Abstract
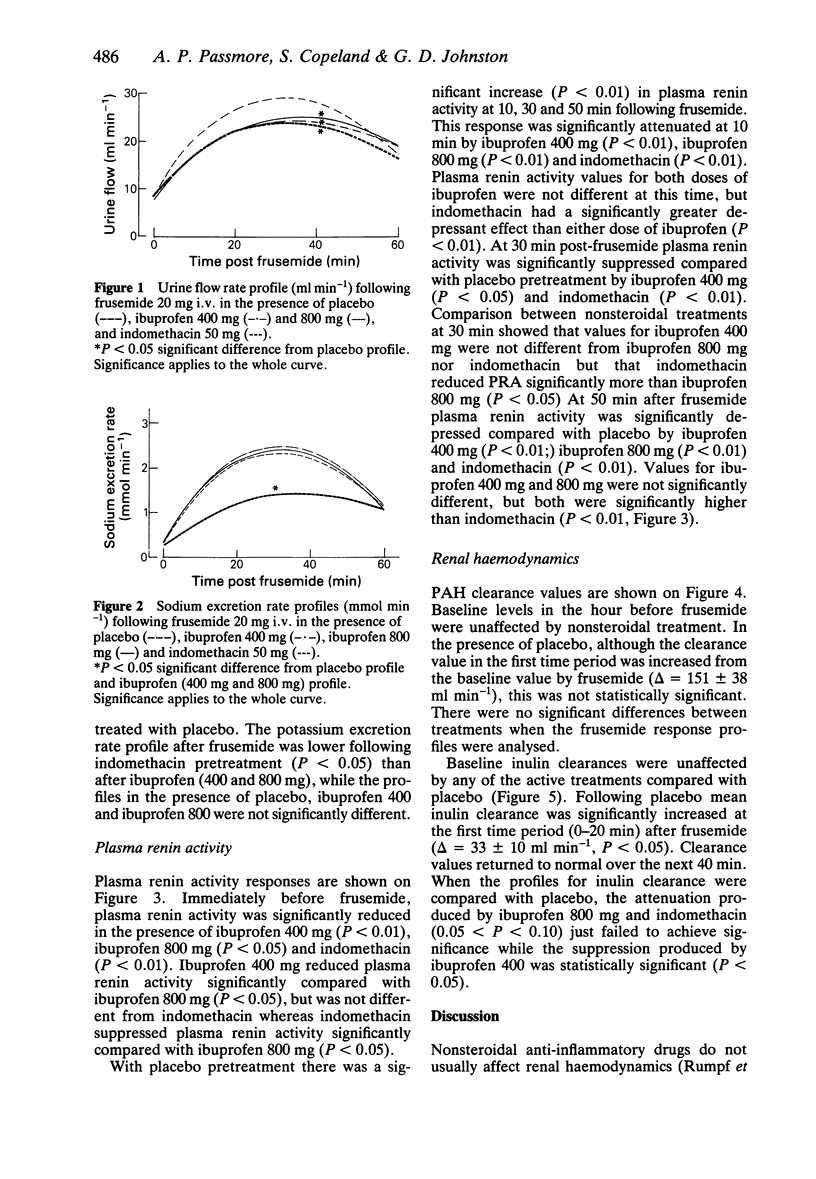
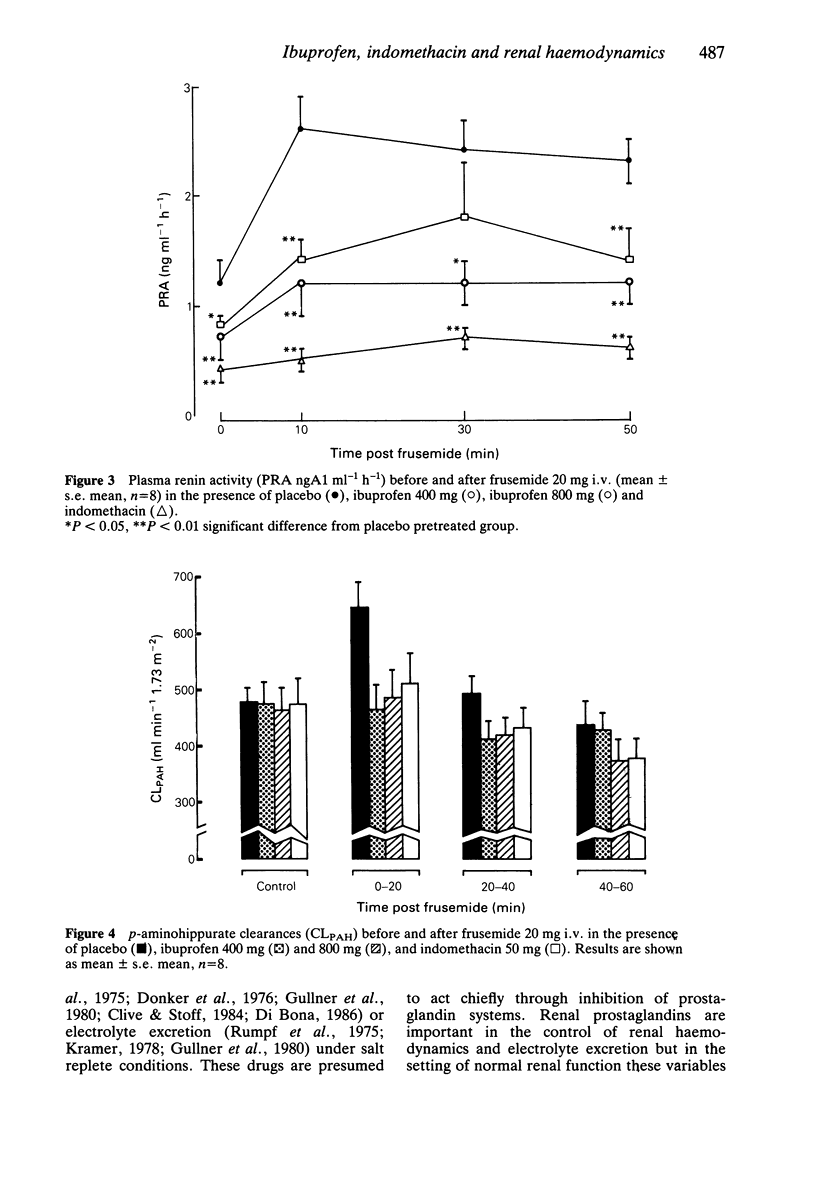
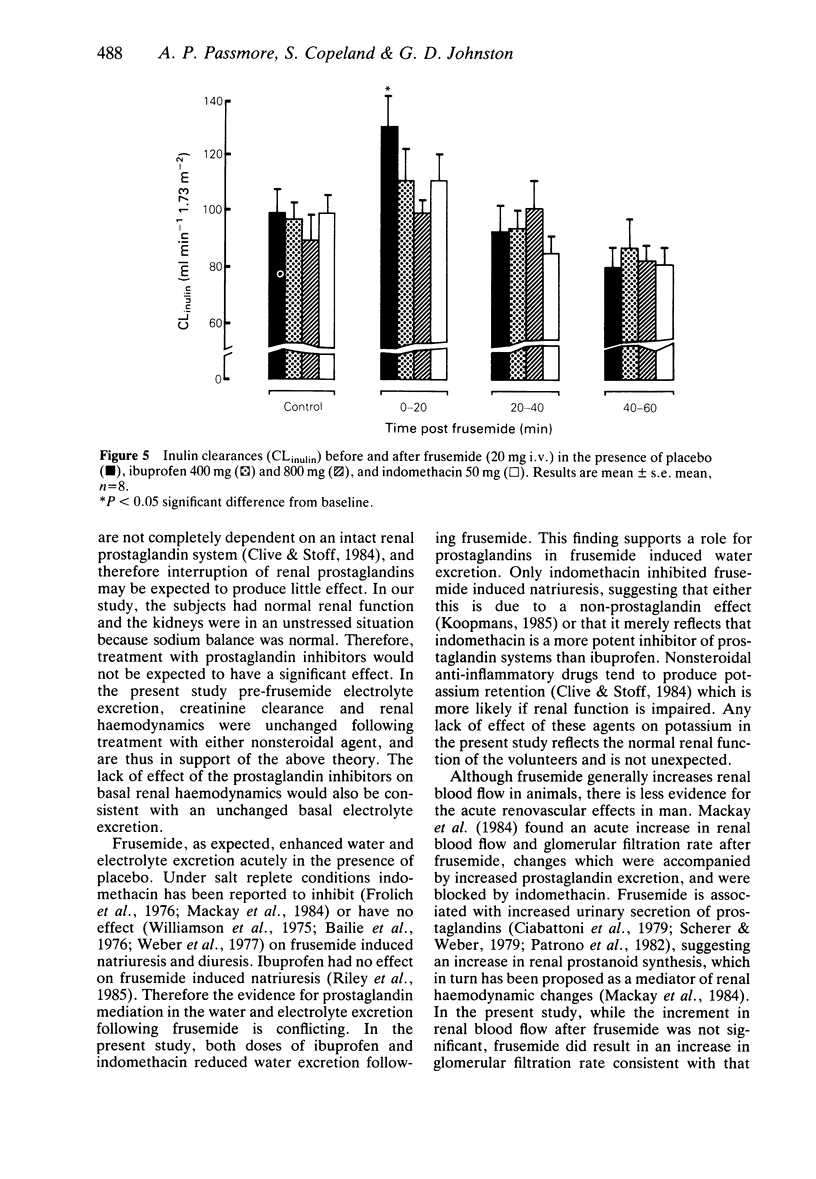
1. This study has compared the effects of ibuprofen and indomethacin upon renal haemodynamics, electrolyte excretion and renin release in the presence and absence of frusemide under sodium replete conditions in eight healthy volunteers. 2. Neither ibuprofen (400 mg and 800 mg) nor indomethacin (50 mg) affected renal blood flow, glomerular filtration rate or electrolyte excretion in the basal state. 3. Frusemide had no effect on renal blood flow, but significantly increased glomerular filtration rate. This latter change was suppressed significantly only by ibuprofen 400 mg. Frusemide-induced diuresis was inhibited by all treatments, while natriuresis following frusemide was inhibited by indomethacin only. 4. Significant increments in plasma renin activity, which were suppressed by all treatments, were observed after frusemide. The degree of inhibition of the renin responses was significantly greater in the presence of indomethacin than with either dose of ibuprofen. 5. In a sodium replete setting in healthy volunteers, indomethacin and ibuprofen had no detrimental effects on basal renal function. In the presence of frusemide, indomethacin had more anti-natriuretic and renin-suppressing effect than ibuprofen. There was no evidence for a dose-related effect of ibuprofen.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailie M. D., Crosslan K., Hook J. B. Natriuretic effect of furosemide after inhibition of prostaglandin synthetase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Nov;199(2):469–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brater D. C. Effect of indomethacin on salt and water homeostasis. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979 Mar;25(3):322–330. doi: 10.1002/cpt1979253322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciabattoni G., Pugliese F., Cinotti G. A., Stirati G., Ronci R., Castrucci G., Pierucci A., Patrono C. Characterization of furosemide-induced activation of the renal prostaglandin system. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Dec 7;60(2-3):181–187. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90217-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clive D. M., Stoff J. S. Renal syndromes associated with nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. N Engl J Med. 1984 Mar 1;310(9):563–572. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198403013100905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donker A. J., Arisz L., Brentjens J. R., van der Hem G. K., Hollemans H. J. The effect of indomethacin on kidney function and plasma renin activity in man. Nephron. 1976;17(4):288–296. doi: 10.1159/000180733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M., Lifschitz M. D., Hoffman D. S., Stein J. H. Relationship between renal prostaglandin E and renal sodium handling during water immersion in normal man. Circ Res. 1979 Jul;45(1):71–80. doi: 10.1161/01.res.45.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frölich J. C., Hollifield J. W., Dormois J. C., Frölich B. L., Seyberth H., Michelakis A. M., Oates J. A. Suppression of plasma renin activity by indomethacin in man. Circ Res. 1976 Sep;39(3):447–452. doi: 10.1161/01.res.39.3.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frölich J. C., Wilson T. W., Sweetman B. J., Smigel M., Nies A. S., Carr K., Watson J. T., Oates J. A. Urinary prostaglandins. Identification and origin. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):763–770. doi: 10.1172/JCI107987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber J. G., Nies A. S., Olsen R. D. Control of canine renin release: macula densa requires prostaglandin synthesis. J Physiol. 1981;319:419–429. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güllner H. G., Gill J. R., Jr, Bartter F. C., Düsing R. The role of the prostaglandin system in the regulation of renal function in normal women. Am J Med. 1980 Nov;69(5):718–724. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90437-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEYROVSKY A. A new method for the determination of inulin in plasma and urine. Clin Chim Acta. 1956 Sep-Oct;1(5):470–474. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(56)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber E., Koerner T., Page L. B., Kliman B., Purnode A. Application of a radioimmunoassay for angiotensin I to the physiologic measurements of plasma renin activity in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Oct;29(10):1349–1355. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-10-1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston G. D., Nicholls D. P., Kondowe G. B., Finch M. B. Comparison of the acute vascular effects of frusemide and bumetanide. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;21(4):359–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb05207.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston G. D., O'Connor P. C., Nicholls D. P., Leahey W. J., Finch M. B. The effects of propranolol and digoxin on the acute vascular responses to frusemide in normal man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1985 Apr;19(4):417–421. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1985.tb02664.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopmans P. P. Pathophysiological and clinical aspects of the interaction between non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) and diuretics. Neth J Med. 1985;28(11):524–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer H. J., Bäcker A., Hinzen S., Düsing R. Effects of inhibition of prostaglandin-synthesis on renal electrolyte excretion and concentrating ability in healthy man. Prostaglandins Med. 1978 Nov;1(5):341–349. doi: 10.1016/0161-4630(78)90121-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer H. J., Stinnesbeck B., Klautke G., Kipnowski J., Klingmueller D., Glaenzer K., Duesing R. Interaction of renal prostaglandins with the renin-angiotensin and renal adrenergic nervous systems in healthy subjects during dietary changes in sodium intake. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Apr;68(4):387–393. doi: 10.1042/cs0680387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay I. G., Muir A. L., Watson M. L. Contribution of prostaglandins to the systemic and renal vascular response to frusemide in normal man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1984 May;17(5):513–519. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1984.tb02383.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patak R. V., Mookerjee B. K., Bentzel C. J., Hysert P. E., Babej M., Lee J. B. Antagonism of the effects of furosemide by indomethacin in normal and hypertensive man. Prostaglandins. 1975 Oct;10(4):649–659. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(75)80012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrono C., Pugliese F., Ciabattoni G., Patrignani P., Maseri A., Chierchia S., Peskar B. A., Cinotti G. A., Simonetti B. M., Pierucci A. Evidence for a direct stimulatory effect of prostacyclin on renin release in man. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jan;69(1):231–239. doi: 10.1172/JCI110435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. J., Jr, Vlasses P. H., Rotmensch H. H., Swanson B. N., Chremos A. N., Johnson C. L., Ferguson R. K. Sulindac and ibuprofen inhibit furosemide-stimulated renin release but not natriuresis in men on a normal sodium diet. Nephron. 1985;41(3):283–288. doi: 10.1159/000183598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumpf K. W., Frenzel S., Lowitz H. D., Scheler F. The effect of indomethacin on plasma renin activity in man under normal conditions and after stimulation of the renin angiotensin system. Prostaglandins. 1975 Oct;10(4):641–648. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(75)80011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer B., Weber P. C. Time-dependent changes in prostaglandin excretion in response to frusemide in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 1979 Jan;56(1):77–81. doi: 10.1042/cs0560077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Finkelstein N., Aliminosa L., Crawford B., Graber M. THE RENAL CLEARANCES OF SUBSTITUTED HIPPURIC ACID DERIVATIVES AND OTHER AROMATIC ACIDS IN DOG AND MAN. J Clin Invest. 1945 May;24(3):388–404. doi: 10.1172/JCI101618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P. C., Larsson C., Scherer B. Prostaglandin E2-9-ketoreductase as a mediator of salt intake-related prostaglandin-renin interaction. Nature. 1977 Mar 3;266(5597):64–66. doi: 10.1038/266065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson H. E., Bourland W. A., Marchand G. R., Farley D. B., Van Orden D. E. Furosemide induced release of prostaglandin E to increase renal blood flow. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Oct;150(1):104–106. doi: 10.3181/00379727-150-38982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


