Abstract
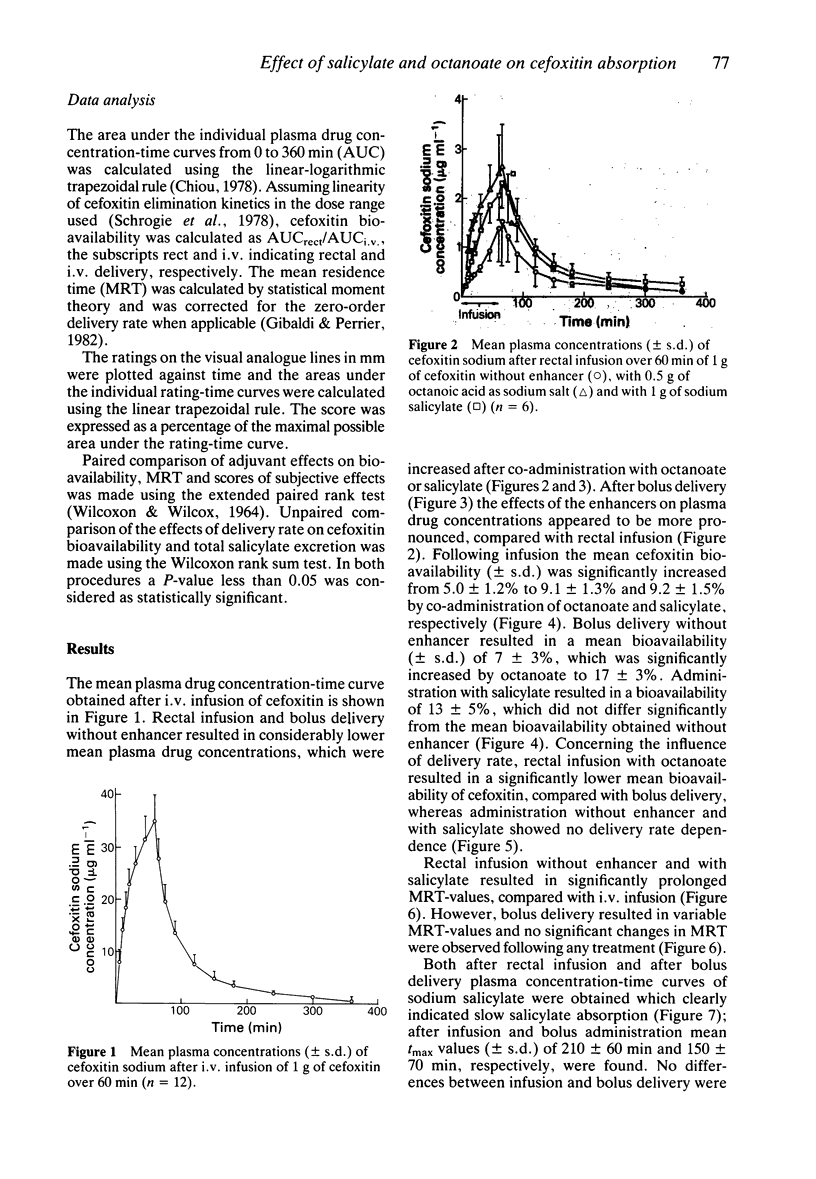
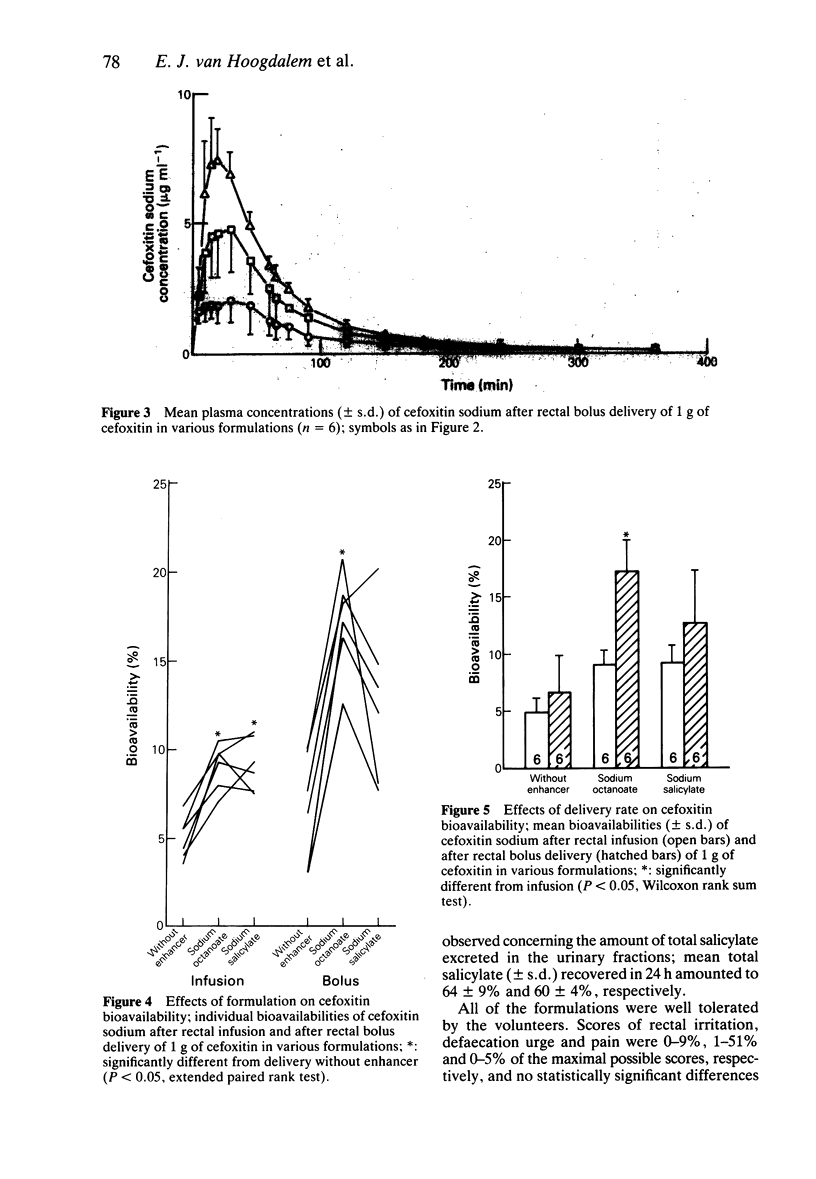
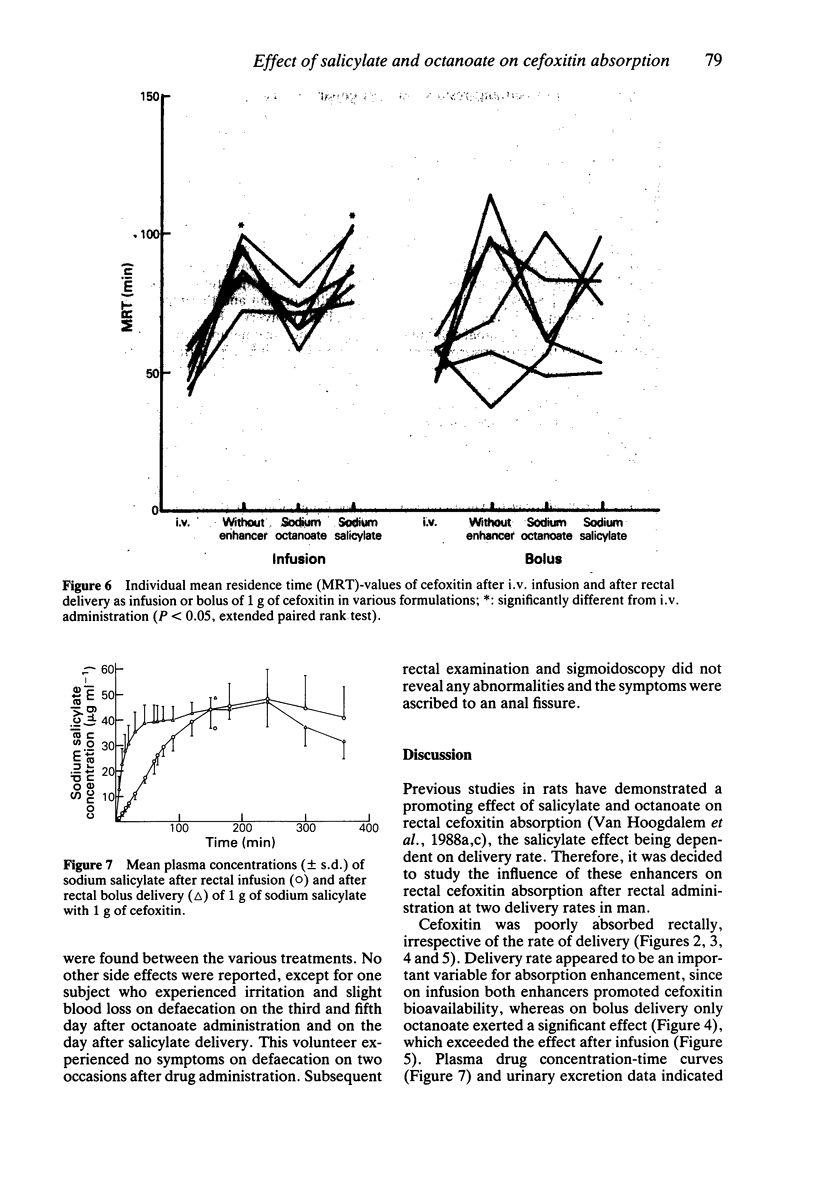
1. The effects of sodium octanoate and sodium salicylate on the rectal absorption of cefoxitin were investigated in healthy volunteers. Drug solutions were given either as a bolus or as a zero-order infusion. 2. On rectal infusion sodium octanoate and sodium salicylate both enhanced mean cefoxitin bioavailability (+/- s.d.) from 5.0 +/- 1.2% to 9.1 +/- 1.3% and 9.2 +/- 1.5%, respectively. After rectal bolus delivery octanoate increased the mean cefoxitin bioavailability from 7 +/- 3% to 17 +/- 3%, whereas bolus salicylate did not produce a statistically significant effect. All formulations were well tolerated by the volunteers. 3. It is concluded that both octanoate and salicylate are capable of enhancing rectal cefoxitin absorption in man; rate of delivery seems to be an important factor.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chiou W. L. Critical evaluation of the potential error in pharmacokinetic studies of using the linear trapezoidal rule method for the calculation of the area under the plasma level--time curve. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1978 Dec;6(6):539–546. doi: 10.1007/BF01062108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choh R., Inagaki H., Nishihata T., Kamada A. Enamine formation of various amino acids with ethyl acetoacetate in aqueous solution in relation to colonic absorption of cefmetazole. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1985 Jul;33(7):3027–3030. doi: 10.1248/cpb.33.3027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S. S., Burnham W. R., Wilson P., O'Brien J. Use of adjuvants for enhancement of rectal absorption of cefoxitin in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):211–215. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fix J. A., Engle K., Porter P. A., Leppert P. S., Selk S. J., Gardner C. R., Alexander J. Acylcarnitines: drug absorption-enhancing agents in the gastrointestinal tract. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 1):G332–G340. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.3.G332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy G., Procknal J. A. Drug biotransformation interactions in man. I. Mutual inhibition in glucuronide formation of salicylic acid and salicylamide in man. J Pharm Sci. 1968 Aug;57(8):1330–1335. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600570811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto E., Tsuji A., Yamana T. Effects of surfactants on the GI absorption of beta-lactam antibiotics in rats. J Pharm Sci. 1983 Jun;72(6):651–654. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600720615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishihata T., Tomida H., Frederick G., Rytting J. H., Higuchi T. Comparison of the effects of sodium salicylate, disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and polyoxyethylene-23-lauryl ether as adjuvants for the rectal absorption of sodium cefoxitin. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1985 Mar;37(3):159–163. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1985.tb05032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura K., Nozaki Y., Yoshimi A., Nakamura S., Kitagawa M., Kakeya N., Kitao K. Studies on the promoting effects of carboxylic acid derivatives on the rectal absorption of beta-lactam antibiotics in rats. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1985 Jan;33(1):282–291. doi: 10.1248/cpb.33.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrogie J. J., Davies R. O., Yeh K. C., Rogers D., Holmes G. I., Skeggs H., Martin C. M. Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of cefoxitin sodium. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 Jul;4(B):69–78. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.suppl_b.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekine M., Terashima H., Sasahara K., Nishimura K., Okada R., Awazu S. Improvement of bioavailability of poorly absorbed drugs. II. Effect of medium chain glyceride base on the intestinal absorption of cefmetazole sodium in rats and dogs. J Pharmacobiodyn. 1985 Apr;8(4):286–295. doi: 10.1248/bpb1978.8.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W. M., Murakami T., Higashi Y., Yata N. Enhancement of the rectal absorption of sodium ampicillin by N-acylamino acids in rats. J Pharm Sci. 1987 Jul;76(7):508–512. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600760703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yata N., Sugihara N., Yamajo R., Murakami T., Higashi Y., Kimata H., Nakayama K., Kuzuki T., Tanaka O. Enhanced small intestinal absorption of beta-lactam antibiotics in rats in the presence of monodesmosides isolated from pericarps of Sapindus mukurossi (Enmei-hi). J Pharmacobiodyn. 1986 Feb;9(2):211–217. doi: 10.1248/bpb1978.9.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshitomi H., Nishihata T., Frederick G., Dillsaver M., Higuchi T. Effect of triglyceride on small intestinal absorption of cefoxitin in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;39(11):887–891. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1987.tb03123.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hoogdalem E. J., Hardens M. A., de Boer A. G., Breimer D. D. Absorption enhancement of rectally infused cefoxitin sodium by medium-chain fatty acids in conscious rats: concentration-effect relationship. Pharm Res. 1988 Jul;5(7):453–456. doi: 10.1023/a:1015948720256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hoogdalem E. J., Stijnen A. M., de Boer A. G., Breimer D. D. Rate-controlled absorption enhancement of rectally administered cefazolin in rats by a glyceride mixture (MGK). J Pharm Pharmacol. 1988 May;40(5):329–332. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1988.tb05261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


