Abstract
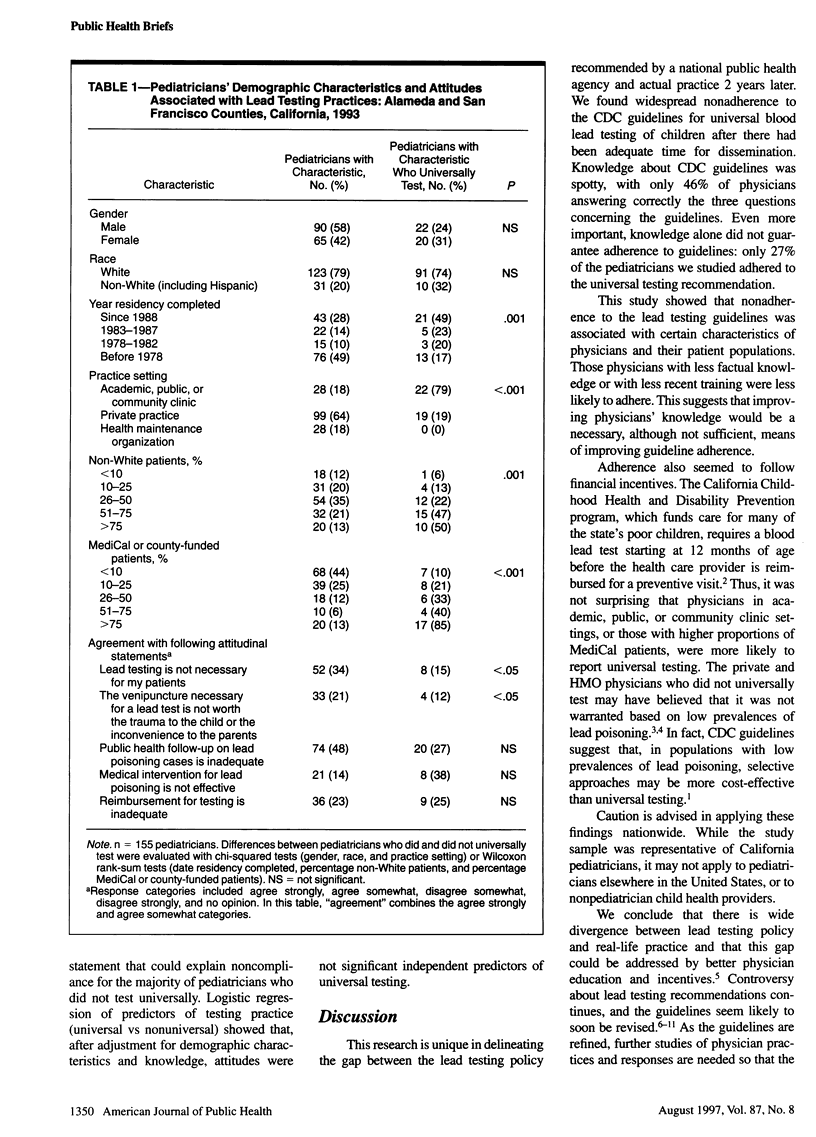
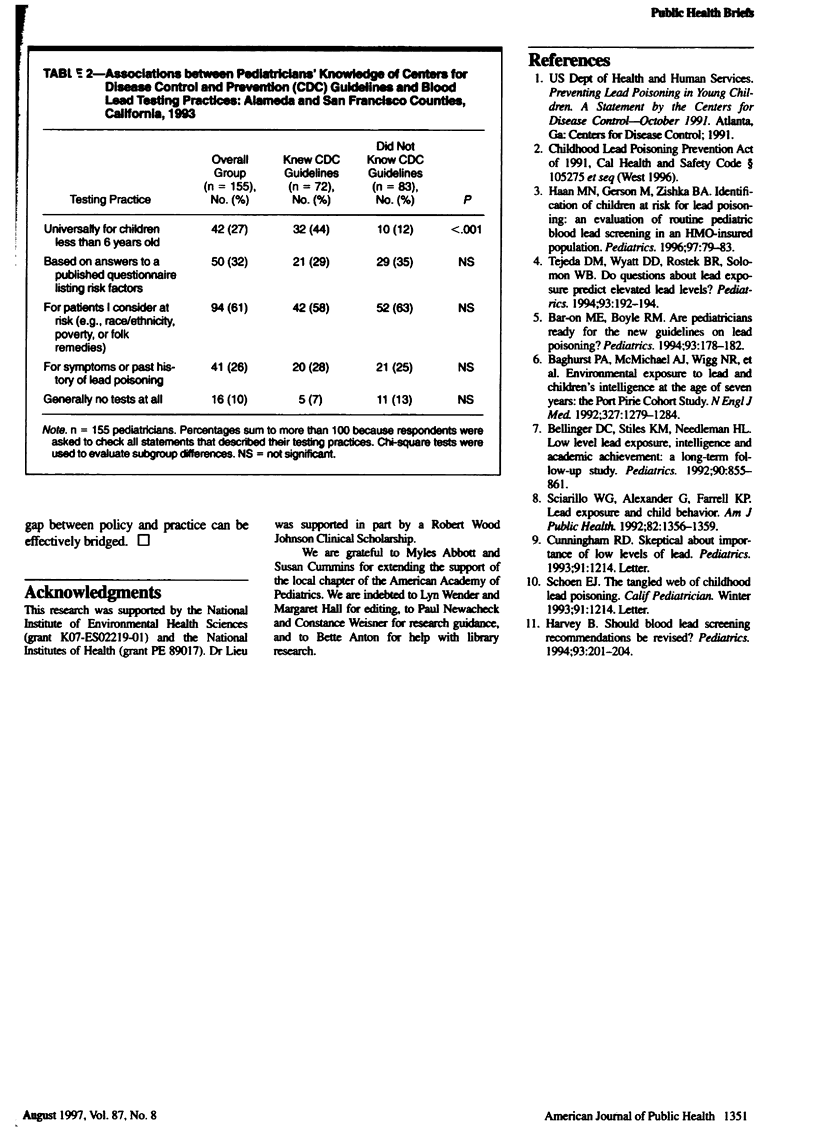
OBJECTIVES: This study aimed to evaluate adherence and identify ways to improve concordance between blood lead testing guidelines and practice. METHODS: One hundred fifty-five pediatricians responded to a questionnaire assessing demographic, knowledge, and attitudinal factors relating to lead testing. RESULTS: Only 27% of the respondents adhered to the guidelines, and less than half knew all of the answers to three factual questions about the recommendations. Adherence was higher among physicians who knew the guidelines, were more recently trained, or had high proportions of Medicaid or minority patients. CONCLUSIONS: Physician education and financial incentives hold the most promise for increasing adherence to blood lead testing guidelines.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baghurst P. A., McMichael A. J., Wigg N. R., Vimpani G. V., Robertson E. F., Roberts R. J., Tong S. L. Environmental exposure to lead and children's intelligence at the age of seven years. The Port Pirie Cohort Study. N Engl J Med. 1992 Oct 29;327(18):1279–1284. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199210293271805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-on M. E., Boyle R. M. Are pediatricians ready for the new guidelines on lead poisoning? Pediatrics. 1994 Feb;93(2):178–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellinger D. C., Stiles K. M., Needleman H. L. Low-level lead exposure, intelligence and academic achievement: a long-term follow-up study. Pediatrics. 1992 Dec;90(6):855–861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham R. D., Jr Skeptical about importance of low levels of lead. Pediatrics. 1993 Jun;91(6):1214–1215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haan M. N., Gerson M., Zishka B. A. Identification of children at risk for lead poisoning: an evaluation of routine pediatric blood lead screening in an HMO-insured population. Pediatrics. 1996 Jan;97(1):79–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey B. Should blood lead screening recommendations be revised? Pediatrics. 1994 Feb;93(2):201–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sciarillo W. G., Alexander G., Farrell K. P. Lead exposure and child behavior. Am J Public Health. 1992 Oct;82(10):1356–1360. doi: 10.2105/ajph.82.10.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tejeda D. M., Wyatt D. D., Rostek B. R., Solomon W. B. Do questions about lead exposure predict elevated lead levels? Pediatrics. 1994 Feb;93(2):192–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


