Abstract
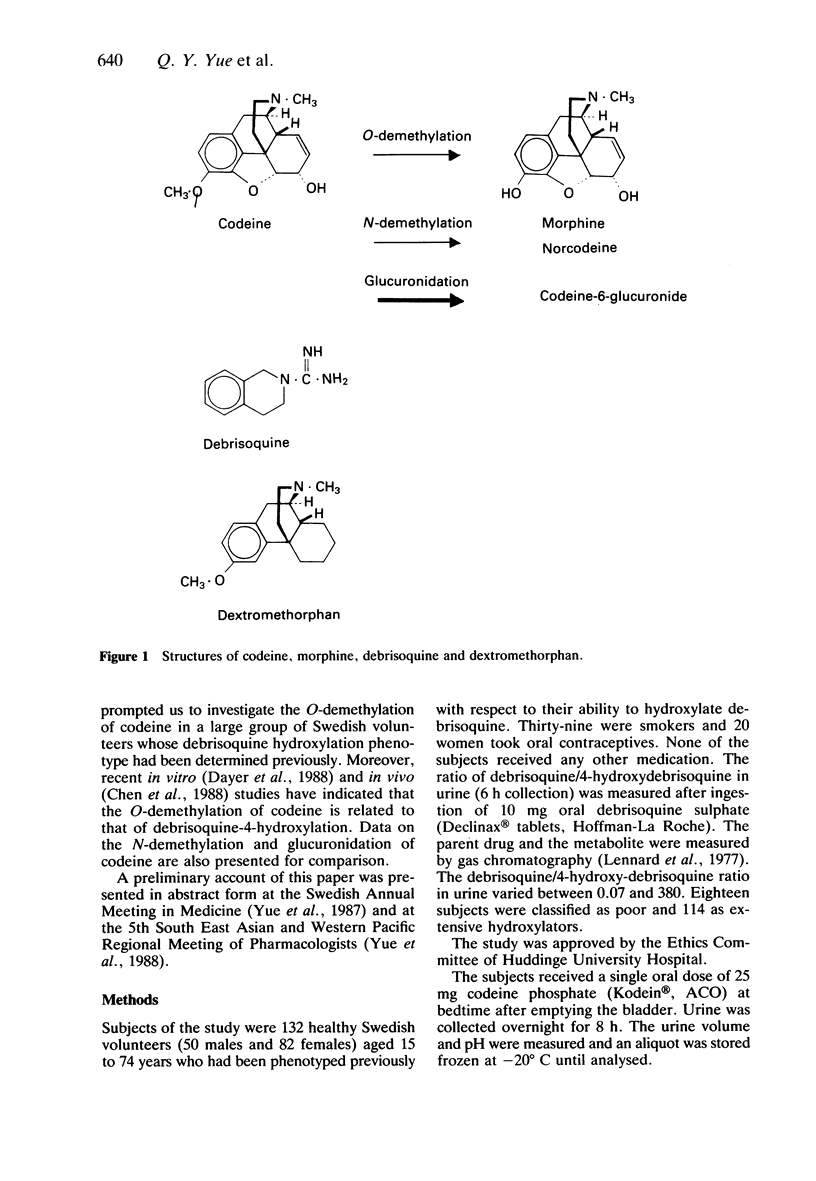
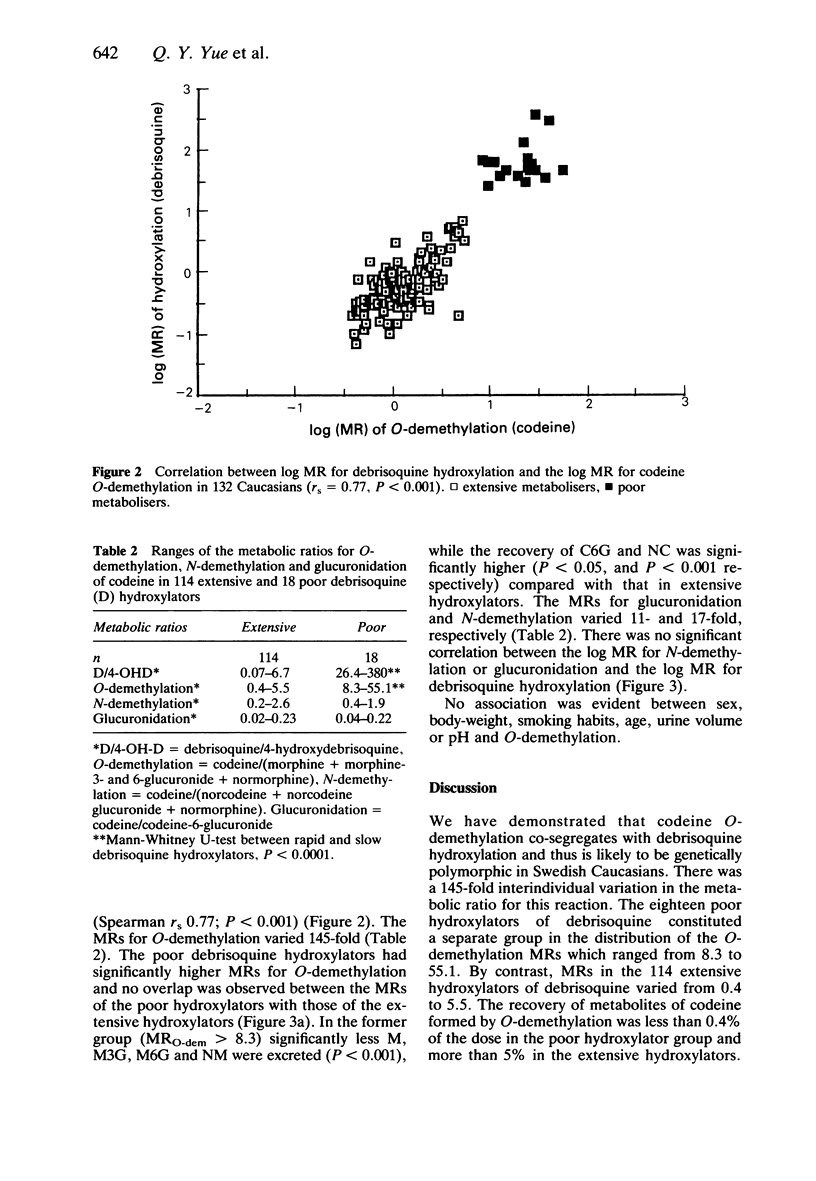
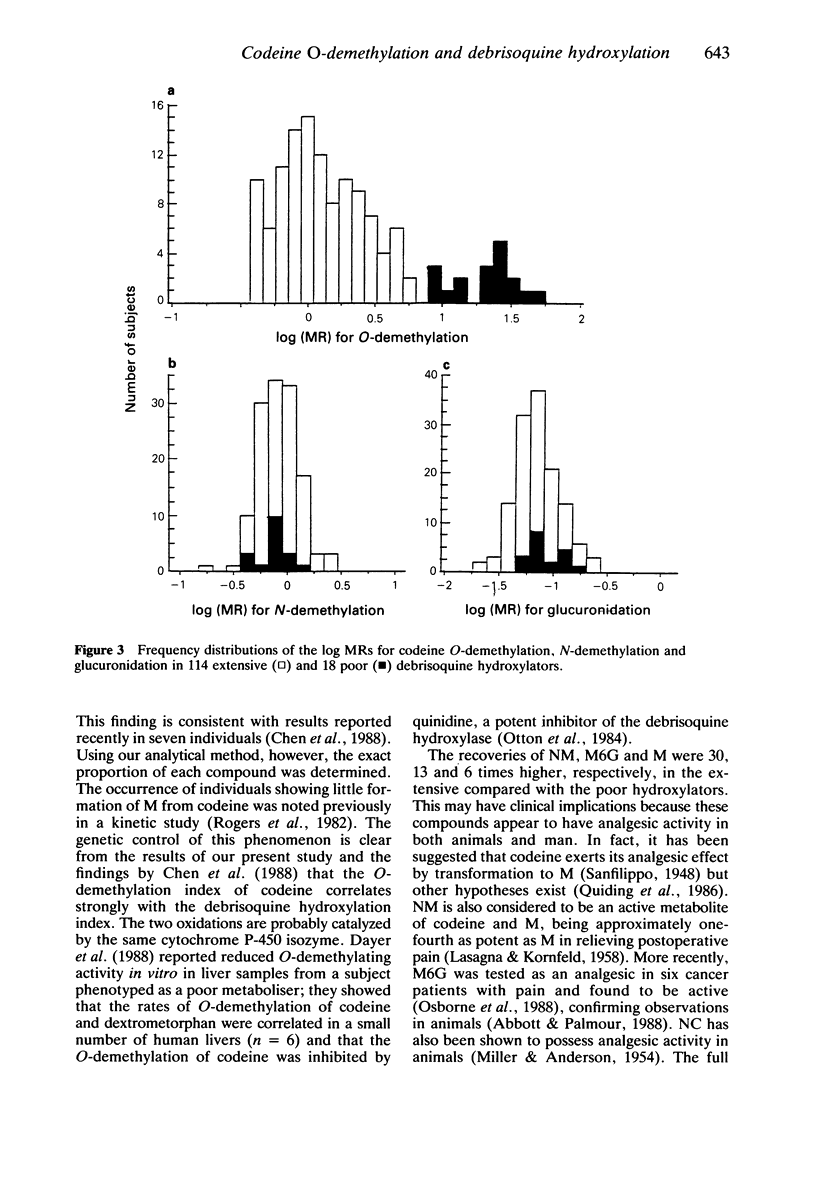
1. A single oral dose of codeine (25 mg) was given to 132 healthy Swedish Caucasians who had previously been phenotyped with respect to debrisoquine hydroxylation. The 'metabolic ratios' (MR) in urine of codeine O-demethylation (codeine/(morphine (M) + morphine-3- and 6-glucuronides (M3G and M6G) + normorphine], N-demethylation (codeine/(norcodeine (NC) + norcodeine glucuronide + normorphine (NM]) and glucuronidation (codeine/codeine-6-glucuronide (C6G] were calculated following h.p.l.c. analysis of urine samples collected over 8 h. 2. There was a significant correlation between the log MR for debrisoquine hydroxylation and the log MR for codeine O-demethylation (rs = 0.77, P less than 0.001). The poor debrisoquine hydroxylators had MRs of codeine O-demethylation between 8.3 and 55.1, while the values for extensive hydroxylators were between 0.4 and 5.5. 3. The poor debrisoquine hydroxylators excreted significantly less M, M3G, M6G and NM, while the urinary recovery of C6G and NC was significantly higher in these subjects compared to the extensive hydroxylators. 4. The MRs for glucuronidation and N-demethylation did not exhibit a bimodal distribution, and were not related to the MR of debrisoquine hydroxylation. 5. No associations were found between sex, body-weight, smoking habits, age, urine volume or urine pH and the O-demethylation of codeine. 6. The O-demethylation of codeine to form M appears to be under the same polymorphic genetic control as the 4-hydroxylation of debrisoquine.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADLER T. K., FUJIMOTO J. M., WAY E. L., BAKER E. M. The metabolic fate of codeine in man. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1955 Jul;114(3):251–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abbott F. V., Palmour R. M. Morphine-6-glucuronide: analgesic effects and receptor binding profile in rats. Life Sci. 1988;43(21):1685–1695. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90479-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boobis A. R., Davies D. S. Human cytochromes P-450. Xenobiotica. 1984 Jan-Feb;14(1-2):151–185. doi: 10.3109/00498258409151404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. R., Somogyi A. A., Bochner F. Polymorphic O-demethylation of codeine. Lancet. 1988 Oct 15;2(8616):914–915. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92529-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer P., Desmeules J., Leemann T., Striberni R. Bioactivation of the narcotic drug codeine in human liver is mediated by the polymorphic monooxygenase catalyzing debrisoquine 4-hydroxylation (cytochrome P-450 dbl/bufI). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 15;152(1):411–416. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80729-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichelbaum M., Bertilsson L., Säwe J., Zekorn C. Polymorphic oxidation of sparteine and debrisoquine: related pharmacogenetic entities. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1982 Feb;31(2):184–186. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1982.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichelbaum M., Spannbrucker N., Steincke B., Dengler H. J. Defective N-oxidation of sparteine in man: a new pharmacogenetic defect. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Sep;16(3):183–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00562059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. A., Mahgoub A., Sloan T. P., Idle J. R., Smith R. L. A family and population study of the genetic polymorphism of debrisoquine oxidation in a white British population. J Med Genet. 1980 Apr;17(2):102–105. doi: 10.1136/jmg.17.2.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Skoda R. C., Kimura S., Umeno M., Zanger U. M., Nebert D. W., Gelboin H. V., Hardwick J. P., Meyer U. A. Characterization of the common genetic defect in humans deficient in debrisoquine metabolism. Nature. 1988 Feb 4;331(6155):442–446. doi: 10.1038/331442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson W. B. Tolerance and side effects during long term treatment of hypertension with debrisoquine. Aust N Z J Med. 1972 Nov;2(4):357–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1972.tb03937.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küpfer A., Preisig R. Pharmacogenetics of mephenytoin: a new drug hydroxylation polymorphism in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1984;26(6):753–759. doi: 10.1007/BF00541938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASAGNA L., DE KORNFELD T. J. Analgesic potency of normorphine in patients with postoperative pain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1958 Nov;124(3):260–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennard M. S., Silas J. H., Smith A. J., Tucker G. T. Determination of debrisoquine and its 4-hydroxy metabolite in biological fluids by gas chromatography with flame-ionization and nitrogen-selective detection. J Chromatogr. 1977 Mar 11;133(1):161–166. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)89216-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER J. W., ANDERSON H. H. The effect of N-demethylation on certain pharmacologic actions of morphine, codeine, and meperidine in the mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1954 Oct;112(2):191–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahgoub A., Idle J. R., Dring L. G., Lancaster R., Smith R. L. Polymorphic hydroxylation of Debrisoquine in man. Lancet. 1977 Sep 17;2(8038):584–586. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91430-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne R., Joel S., Trew D., Slevin M. Analgesic activity of morphine-6-glucuronide. Lancet. 1988 Apr 9;1(8589):828–828. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91691-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiding H., Anderson P., Bondesson U., Boréus L. O., Hynning P. A. Plasma concentrations of codeine and its metabolite, morphine, after single and repeated oral administration. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1986;30(6):673–677. doi: 10.1007/BF00608214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. F., Findlay J. W., Hull J. H., Butz R. F., Jones E. C., Bustrack J. A., Welch R. M. Codeine disposition in smokers and nonsmokers. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1982 Aug;32(2):218–227. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1982.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid B., Bircher J., Preisig R., Küpfer A. Polymorphic dextromethorphan metabolism: co-segregation of oxidative O-demethylation with debrisoquin hydroxylation. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1985 Dec;38(6):618–624. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1985.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner E., Iselius L., Alván G., Lindsten J., Sjöqvist F. A family study of genetic and environmental factors determining polymorphic hydroxylation of debrisoquin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1985 Oct;38(4):394–401. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1985.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson J. O., Rane A., Säwe J., Sjöqvist F. Determination of morphine, morphine-3-glucuronide and (tentatively) morphine-6-glucuronide in plasma and urine using ion-pair high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1982 Jul 9;230(2):427–432. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)80494-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedlund P. J., Aslanian W. S., McAllister C. B., Wilkinson G. R., Branch R. A. Mephenytoin hydroxylation deficiency in Caucasians: frequency of a new oxidative drug metabolism polymorphism. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1984 Dec;36(6):773–780. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1984.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue Q. Y., Svensson J. O., Alm C., Sjöqvist F., Säwe J. Interindividual and interethnic differences in the demethylation and glucuronidation of codeine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;28(6):629–637. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb03555.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


