Abstract
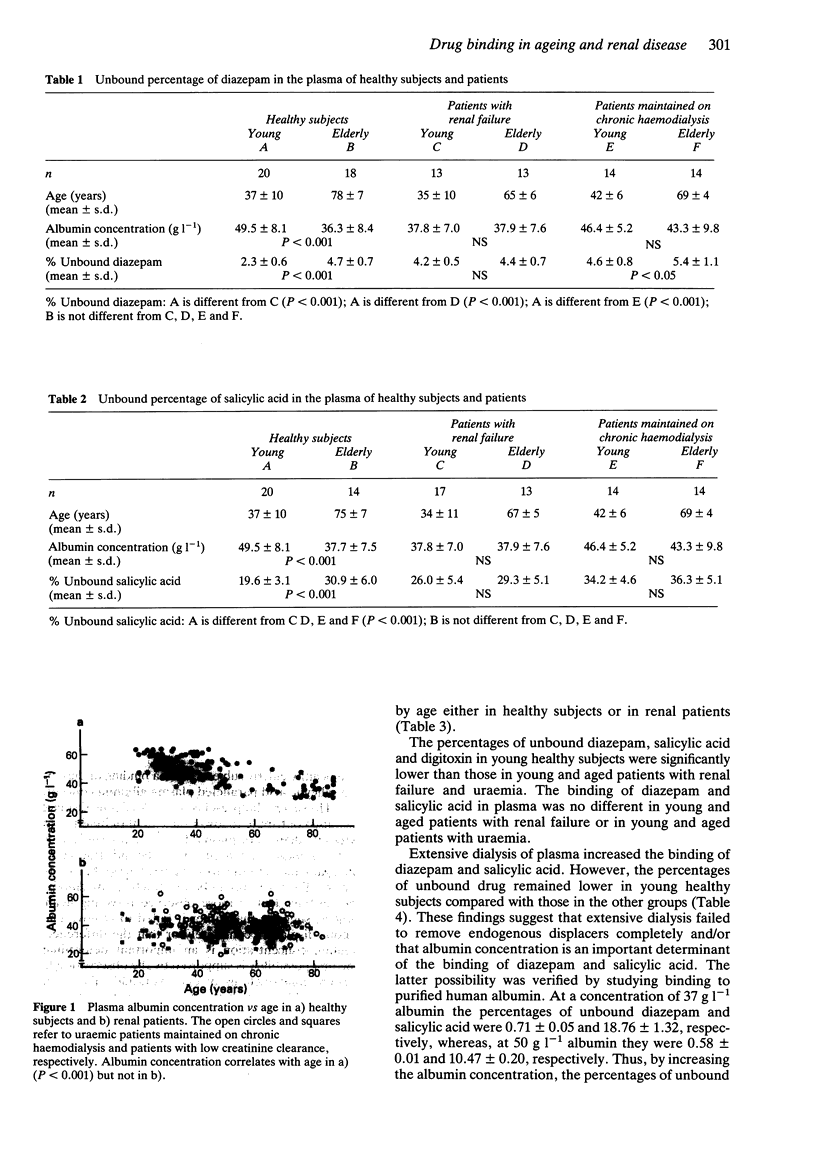
1. Plasma albumin concentration was measured in 118 healthy subjects (aged between 18 and 87 years), in 95 renal patients with creatinine clearances between 15 and 50 ml min-1 (aged between 14 and 79 years) and in 101 uraemic patients maintained on chronic haemodialysis (aged between 27 and 83 years). 2. There was a significant (P less than 0.001) negative correlation between albumin concentration and age in healthy subjects, but no correlation in patients with low creatinine clearance or in uraemic patients. 3. The ex vivo plasma binding of diazepam (1 microM), salicylic acid (2 mM) and digitoxin (37 nM) was studied in groups of age-selected young and aged healthy subjects in patients with low creatinine clearance and in patients with uraemia. The unbound fractions of diazepam and salicylic acid were about double in old compared with young healthy subjects whereas they were similar in young and old patients with lowered creatinine clearance. In uraemic patients, ageing did not affect the binding of salicylic acid whereas the unbound fraction of diazepam was slightly but significantly greater in elderly subjects. The unbound fraction of digitoxin was independent of age in both healthy subjects and in those with renal disease. 4. Decreased plasma binding of diazepam and salicylic acid was partially corrected by extensive dialysis of plasma. The lower plasma binding of diazepam and salicylic acid associated with ageing may be ascribed to the effects of endogenous displacers and to hypoalbuminaemia. The influence of these two factors appears to be drug-dependent.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen F. Protein binding of drugs in plasma from patients with acute renal failure. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1973;32(6):417–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1973.tb01488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreasen F. The effect of dialysis on the protein binding of drugs in the plasma of patients with acute renal failure. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1974 Apr;34(4):284–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1974.tb03525.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgå O., Cederlöf I. O., Ringberger V. A., Norlin A. Protein binding of salicylate in uremic and normal plasma. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Oct;20(4):464–475. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976204464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis D., Grossman S. H., Kitchell B. B., Shand D. G., Routledge P. A. The effects of age and smoking on the plasma protein binding of lignocaine and diazepam. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;19(2):261–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1985.tb02641.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gugler R., Azarnoff D. L. Drug protein binding and the nephrotic syndrome. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1976;1(1):25–35. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197601010-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S. J., Lindup W. E. Interaction of 3-carboxy-4-methyl-5-propyl-2-furanpropanoic acid, an inhibitor of plasma protein binding in uraemia, with human albumin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Dec 1;40(11):2543–2548. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kober A., Ekman B., Sjöholm I. Direct and indirect determination of binding constants of drug-protein complexes with microparticles. J Pharm Sci. 1978 Jan;67(1):107–109. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600670127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kober A., Sjöholm I., Borgå O., Odar-Cederlöf I. Protein binding of diazepam and digitoxin in uremic and normal serum. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Apr 1;28(7):1037–1042. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90300-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy G. Pharmacokinetics of salicylate in man. Drug Metab Rev. 1979;9(1):3–19. doi: 10.3109/03602537909046431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas D., Ménez J. F., Daniel J. Y., Bardou L. G., Floch H. H. Acetaldehyde adducts with serum proteins: effect on diazepam and phenytoin binding. Pharmacology. 1986;32(3):134–140. doi: 10.1159/000138162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Wollert U. Characterization of the binding of benzodiazepines to human serum albumin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1973;280(3):229–237. doi: 10.1007/BF00501348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacifici G. M., Viani A., Taddeucci-Brunelli G., Rizzo G., Carrai M. Plasma protein binding of dicloxacillin: effects of age and diseases. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1987 Nov;25(11):622–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacifici G. M., Viani A., Taddeucci-Brunelli G., Rizzo G., Carrai M., Schulz H. U. Effects of development, aging, and renal and hepatic insufficiency as well as hemodialysis on the plasma concentrations of albumin and alpha 1-acid glycoprotein: implications for binding of drugs. Ther Drug Monit. 1986;8(3):259–263. doi: 10.1097/00007691-198609000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidenberg M. M., Drayer D. E. Alteration of drug-protein binding in renal disease. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1984 Jan;9 (Suppl 1):18–26. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198400091-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöholm I., Ekman B., Kober A., Ljungstedt-Påhlman I., Seiving B., Sjödin T. Binding of drugs to human serum albumin:XI. The specificity of three binding sites as studied with albumin immobilized in microparticles. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;16(3):767–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöholm I., Kober A., Odar-Cederlöf I., Borgåa O. Protein binding of drugs in uremic and normal serum: the role of endogenous binding inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 May 15;25(10):1205–1213. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90370-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiula E., Tallgren L. G., Neuvonen P. J. Serum protein binding of phenytoin, diazepam and propranolol in chronic renal diseases. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1987 Oct;25(10):545–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veering B. T., Burm A. G., Souverijn J. H., Serree J. M., Spierdijk J. The effect of age on serum concentrations of albumin and alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;29(2):201–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1990.tb03620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viani A., Pacifici G. M. Bilirubin displaces furosemide from serum protein: the effect is greater in newborn infants than adult subjects. Dev Pharmacol Ther. 1989;14(2):90–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace S. M., Verbeeck R. K. Plasma protein binding of drugs in the elderly. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1987 Jan;12(1):41–72. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198712010-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace S., Whiting B. Factors affecting drug binding in plasma of elderly patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Apr;3(2):327–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1976.tb00611.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaroslinski J. F., Keresztes-Nagy S., Mais R. F., Oester Y. T. Effect of temperature on the binding of salicylate by human serum albumin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Jun 15;23(12):1767–1776. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90403-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


