Abstract
1 Vigabatrin (GVG) was given in a single-blind fashion to 89 patients with complex partial seizures (CPS) refractory to conventional drugs.
2 The median number of CPS per month decreased from 11.0 to 5.0 after addition of GVG, and 51% of patients had a 50% or greater decrease in CPS frequency (P < 0.001).
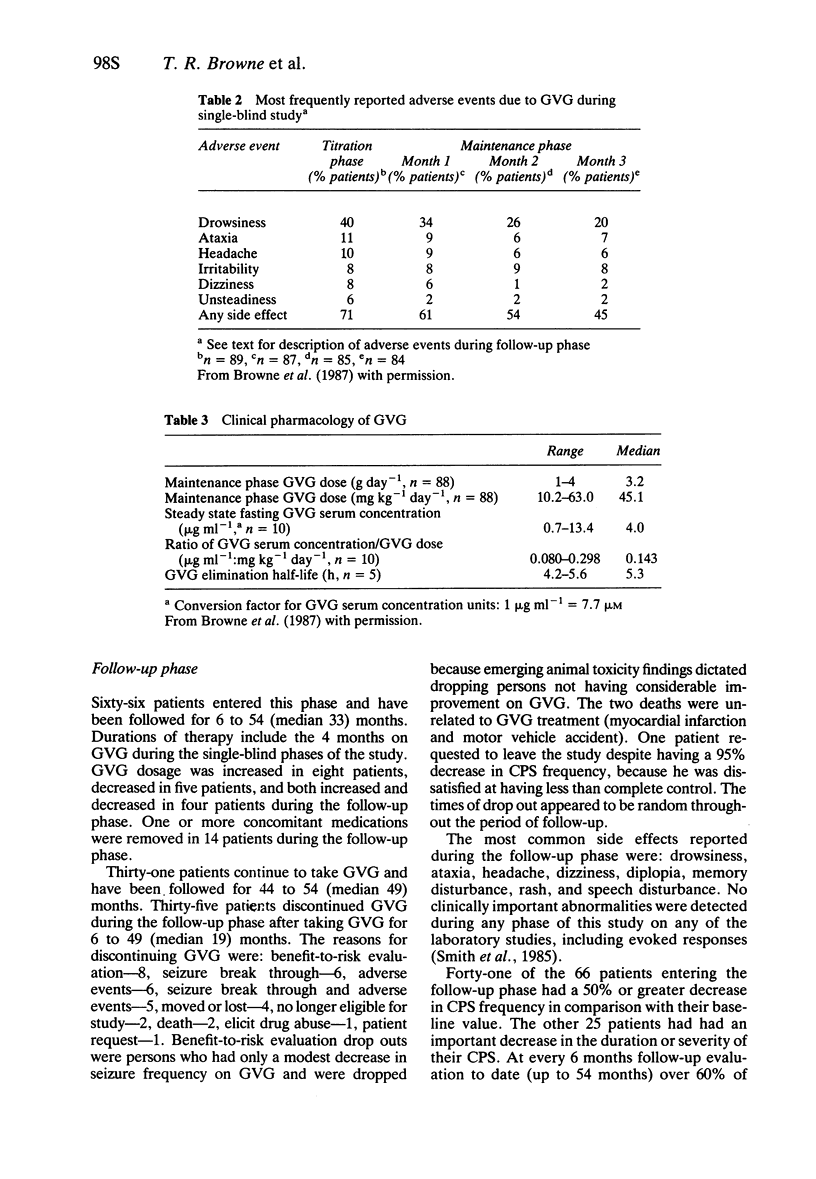
3 Side effects (principally drowsiness, ataxia, headache) occurred mainly during the initiation of therapy and decreased during therapy. After 12 weeks on GVG side effects significantly interfered with functioning in only 13% of patients, and the efficacy: toxicity ratio warranted continued administration in 74% of patients.
4 Co-administration of GVG resulted in a mean decrease of 20% in phenytoin serum concentration (P < 0.001).
5 Sixty-six patients having a favourable response to GVG during the single-blind study have been followed for 6-54 (median 33) months on GVG. Only 17 patients have dropped out of long-term follow-up due to break through seizures and/or side effects. No serious systemic or neurological toxicity has been detected.
Keywords: vigabatrin, complex partial seizures, epilepsy
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Browne T. R., Feldman R. G., Buchanan R. A., Allen N. C., Fawcett-Vickers L., Szabo G. K., Mattson G. F., Norman S. E., Greenblatt D. J. Methsuximide for complex partial seizures: efficacy, toxicity, clinical pharmacology, and drug interactions. Neurology. 1983 Apr;33(4):414–418. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.4.414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne T. R., Mattson R. H., Penry J. K., Smith D. B., Treiman D. M., Wilder B. J., Ben-Menachem E., Napoliello M. J., Sherry K. M., Szabo G. K. Vigabatrin for refractory complex partial seizures: multicenter single-blind study with long-term follow-up. Neurology. 1987 Feb;37(2):184–189. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gram L., Klosterskov P., Dam M. gamma-Vinyl GABA: a double-blind placebo-controlled trial in partial epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 1985 Mar;17(3):262–266. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liegeois-Chauvel C., Marquis P., Gisselbrecht D., Pantieri R., Beaumont D., Chauvel P. Effects of long term vigabatrin on somatosensory evoked potentials in epileptic patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;27 (Suppl 1):69S–72S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb03464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loiseau P., Hardenberg J. P., Pestre M., Guyot M., Schechter P. J., Tell G. P. Double-blind, placebo-controlled study of vigabatrin (gamma-vinyl GABA) in drug-resistant epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1986 Mar-Apr;27(2):115–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1986.tb03512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumford J. P., Dam M. Meta-analysis of European placebo controlled studies of vigabatrin in drug resistant epilepsy. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;27 (Suppl 1):101S–107S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb03469.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S. A., Klosterskov P., Gram L., Dam M. Long-term study of gamma-vinyl GABA in the treatment of epilepsy. Acta Neurol Scand. 1985 Sep;72(3):295–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1985.tb00873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimmer E. M., Richens A. Double-blind study of gamma-vinyl GABA in patients with refractory epilepsy. Lancet. 1984 Jan 28;1(8370):189–190. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92112-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithers J. A., Lang J. F., Okerholm R. A. Quantitative analysis of vigabatrin in plasma and urine by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1985 May 31;341(1):232–238. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)84035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo G. K., Browne T. R. Improved isocratic liquid-chromatographic simultaneous measurement of phenytoin, phenobarbital, primidone, carbamazepine, ethosuximide, and N-desmethylmethsuximide in serum. Clin Chem. 1982 Jan;28(1):100–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartara A., Manni R., Galimberti C. A., Hardenberg J., Orwin J., Perucca E. Vigabatrin in the treatment of epilepsy: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Epilepsia. 1986 Nov-Dec;27(6):717–723. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1986.tb03600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassinari C. A., Michelucci R., Ambrosetto G., Salvi F. Double-blind study of vigabatrin in the treatment of drug-resistant epilepsy. Arch Neurol. 1987 Sep;44(9):907–910. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1987.00520210009010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



