Abstract
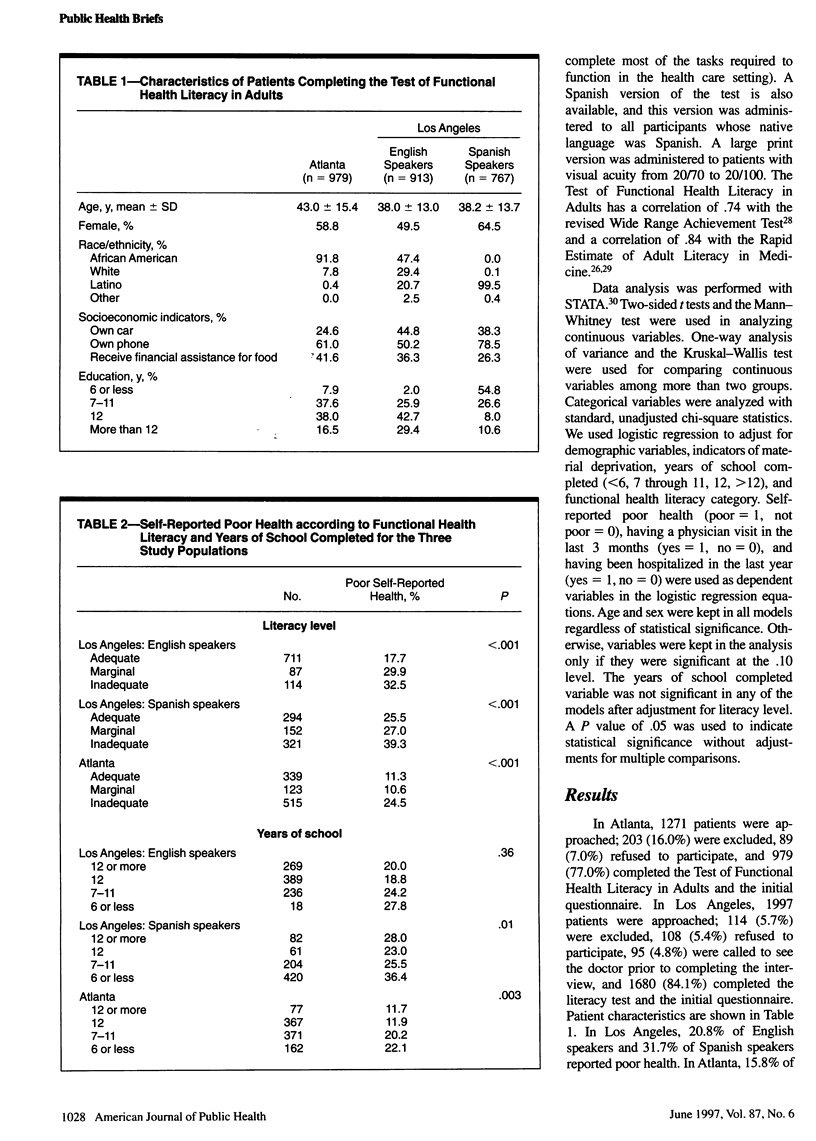
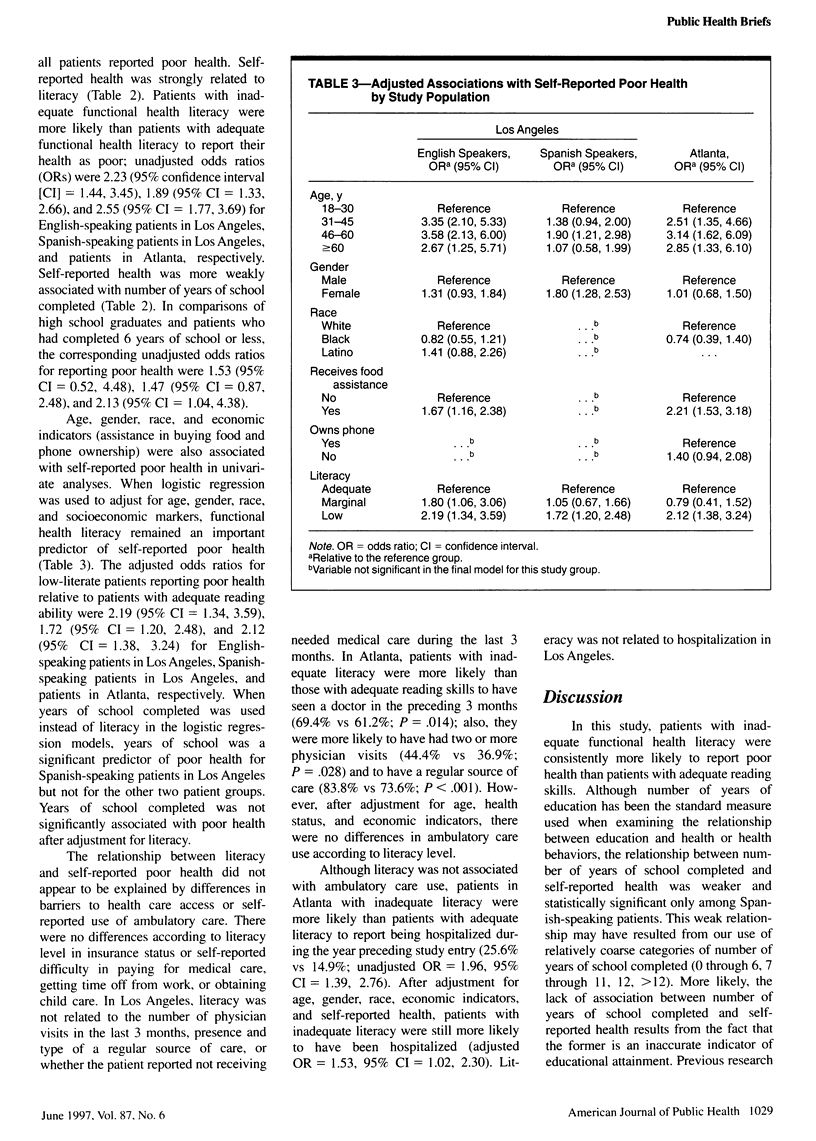
OBJECTIVES: This study examined the relationship of functional health literacy to self-reported health and use of health services. METHODS: Patients presenting to two large, urban public hospitals in Atlanta, Ga, and Torrance, Calif, were administered a health literacy test about their overall health and use of health care services during the 3 months preceding their visit. RESULTS: Patients with inadequate functional health literacy were more likely than patients with adequate literacy to report their health as poor. Number of years of school completed was less strongly associated with self-reported health. Literacy was not related to regular source of care or physician visits, but patients in Atlanta with inadequate literacy were more likely than patients with adequate literacy to report a hospitalization in the previous year. CONCLUSIONS: Low literacy is strongly associated with self-reported poor health and is more closely associated with self-reported health than number of years of school completed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler N. E., Boyce W. T., Chesney M. A., Folkman S., Syme S. L. Socioeconomic inequalities in health. No easy solution. JAMA. 1993 Jun 23;269(24):3140–3145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bairagi R. Is income the only constraint on child nutrition in rural Bangladesh? Bull World Health Organ. 1980;58(5):767–772. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choe M. K., Retherford R. D., Gubhaju B. B., Thapa S. Ethnic differentials in early childhood mortality in Nepal. J Biosoc Sci. 1989 Apr;21(2):223–233. doi: 10.1017/s0021932000017910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis T. C., Long S. W., Jackson R. H., Mayeaux E. J., George R. B., Murphy P. W., Crouch M. A. Rapid estimate of adult literacy in medicine: a shortened screening instrument. Fam Med. 1993 Jun;25(6):391–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Educational level and 5-year all-cause mortality in the Hypertension Detection and Follow-up Program. Hypertension Detection and Follow-up Program Cooperative Group. Hypertension. 1987 Jun;9(6):641–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esrey S. A., Habicht J. P. Maternal literacy modifies the effect of toilets and piped water on infant survival in Malaysia. Am J Epidemiol. 1988 May;127(5):1079–1087. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman J. J., Makuc D. M., Kleinman J. C., Cornoni-Huntley J. National trends in educational differentials in mortality. Am J Epidemiol. 1989 May;129(5):919–933. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flegg A. T. Inequality of income, illiteracy and medical care as determinants of infant mortality in underdeveloped countries. Popul Stud (Camb) 1982 Nov;36(3):441–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foege W. H., Henderson D. A. Selective primary health care. XXV. Management priorities. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 May-Jun;8(3):467–475. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.3.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosse R. N., Auffrey C. Literacy and health status in developing countries. Annu Rev Public Health. 1989;10:281–297. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pu.10.050189.001433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guralnik J. M., Land K. C., Blazer D., Fillenbaum G. G., Branch L. G. Educational status and active life expectancy among older blacks and whites. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jul 8;329(2):110–116. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199307083290208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurowitz J. C. Toward a social policy for health. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jul 8;329(2):130–133. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199307083290213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil J. E., Sutherland S. E., Knapp R. G., Lackland D. T., Gazes P. C., Tyroler H. A. Mortality rates and risk factors for coronary disease in black as compared with white men and women. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jul 8;329(2):73–78. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199307083290201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. D., Jr Socioeconomic status and childhood mortality in North Carolina. Am J Public Health. 1992 Aug;82(8):1131–1133. doi: 10.2105/ajph.82.8.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappas G., Queen S., Hadden W., Fisher G. The increasing disparity in mortality between socioeconomic groups in the United States, 1960 and 1986. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jul 8;329(2):103–109. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199307083290207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. M., Baker D. W., Williams M. V., Nurss J. R. The test of functional health literacy in adults: a new instrument for measuring patients' literacy skills. J Gen Intern Med. 1995 Oct;10(10):537–541. doi: 10.1007/BF02640361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers R. D. Emergency department patient literacy and the readability of patient-directed materials. Ann Emerg Med. 1988 Feb;17(2):124–126. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0644(88)80295-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandorfer J. M., Karras D. J., Hughes L. A., Caputo C. Comprehension of discharge instructions by patients in an urban emergency department. Ann Emerg Med. 1995 Jan;25(1):71–74. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0644(95)70358-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tofler G. H., Muller J. E., Stone P. H., Davies G., Davis V. G., Braunwald E. Comparison of long-term outcome after acute myocardial infarction in patients never graduated from high school with that in more educated patients. Multicenter Investigation of the Limitation of Infarct Size (MILIS). Am J Cardiol. 1993 May 1;71(12):1031–1035. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(93)90568-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B. D., Hart G., McGee D. L., D'Estelle S. Health status of illiterate adults: relation between literacy and health status among persons with low literacy skills. J Am Board Fam Pract. 1992 May-Jun;5(3):257–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B. D., Hart G., Pust R. E. The relationship between literacy and health. J Health Care Poor Underserved. 1991 Spring;1(4):351–363. doi: 10.1353/hpu.2010.0294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. V., Parker R. M., Baker D. W., Parikh N. S., Pitkin K., Coates W. C., Nurss J. R. Inadequate functional health literacy among patients at two public hospitals. JAMA. 1995 Dec 6;274(21):1677–1682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



