Abstract
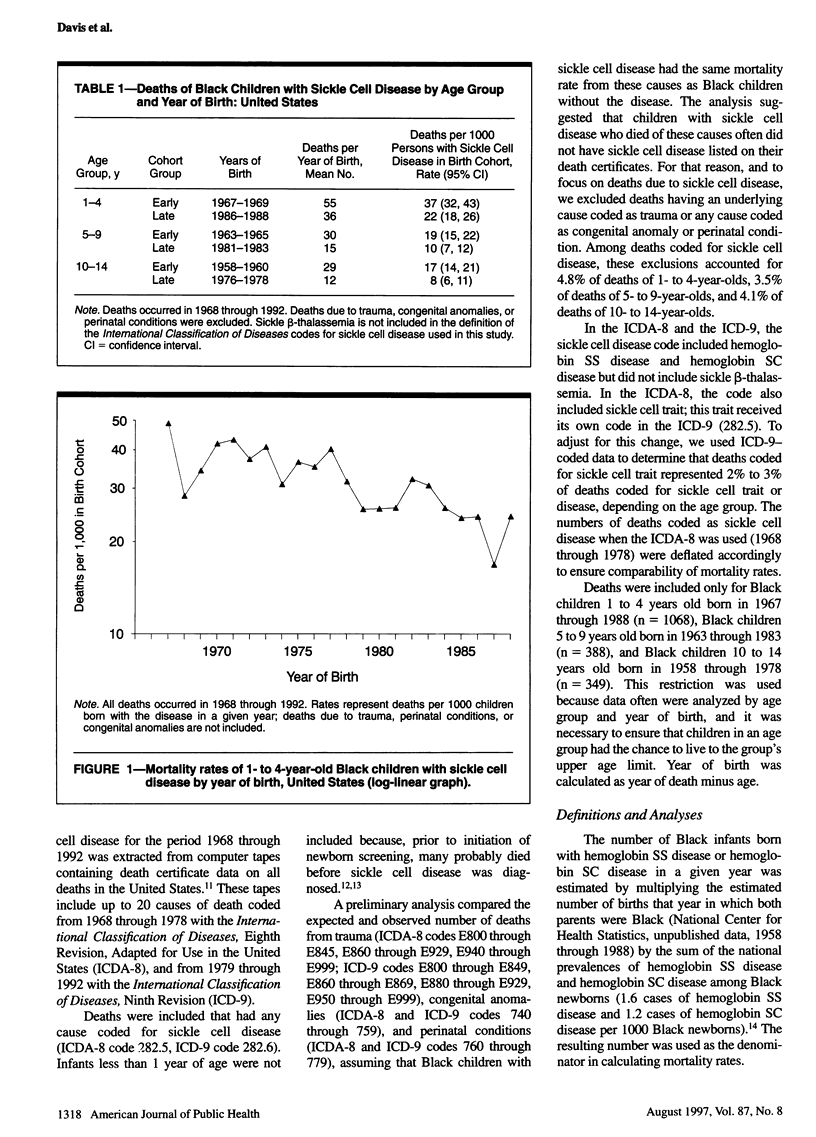
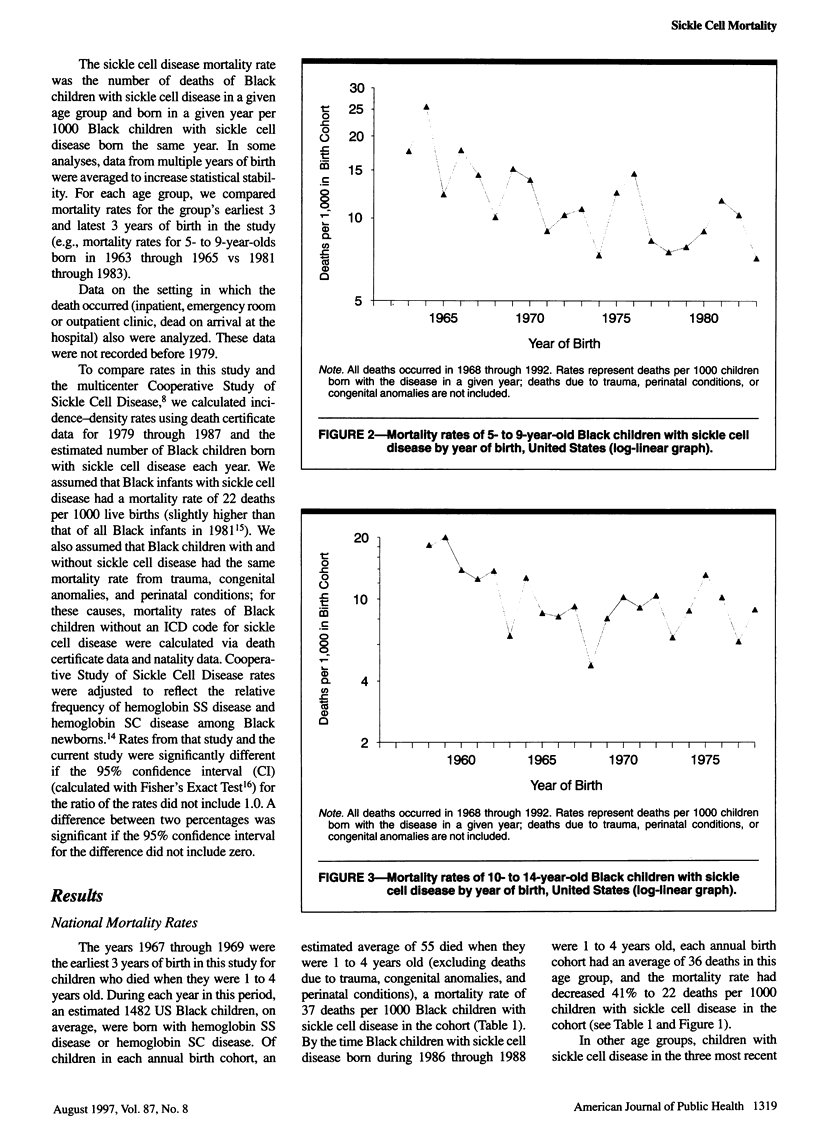
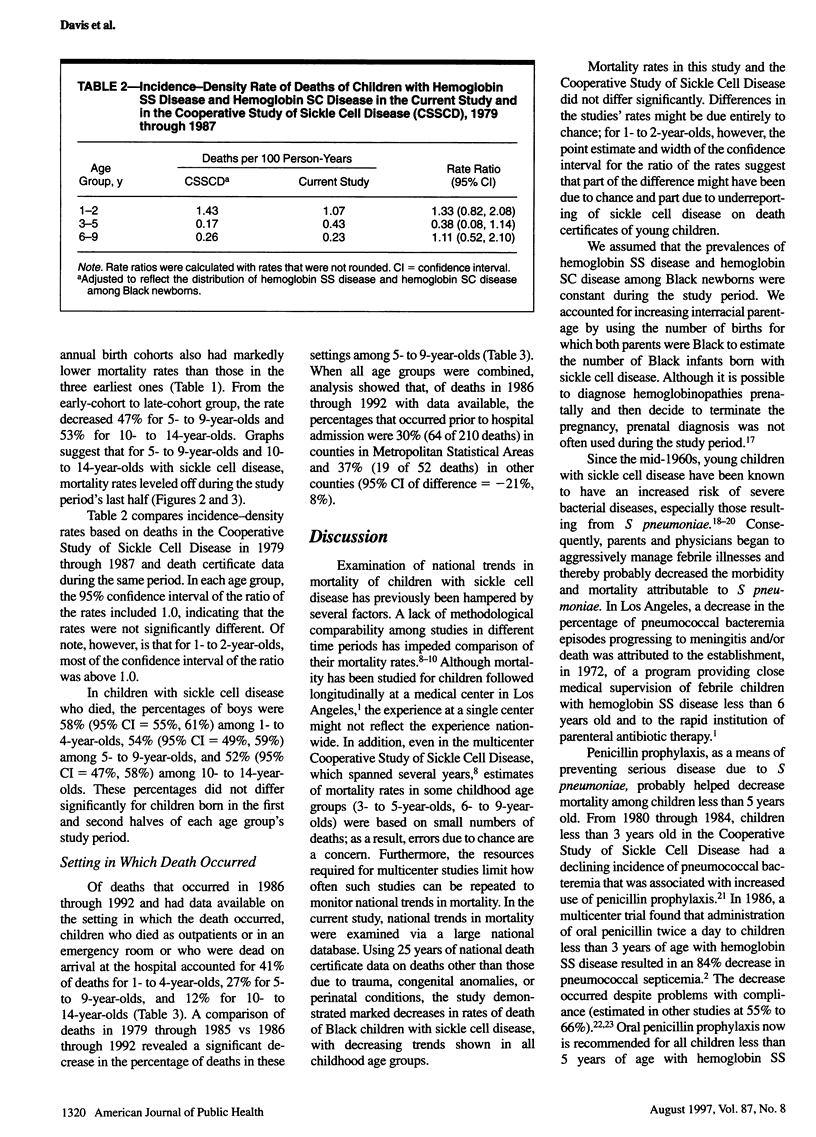
OBJECTIVES: This paper describes national trends in mortality of children with sickle cell disease and the settings in which death occurred. METHODS: United States death certificate data from 1968 through 1992 were used to calculate mortality rates of Black children with sickle cell disease 1 to 14 years old. Deaths from trauma, congenital anomalies, and perinatal conditions were excluded. RESULTS: Between 1968 and 1992, mortality rates of Black children with sickle cell disease decreased 41% for 1- to 4-year-olds, 47% for 5- to 9-year-olds, and 53% for 10- to 14-year-olds. During 1986 through 1992, children who died before hospital admission accounted for 41% of deaths among 1- to 4-year-olds, 27% among 5- to 9-year-olds, and 12% among 10- to 14-year-olds. CONCLUSIONS: Survival of Black children with sickle cell disease has improved markedly since 1968. A substantial proportion of deaths continue to occur prior to hospital admission. Trends in sickle cell mortality can be monitored inexpensively with death-certificate data.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bainbridge R., Higgs D. R., Maude G. H., Serjeant G. R. Clinical presentation of homozygous sickle cell disease. J Pediatr. 1985 Jun;106(6):881–885. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80230-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broome C. V., Facklam R. R., Fraser D. W. Pneumococcal disease after pneumococcal vaccination: an alternative method to estimate the efficacy of pneumococcal vaccine. N Engl J Med. 1980 Sep 4;303(10):549–552. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198009043031003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan G. R., Siegel J. D., Smith S. J., DePasse B. M. Oral penicillin prophylaxis in children with imparied splenic function: a study of compliance. Pediatrics. 1982 Dec;70(6):926–930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eeckels R., Gatti F., Renoirte A. M. Abnormal distribution of haemoglobin genotypes in Negro children with severe bacterial infections. Nature. 1967 Oct 28;216(5113):382–382. doi: 10.1038/216382a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emond A. M., Collis R., Darvill D., Higgs D. R., Maude G. H., Serjeant G. R. Acute splenic sequestration in homozygous sickle cell disease: natural history and management. J Pediatr. 1985 Aug;107(2):201–206. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston M. H., Verter J. I., Woods G., Pegelow C., Kelleher J., Presbury G., Zarkowsky H., Vichinsky E., Iyer R., Lobel J. S. Prophylaxis with oral penicillin in children with sickle cell anemia. A randomized trial. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jun 19;314(25):1593–1599. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198606193142501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover R. Newborn screening for sickle cell disease and other hemoglobinopathies. Newborn screening in New York City. Pediatrics. 1989 May;83(5 Pt 2):819–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guess H. A., Lydick E. G., Small R. D., Miller L. P. Epidemiologic programs for computers and calculators. Exact binomial confidence intervals for the relative risk in follow-up studies with sparsely stratified incidence density data. Am J Epidemiol. 1987 Feb;125(2):340–347. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabins S. A., Lerner C. Fulminant pneumococcemia and sickle cell anemia. JAMA. 1970 Jan 19;211(3):467–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leikin S. L., Gallagher D., Kinney T. R., Sloane D., Klug P., Rida W. Mortality in children and adolescents with sickle cell disease. Cooperative Study of Sickle Cell Disease. Pediatrics. 1989 Sep;84(3):500–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobel J. S., Cameron B. F., Johnson E., Smith D., Kalinyak K. Value of screening umbilical cord blood for hemoglobinopathy. Pediatrics. 1989 May;83(5 Pt 2):823–826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack A. K. Florida's experience with newborn screening. Pediatrics. 1989 May;83(5 Pt 2):861–863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motulsky A. G. Frequency of sickling disorders in U.S. blacks. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jan 4;288(1):31–33. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197301042880108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overturf G. D., Selzer J. W., Chan L., Weiss J., Field R., Rigau-Perez J. G., Powars D., Uy C., Pang E. J., Honig G. Pneumococcal polysaccharide immunization of children with sickle cell disease. II. Serologic response and pneumococcal disease following immunization. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1982 Spring;4(1):25–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegelow C. H., Armstrong F. D., Light S., Toledano S. R., Davis J. Experience with the use of prophylactic penicillin in children with sickle cell anemia. J Pediatr. 1991 May;118(5):736–738. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powars D. Diagnosis at birth improves survival of children with sickle cell anemia. Pediatrics. 1989 May;83(5 Pt 2):830–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powars D., Overturf G., Weiss J., Lee S., Chan L. Pneumococcal septicemia in children with sickle cell anemia. Changing trend of survival. JAMA. 1981 May 8;245(18):1839–1842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. G., Watson R. J. Pneumococcal meningitis in sickle-cell anemia. N Engl J Med. 1966 May 5;274(18):1006–1008. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196605052741806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley P. T. Prenatal diagnosis for sickle cell disease. A survey of the United States and Canada. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;565:48–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb24149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. B. Health care priority and sickle cell anemia. JAMA. 1970 Oct 26;214(4):731–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vichinsky E., Hurst D., Earles A., Kleman K., Lubin B. Newborn screening for sickle cell disease: effect on mortality. Pediatrics. 1988 Jun;81(6):749–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S., Maude G. H., Serjeant G. R. Clinical presentation of sickle cell-hemoglobin C disease. J Pediatr. 1986 Oct;109(4):586–589. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80217-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarkowsky H. S., Gallagher D., Gill F. M., Wang W. C., Falletta J. M., Lande W. M., Levy P. S., Verter J. I., Wethers D. Bacteremia in sickle hemoglobinopathies. J Pediatr. 1986 Oct;109(4):579–585. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80216-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


