Abstract
OBJECTIVES: An investigation was conducted to determine whether ongoing transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis was occurring in a California state prison. METHOD: Prison pharmacy records were used to identify cases of active tuberculosis (TB). RESULTS: Ten of the 18 cases of active TB treated at the facility during 1991 were diagnosed at the prison that same year (an incidence of 184 per 100,000). Three inmates were infectious for a total of 7 months while imprisoned. The prevalence of TB skin test-positivity among inmates was 30%, and the incidence of new infection attributable to incarceration was 5.9 per 100 inmates per year. CONCLUSIONS: Transmission of M. tuberculosis may be occurring in the California prison system.
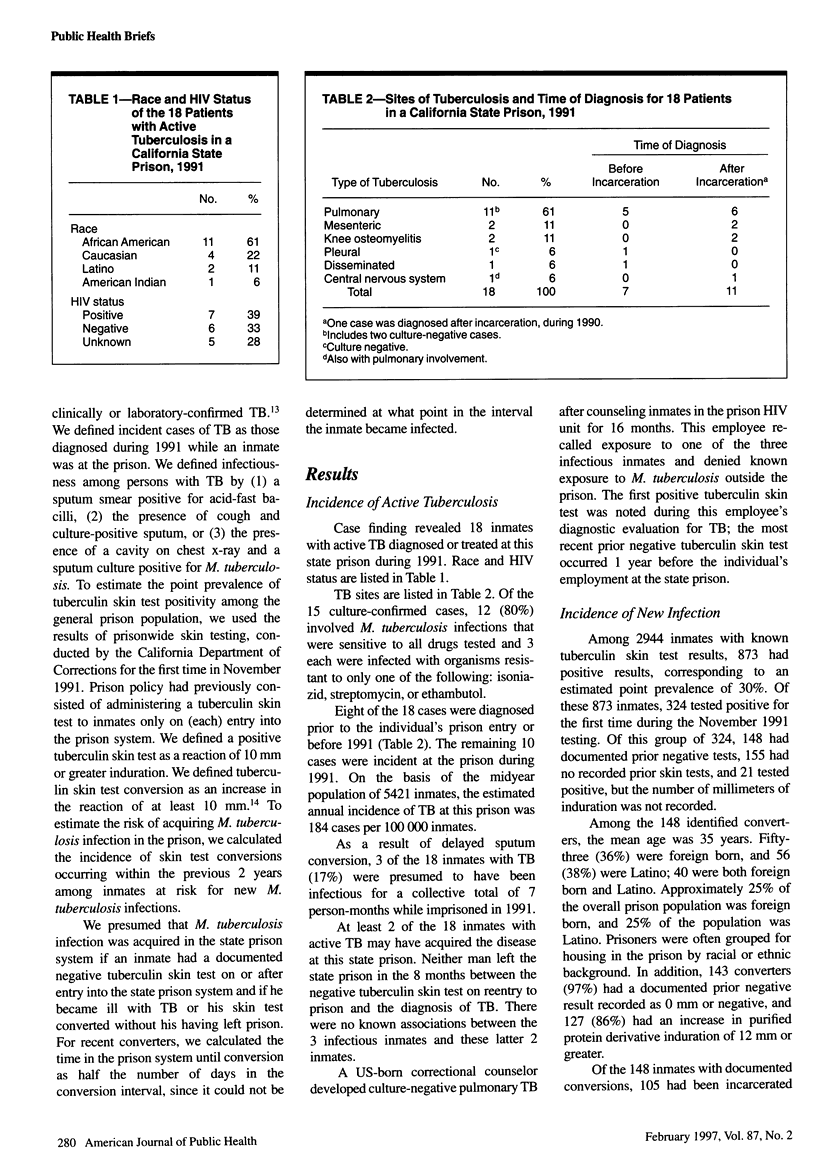
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeles H., Feibes H., Mandel E., Girard J. A. The large city prison--a reservoir of tuberculosis. Tuberculosis control among sentenced male prisoners in New York City. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1970 May;101(5):706–709. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1970.101.5.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellin E. Y., Fletcher D. D., Safyer S. M. Association of tuberculosis infection with increased time in or admission to the New York City jail system. JAMA. 1993 May 5;269(17):2228–2231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun M. M., Truman B. I., Maguire B., DiFerdinando G. T., Jr, Wormser G., Broaddus R., Morse D. L. Increasing incidence of tuberculosis in a prison inmate population. Association with HIV infection. JAMA. 1989 Jan 20;261(3):393–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comstock G. W., Woolpert S. F. Tuberculin conversions: true or false? Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Aug;118(2):215–217. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser J. B., Aboujaoude J. K., Greifinger R. Tuberculin skin test conversion among HIV-infected prison inmates. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1992;5(4):430–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton M. D., Cauthen G. M., Bloch A. B. Results of a 29-state survey of tuberculosis in nursing homes and correctional facilities. Public Health Rep. 1993 May-Jun;108(3):305–314. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King L., Geis G. Tuberculosis transmission in a large urban jail. JAMA. 1977 Feb 21;237(8):791–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laroche R. R., Campbell R. C. Intracorneal hemorrhage induced by chronic extended wear of a soft contact lens. CLAO J. 1987 Jan-Feb;13(1):39–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse D. L., Truman B. I., Hanrahan J. P., Mikl J., Broaddus R. K., Maguire B. H., Grabau J. C., Kain-Hyde S., Han Y., Lawrence C. E. AIDS behind bars. Epidemiology of New York State prison inmate cases, 1980-1988. N Y State J Med. 1990 Mar;90(3):133–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narain R., Nair S. S., Rao G. R., Chandrasekhar P., Lal P. Enhancing of tuberculin allergy by previous tuberculin testing. Bull World Health Organ. 1966;34(4):623–638. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson M. L., Jereb J. A., Frieden T. R., Crawford J. T., Davis B. J., Dooley S. W., Jarvis W. R. Nosocomial transmission of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A risk to patients and health care workers. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Aug 1;117(3):191–196. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-3-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj Narain Tuberculin conversions: true or false? Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Jun;119(6):1039–1040. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.6.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn P. A., Hartel D., Lewis V. A., Schoenbaum E. E., Vermund S. H., Klein R. S., Walker A. T., Friedland G. H. A prospective study of the risk of tuberculosis among intravenous drug users with human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1989 Mar 2;320(9):545–550. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198903023200901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton J. A., Perkins C. I., Trachtenberg A. I., Hughes M. J., Kizer K. W., Ascher M. HIV antibody seroprevalence among prisoners entering the California correctional system. West J Med. 1990 Oct;153(4):394–399. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider D. E., Jr, Hutton M. D. Tuberculosis in correctional institutions. JAMA. 1989 Jan 20;261(3):436–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer S. S., Morton A. R. Tuberculosis surveillance in a state prison system. Am J Public Health. 1989 Apr;79(4):507–509. doi: 10.2105/ajph.79.4.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead W. W., To T. The significance of the tuberculin skin test in elderly persons. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Dec;107(6):837–842. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-6-837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead W. W. Undetected tuberculosis in prison. Source of infection for community at large. JAMA. 1978 Dec 1;240(23):2544–2547. doi: 10.1001/jama.240.23.2544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. J., Glassroth J. L., Snider D. E., Jr, Farer L. S. The booster phenomenon in serial tuberculin testing. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Apr;119(4):587–597. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.4.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


