Abstract
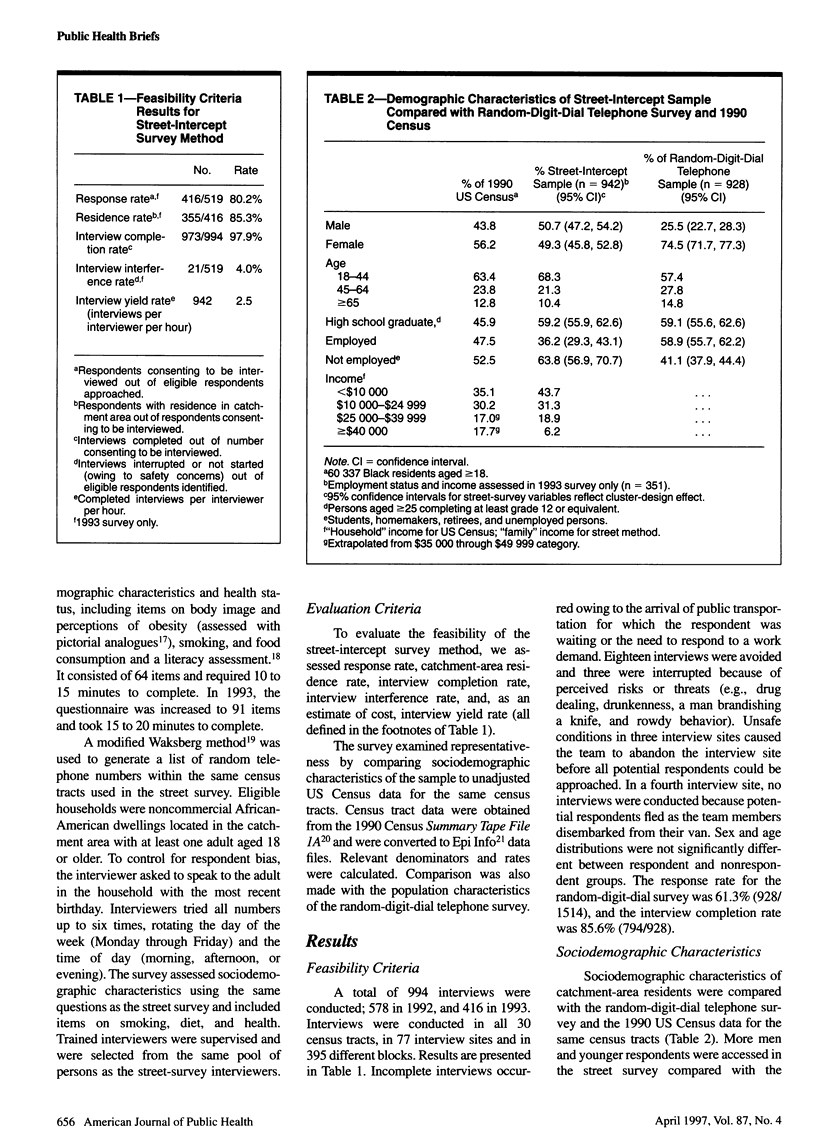
OBJECTIVES: This study evaluates the feasibility of a nonquota, street-intercept survey method that utilized random selection of interview sites. METHODS: The street-intercept survey was compared with a random digit-dial telephone survey conducted in the same catchment area among African-American adults aged 18 or older. RESULTS: The street-intercept survey's response rate was 80.2%; residence rate, 85.3%; interview completion rate, 97.9%; interference rate, 4.0%; and yield rate, 2.5 interviews per interviewer per hour. The street-intercept method produced more representative distributions of age and sex than the random-digit-dial survey. CONCLUSIONS: The street-intercept method is a feasible alternative to traditional population survey methods and may provide better access to harder-to-reach segments of the urban population in a safe manner.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aquilino W. S. Telephone versus face-to-face interviewing for household drug use surveys. Int J Addict. 1992 Jan;27(1):71–91. doi: 10.3109/10826089109063463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brambilla D. J., McKinlay S. M. A comparison of responses to mailed questionnaires and telephone interviews in a mixed mode health survey. Am J Epidemiol. 1987 Nov;126(5):962–971. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman H. E., Kiecolt K. J., Nicholls W. L., 2nd, Shanks J. M. Telephone sampling bias in surveying disability. Public Opin Q. 1982 Fall;46(3):392–407. doi: 10.1086/268736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins W., Frank B. Street studies that work and what they show in New York City. J Addict Dis. 1991;11(1):89–97. doi: 10.1300/j069v11n01_08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. C., Crane L. A. Telephone surveys in public health research. Med Care. 1986 Feb;24(2):97–112. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198602000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mays V. M., Jackson J. S. AIDS survey methodology with black Americans. Soc Sci Med. 1991;33(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(91)90449-m. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebot M., Celentano D. D., Burwell L., Davis A., Davis M., Polacsek M., Santelli J. AIDS and behavioural risk factors in women in inner city Baltimore: a comparison of telephone and face to face surveys. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1994 Aug;48(4):412–418. doi: 10.1136/jech.48.4.412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole B. I., Battistutta D., Long A., Crouch K. A comparison of costs and data quality of three health survey methods: mail, telephone and personal home interview. Am J Epidemiol. 1986 Aug;124(2):317–328. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orleans C. T., Schoenbach V. J., Salmon M. A., Strecher V. J., Kalsbeek W., Quade D., Brooks E. F., Konrad T. R., Blackmon C., Watts C. D. A survey of smoking and quitting patterns among black Americans. Am J Public Health. 1989 Feb;79(2):176–181. doi: 10.2105/ajph.79.2.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice D. P., Drury T. F., Mugge R. H. Household health interviews and minority health: the NCHS perspective. Med Care. 1980 Mar;18(3):327–335. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198003000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooner C., Flaherty B. Comparison of three data collection methodologies for the study of young illicit drug users. Aust J Public Health. 1993 Sep;17(3):195–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudman S., Sirken M. G., Cowan C. D. Sampling rare and elusive populations. Science. 1988 May 20;240(4855):991–996. doi: 10.1126/science.240.4855.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


