Abstract
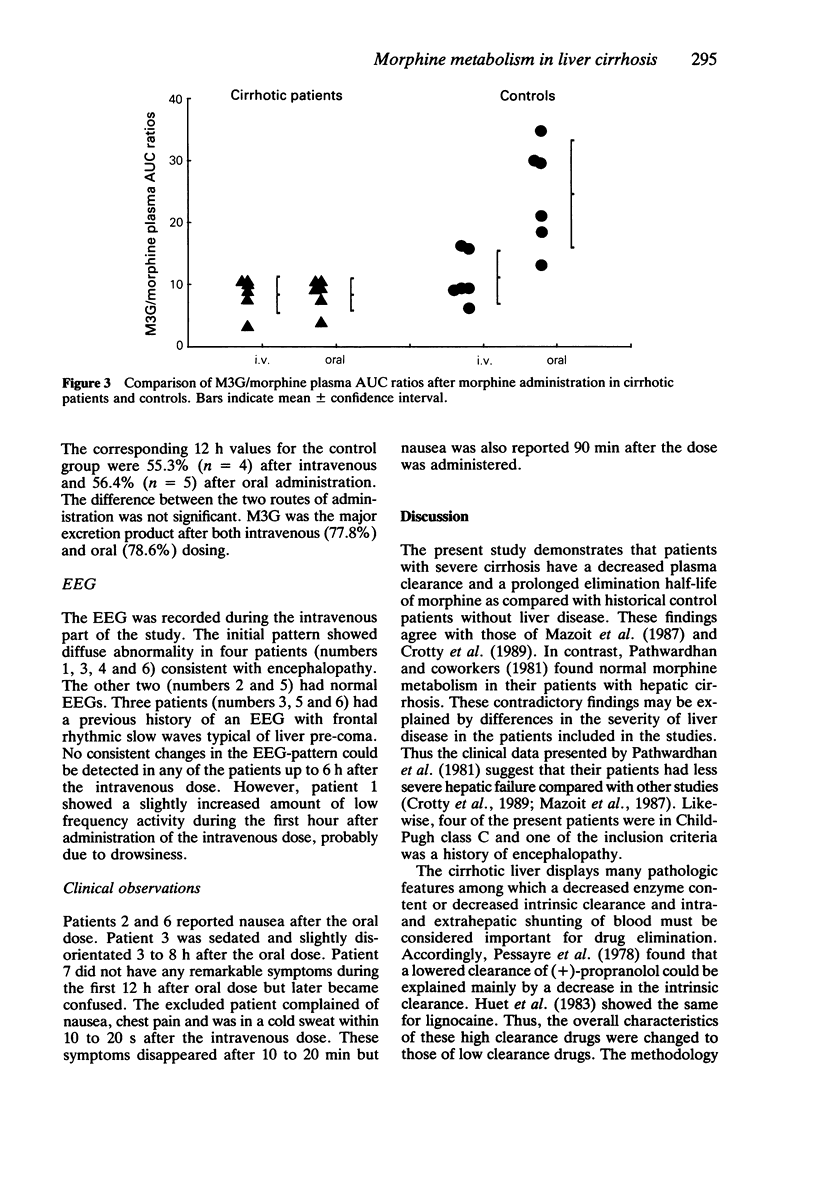
1. The oral and intravenous kinetics of morphine were investigated in seven cirrhotic patients with a history of encephalopathy. The plasma concentrations of morphine and its metabolites morphine-3 (M3G) and morphine-6 (M6G) were measured by h.p.l.c. 2. The mean terminal elimination half-life of morphine was 4.2 h (95% CI 3.6-4.8) the mean volume of distribution was 4.1 l kg-1 (95% CI 2.9-5.4) and the mean plasma clearance was 11.4 ml min-1 kg-1 (95% CI 8.1-14.7). The mean oral bioavailability was 101% (95% CI 56-147). 3. The plasma clearance of morphine was significantly lower, its terminal elimination half-life longer and its oral bioavailability greater in the cirrhotic patients compared with patients with normal liver function. The metabolic ratio M3G/morphine was significantly lower in the cirrhotic patients than in control subjects after oral dosing, but did not differ after intravenous dosing. 4. The average urinary recoveries of morphine plus M3G and M6G were 49.9% after i.v. and 57.7% after oral administration. There were no statistically significant differences in the urinary recovery between the two routes of administration or between the cirrhotic patients and controls. 5. Specific changes in the EEG pattern could not be detected after intravenous dosage. 6. The metabolism of morphine is impaired significantly in patients with severe cirrhosis. Clinically important findings were a high oral bioavailability and a long elimination half-life. These findings call for cautious dosing of oral and intravenous morphine in patients with severe end stage liver disease.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chu H., Klemp A., Stille G. Effects of furosemide and spironolactone on the behavior of morphine-tolerant rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1978 Dec 8;59(3):309–310. doi: 10.1007/BF00426640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn H. O. Trailmaking and number-connection tests in the assessment of mental state in portal systemic encephalopathy. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Jun;22(6):541–550. doi: 10.1007/BF01072510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crotty B., Watson K. J., Desmond P. V., Mashford M. L., Wood L. J., Colman J., Dudley F. J. Hepatic extraction of morphine is impaired in cirrhosis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;36(5):501–506. doi: 10.1007/BF00558076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser C. L., Arieff A. I. Hepatic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 1985 Oct 3;313(14):865–873. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198510033131406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet P. M., Villeneuve J. P. Determinants of drug disposition in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1983 Nov-Dec;3(6):913–918. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAIDLAW J., READ A. E., SHERLOCK S. Morphine tolerance in hepatic cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1961 Mar;40:389–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrec D., Bataille C., Bercoff E., Valla D. Hemodynamic changes in patients with portal venous obstruction. Hepatology. 1983 Jul-Aug;3(4):550–553. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIRSKY A. F., KORNETSKY C. ON THE DISSIMILAR EFFECTS OF DRUGS ON THE DIGIT SYMBOL SUBSTITUTION AND CONTINOUS PERFORMANCE TESTS. A REVIEW AND PRELIMINARY INTEGRATION OF BEHAVIORAL AND PHYSIOLOGICAL EVIDENCE. Psychopharmacologia. 1964 Feb 12;5:161–177. doi: 10.1007/BF00413239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazoit J. X., Sandouk P., Zetlaoui P., Scherrmann J. M. Pharmacokinetics of unchanged morphine in normal and cirrhotic subjects. Anesth Analg. 1987 Apr;66(4):293–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal E. A., Meffin P. J., Gregory P. B., Blaschke T. F. Enhanced bioavailability and decreased clearance of analgesics in patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1979 Jul;77(1):96–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi K., Sato S., Pugliese D., Tsunoda T., Saito M., Okuda K. Changes of splanchnic circulation with progression of chronic liver disease studied by echo-Doppler flowmetry. Am J Gastroenterol. 1987 Jun;82(6):507–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. D. Morphine binding to human plasma proteins. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Jan;17(1):31–35. doi: 10.1002/cpt197517131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacifici G. M., Bencini C., Rane A. Presystemic glucuronidation of morphine in humans and rhesus monkeys: subcellular distribution of the UDP-glucuronyltransferase in the liver and intestine. Xenobiotica. 1986 Feb;16(2):123–128. doi: 10.3109/00498258609043514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patwardhan R. V., Johnson R. F., Hoyumpa A., Jr, Sheehan J. J., Desmond P. V., Wilkinson G. R., Branch R. A., Schenker S. Normal metabolism of morphine in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1981 Dec;81(6):1006–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentikainen P. J., Neuvonen P. J., Tarpila S., Syvälahti E. Effect of cirrhosis of the liver on the pharmacokinetics of chlormethiazole. Br Med J. 1978 Sep 23;2(6141):861–863. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6141.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessayre D., Lebrec D., Descatoire V., Peignoux M., Benhamou J. P. Mechanism for reduced drug clearance in patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1978 Mar;74(3):566–571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh R. N., Murray-Lyon I. M., Dawson J. L., Pietroni M. C., Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973 Aug;60(8):646–649. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800600817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S., Ohnishi K., Sugita S., Okuda K. Splenic artery and superior mesenteric artery blood flow: nonsurgical Doppler US measurement in healthy subjects and patients with chronic liver disease. Radiology. 1987 Aug;164(2):347–352. doi: 10.1148/radiology.164.2.2955448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selye H., Mécs I., Savoie L. Inhibition of anesthetics and sedative actions by spironolactone. Anesthesiology. 1969 Sep;31(3):261–264. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196909000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotaniemi E. A., Niemelä O., Risteli L., Stenbäck F., Pelkonen R. O., Lahtela J. T., Risteli J. Fibrotic process and drug metabolism in alcoholic liver disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1986 Jul;40(1):46–55. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1986.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson J. O., Rane A., Säwe J., Sjöqvist F. Determination of morphine, morphine-3-glucuronide and (tentatively) morphine-6-glucuronide in plasma and urine using ion-pair high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1982 Jul 9;230(2):427–432. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)80494-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Säwe J., Dahlström B., Paalzow L., Rane A. Morphine kinetics in cancer patients. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Nov;30(5):629–635. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Säwe J., Kager L., Svensson Eng J. O., Rane A. Oral morphine in cancer patients: in vivo kinetics and in vitro hepatic glucuronidation. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1985 Apr;19(4):495–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1985.tb02675.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson G. R., Shand D. G. Commentary: a physiological approach to hepatic drug clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Oct;18(4):377–390. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975184377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue Q. Y., Odar-Cederlöf I., Svensson J. O., Säwe J. Glucuronidation of morphine in human kidney microsomes. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1988 Nov;63(5):337–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1988.tb00965.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



