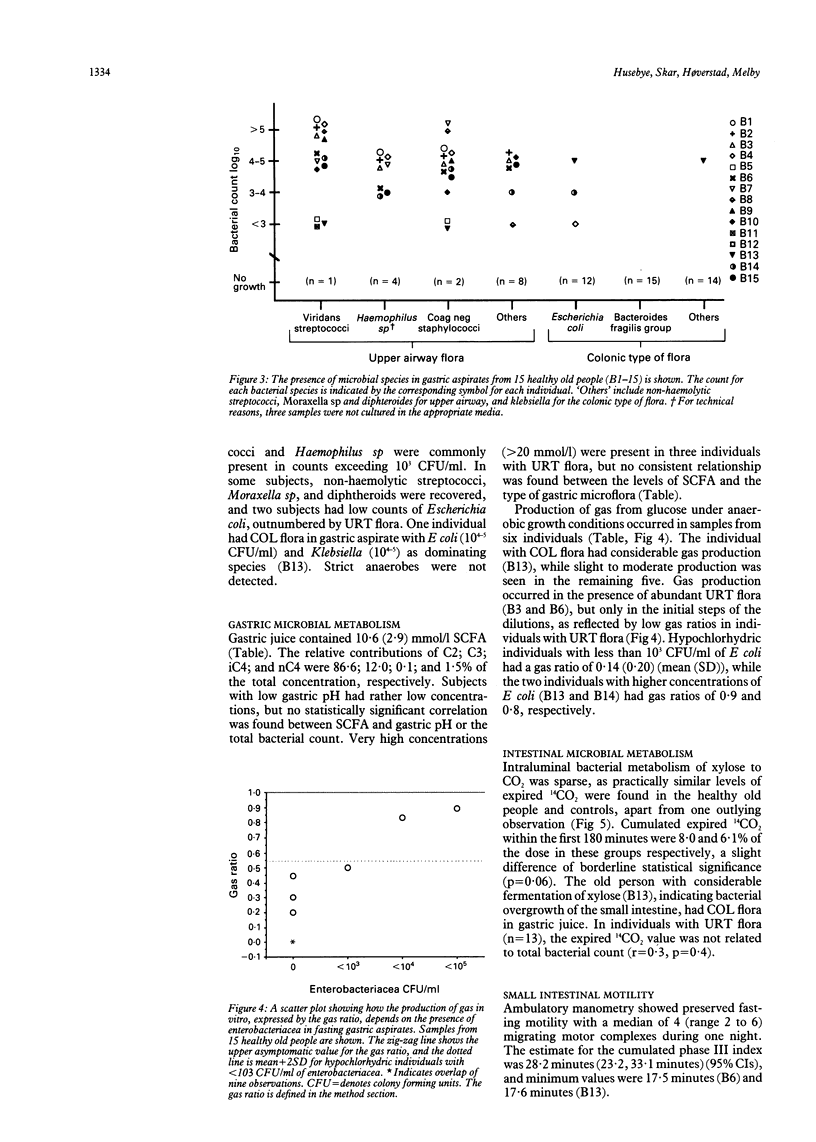
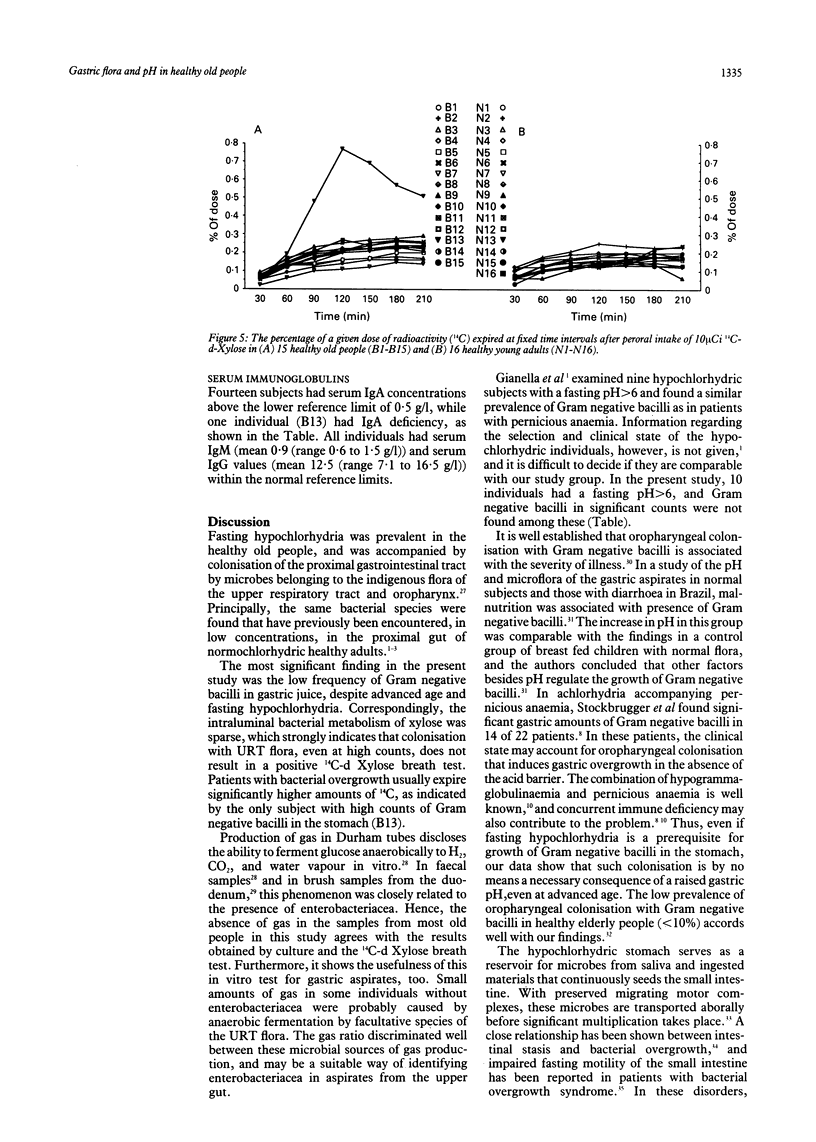
Fifteen healthy old people mean age 84 years (range 80-91 years), were examined to assess the effect of advanced age on the microecology of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Twelve of 15 (80%) were hypochlorhydric with pH 6.6 (0.3) (mean (SEM) and a mean bacterial count of 10(8) colony forming units (CFU) per ml (range 10(5)-10(10)) in fasting gastric aspirate. Normochlorhydric subjects had low counts (< or = 10(1) CFU/ml). The microbial flora was dominated by viridans streptococci, coagulase negative staphylococci, and Haemophilus sp. Only one subject harboured significant concentrations of Gram negative bacilli with Escherichia coli (10(4-5) CFU/ml) and Klebsiella (10(4-5)). Strict anaerobes were not found. The total concentration of short chain fatty acids in gastric aspirate was 10.6 (2.9) mmol/l (mean (SEM). Absence of significant, intraluminal fermentation of xylose to CO2 was shown by the 14C-d Xylose breath test, and ambulatory manometry showed preserved fasting motility pattern of the small intestine. Serum immunoglobulins were normal. Advanced age is accompanied by fasting hypochlorhydria and colonisation with mainly Gram positive flora in the upper gut. Other factors than old age and fasting hypochlorhydria are required for colonisation with Gram negative bacilli.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird T., Hall M. R., Schade R. O. Gastric histology and its relation to anaemia in the elderly. Gerontology. 1977;23(4):309–321. doi: 10.1159/000212201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjørneklett A., Midtvedt T. Influence of three antimicrobial agents--penicillin, metronidazole, and doxycyclin--on the intestinal microflora of healthy humans. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1981;16(4):473–480. doi: 10.3109/00365528109182001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland J. M., Altman D. G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986 Feb 8;1(8476):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borriello S. P., Reed P. J., Dolby J. M., Barclay F. E., Webster A. D. Microbial and metabolic profile of achlorhydric stomach: comparison of pernicious anaemia and hypogammaglobulinaemia. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Aug;38(8):946–953. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.8.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning G. G., Buchan K. A., Mackay C. The effect of vagotomy and drainage on the small bowel flora. Gut. 1974 Feb;15(2):139–142. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.2.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen P. M. The incidence of achlorhydria and hypochlorhydria in healthy subjects and patients with gastrointestinal diseases. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1968;3(5):497–508. doi: 10.3109/00365526809179909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON J. M. The fate of bacteria in the small intestine. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1960 Jan;79:131–140. doi: 10.1002/path.1700790116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolby J. M., Webster A. D., Borriello S. P., Barclay F. E., Bartholomew B. A., Hill M. J. Bacterial colonization and nitrite concentration in the achlorhydric stomachs of patients with primary hypogammaglobulinaemia or classical pernicious anaemia. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1984 Jan;19(1):105–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drasar B. S., Shiner M., McLeod G. M. Studies on the intestinal flora. I. The bacterial flora of the gastrointestinal tract in healthy and achlorhydric persons. Gastroenterology. 1969 Jan;56(1):71–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman M., Barnett C. Fasting gastric pH and its relationship to true hypochlorhydria in humans. Dig Dis Sci. 1991 Jul;36(7):866–869. doi: 10.1007/BF01297133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fimmel C. J., Etienne A., Cilluffo T., von Ritter C., Gasser T., Rey J. P., Caradonna-Moscatelli P., Sabbatini F., Pace F., Bühler H. W. Long-term ambulatory gastric pH monitoring: validation of a new method and effect of H2-antagonists. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jun;88(6):1842–1851. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederiksen W., Bruusgaard A., Thaysen E. H. Assessment of the relationship between gastric secretory capacity and jejunal bacteriology. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1973;8(4):353–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganguli P. C., Cullen D. R., Irvine W. J. Radioimmunoassay of plasmagastrin in pernicious anaemia, achlorhydria without pernicious anaemia, hypochlorhydria, and in controls. Lancet. 1971 Jan 23;1(7691):155–158. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91932-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Broitman S. A., Zamcheck N. Gastric acid barrier to ingested microorganisms in man: studies in vivo and in vitro. Gut. 1972 Apr;13(4):251–256. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.4.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Plaut A. G., Nahas L., Weinstein L., Spanknebel G., Levitan R. Studies of intestinal microflora. II. Microorganisms of the small intestine and their relations to oral and fecal flora. Gastroenterology. 1967 Dec;53(6):856–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. D., Shiner M. Influence of gastric pH on gastric and jejunal flora. Gut. 1967 Dec;8(6):574–581. doi: 10.1136/gut.8.6.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B. E., Midtvedt T., Norman A. Isolated fecal microorganisms capable of 7-alpha-dehydroxylating bile acids. J Exp Med. 1966 Feb 1;123(2):413–432. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.2.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. R., Rosenberg I. H., Russell R. M. Causes and consequences of hypochlorhydria in the elderly. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 Jun;34(6):933–937. doi: 10.1007/BF01540281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz M., Maddern G. J., Chatterton B. E., Collins P. J., Harding P. E., Shearman D. J. Changes in gastric emptying rates with age. Clin Sci (Lond) 1984 Aug;67(2):213–218. doi: 10.1042/cs0670213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husebye E., Engedal K. The patterns of motility are maintained in the human small intestine throughout the process of aging. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1992 May;27(5):397–404. doi: 10.3109/00365529209000095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husebye E., Skar V., Aalen O. O., Osnes M. Digital ambulatory manometry of the small intestine in healthy adults. Estimates of variation within and between individuals and statistical management of incomplete MMC periods. Dig Dis Sci. 1990 Sep;35(9):1057–1065. doi: 10.1007/BF01537575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høverstad T., Bjørneklett A., Midtvedt T., Fausa O., Bøhmer T. Short-chain fatty acids in the proximal gastrointestinal tract of healthy subjects. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1984 Nov;19(8):1053–1058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høverstad T., Fausa O., Bjørneklett A., Bøhmer T. Short-chain fatty acids in the normal human feces. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1984 May;19(3):375–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson W. G., Pierce A. K., Sanford J. P. Changing pharyngeal bacterial flora of hospitalized patients. Emergence of gram-negative bacilli. N Engl J Med. 1969 Nov 20;281(21):1137–1140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196911202812101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstedt G., Olbe L., Kilander A. F., Armbrecht U., Jagenburg R., Runsteen D., Lundberg P. A. Analytical and clinical evaluation of a radioimmunoassay for gastrin. Clin Chem. 1985 Jan;31(1):76–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maffei H. V., Nóbrega F. J. Gastric pH and microflora of normal and diarrhoeic infants. Gut. 1975 Sep;16(9):719–726. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.9.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLoughlin G. A., Hede J. E., Temple J. G., Bradley J., Chapman D. M., McFarland J. The role of IgA in the prevention of bacterial colonization of the jejunum in the vagotomized subject. Br J Surg. 1978 Jun;65(6):435–437. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800650619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton-Thompson G. J., Lightfoot N. F., Ahmet Z., Hunt R. H., Barnard J., Bavin P. M., Brimblecombe R. W., Darkin D. W., Moore P. J., Viney N. Intragastric acidity, bacteria, nitrite, and N-nitroso compounds before, during, and after cimetidine treatment. Lancet. 1982 May 15;1(8281):1091–1095. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. G., Tweedy C., Christian P. E., Datz F. L. Effect of age on gastric emptying of liquid--solid meals in man. Dig Dis Sci. 1983 Apr;28(4):340–344. doi: 10.1007/BF01324951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscroft T. J., Deane S. A., Youngs D., Burdon D. W., Keighley M. R. The microflora of the postoperative stomach. Br J Surg. 1981 Aug;68(8):560–564. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800680813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson W. L., Barnett C., Feldman M., Richardson C. T. Reduction of twenty-four-hour gastric acidity with combination drug therapy in patients with duodenal ulcer. Gastroenterology. 1979 Nov;77(5):1015–1020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts S. H., James O., Jarvis E. H. Bacterial overgrowth syndrome without "blind loop": A cause for malnutrition in the elderly. Lancet. 1977 Dec 10;2(8050):1193–1195. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90436-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma B. K., Santana I. A., Wood E. C., Walt R. P., Pereira M., Noone P., Smith P. L., Walters C. L., Pounder R. E. Intragastric bacterial activity and nitrosation before, during, and after treatment with omeprazole. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Sep 22;289(6447):717–719. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6447.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon G. L., Gorbach S. L. Intestinal flora in health and disease. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jan;86(1):174–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siurala M., Isokoski M., Varis K., Kekki M. Prevalence of gastritis in a rural population. Bioptic study of subjects selected at random. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1968;3(2):211–223. doi: 10.3109/00365526809180125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skar V., Larsen S., Osnes M. The 1-g 14C-D-xylose breath test in gallstone patients with and without duodenal diverticula. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1985 May;20(4):447–451. doi: 10.3109/00365528509089678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skar V., Skar A. G., Osnes M. The duodenal bacterial flora in the region of papilla of Vater in patients with and without duodenal diverticula. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1989 Aug;24(6):649–656. doi: 10.3109/00365528909093104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snepar R., Poporad G. A., Romano J. M., Kobasa W. D., Kaye D. Effect of cimetidine and antacid on gastric microbial flora. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):518–524. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.518-524.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockbruegger R. W., Cotton P. B., Menon G. G., Beilby J. O., Bartholomew B. A., Hill M. J., Walters C. L. Pernicious anaemia, intragastric bacterial overgrowth, and possible consequences. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1984 May;19(3):355–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vantrappen G., Janssens J., Hellemans J., Ghoos Y. The interdigestive motor complex of normal subjects and patients with bacterial overgrowth of the small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1158–1166. doi: 10.1172/JCI108740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



