Abstract
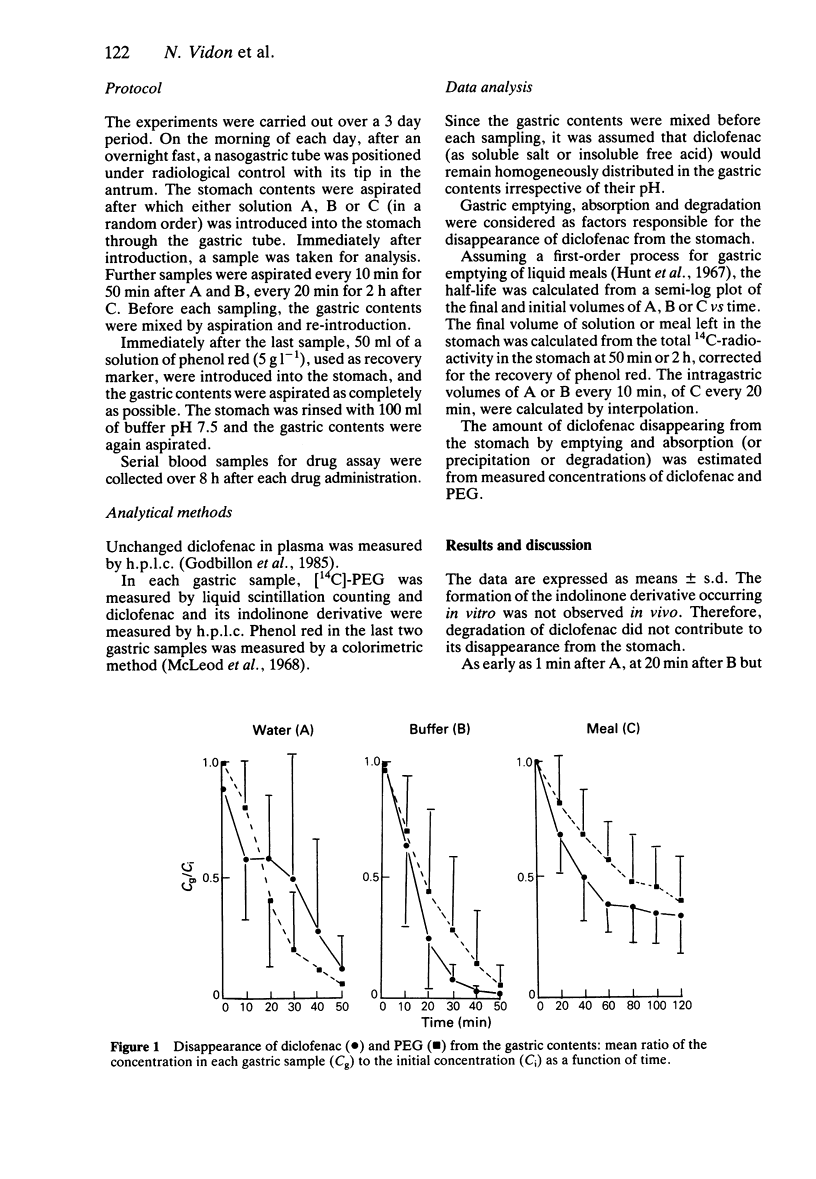
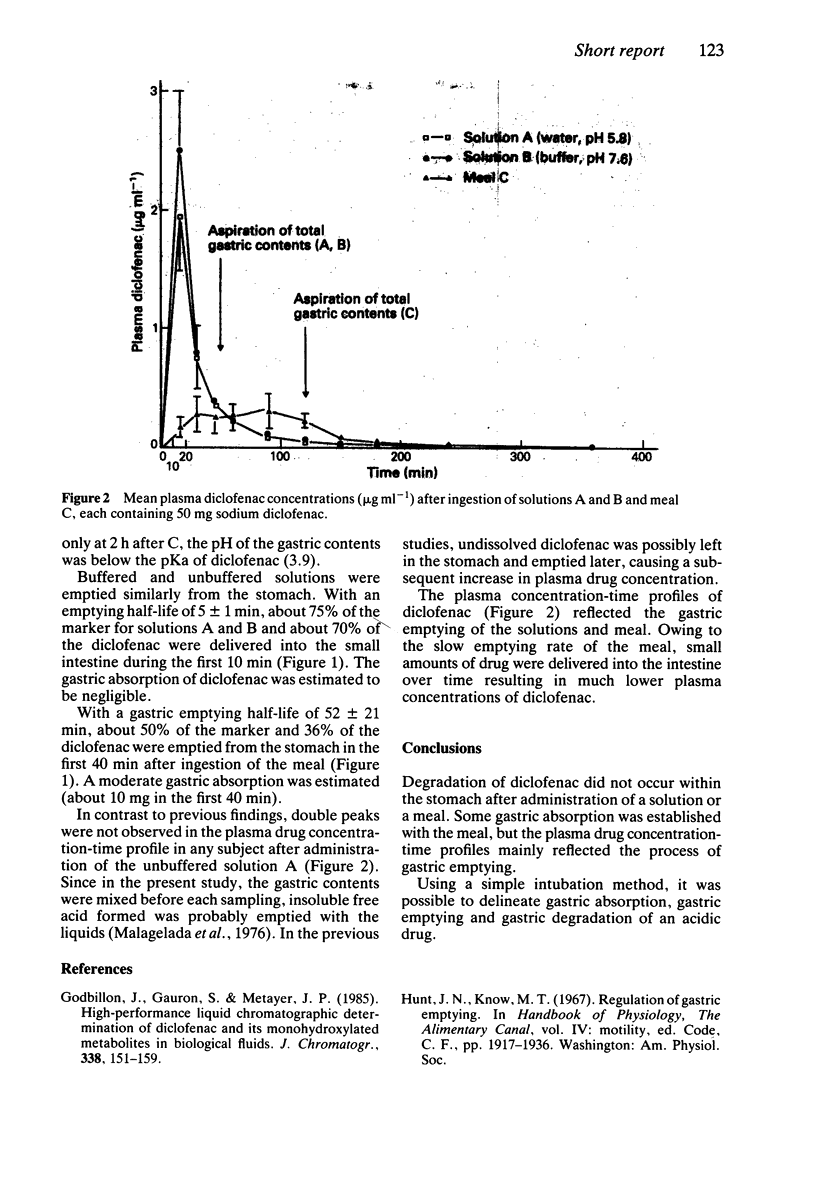
Sodium diclofenac (50 mg) together with [14 C]-PEG as a non-absorbable marker were dissolved in 400 ml of water (A), phosphate buffer pH 7.5 (B) or a homogenized meal (C). Each of these was ingested in random order by six volunteers on 3 consecutive days. Some gastric absorption of the drug was established with C but the plasma drug concentration-time profiles mainly reflected the process of gastric emptying.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Godbillon J., Gauron S., Metayer J. P. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of diclofenac and its monohydroxylated metabolites in biological fluids. J Chromatogr. 1985 Feb 27;338(1):151–159. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(85)80079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malagelada J. R., Longstreth G. F., Summerskill W. H., Go V. L. Measurement of gastric functions during digestion of ordinary solid meals in man. Gastroenterology. 1976 Feb;70(2):203–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod G. M., French A. B., Good C. J., Wright F. S. Gastrointestinal absorption and biliary excretion of phenolsulfonphthalein (phenol red) in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Feb;71(2):192–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


