Abstract
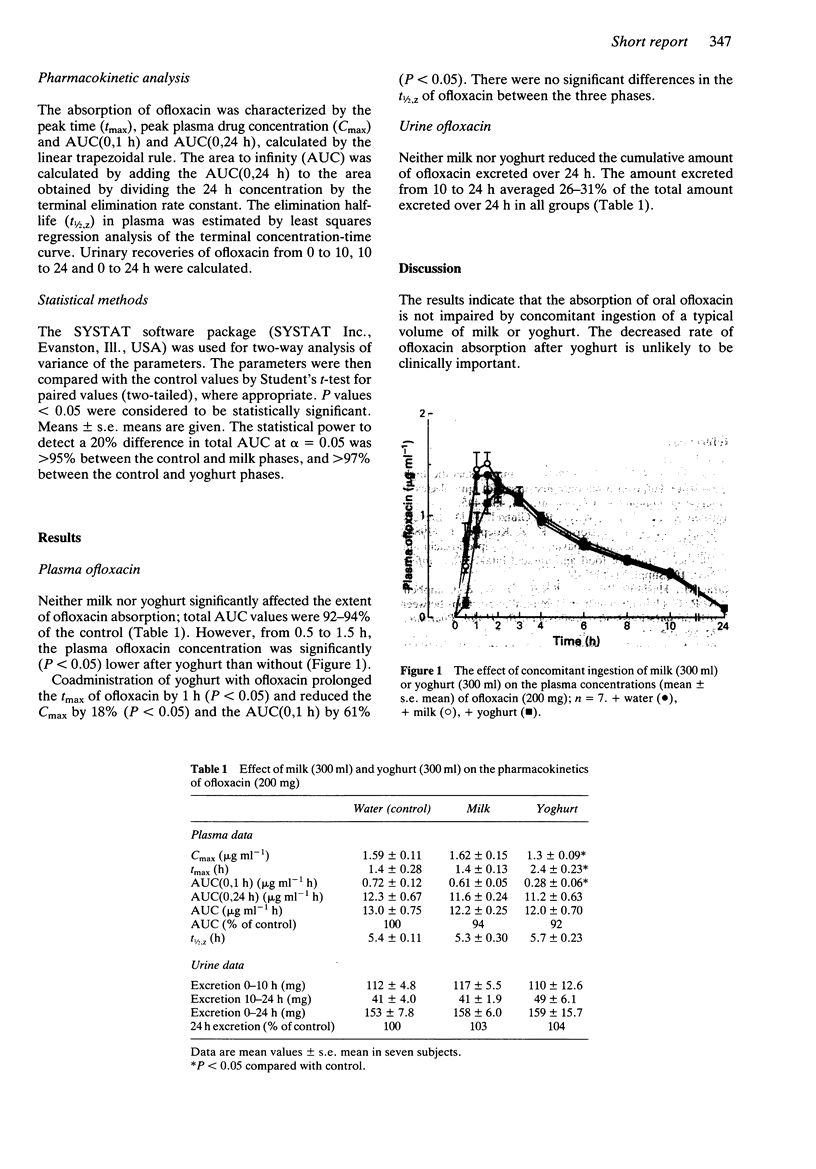
The effects of milk and yoghurt on the oral absorption of ofloxacin were studied in seven healthy volunteers in a randomized cross-over trial. After an overnight fast, 200 mg ofloxacin was given with 300 ml water, milk or yoghurt. Plasma concentrations and urinary excretion of ofloxacin were determined up to 24 h. Values of total plasma AUC and 24 h urinary excretion of ofloxacin were not affected by milk or yoghurt. Plasma ofloxacin concentrations from 0.5 to 1.5 h and the peak concentration were lower (P less than 0.05) after yoghurt than without and the time to peak was prolonged by 1 h (P less than 0.05).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- De Gruttola V., Mayer K. H. Assessing and modeling heterosexual spread of the human immunodeficiency virus in the United States. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jan-Feb;10(1):138–150. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.1.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs D. J., Wise R. A simple isocratic high-pressure liquid chromatographic assay of quinolones in serum. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Sep;24(3):437–445. doi: 10.1093/jac/24.3.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kara M., Hasinoff B. B., McKay D. W., Campbell N. R. Clinical and chemical interactions between iron preparations and ciprofloxacin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;31(3):257–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1991.tb05526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lode H., Höffken G., Prinzing C., Glatzel P., Wiley R., Olschewski P., Sievers B., Reimnitz D., Borner K., Koeppe P. Comparative pharmacokinetics of new quinolones. Drugs. 1987;34 (Suppl 1):21–25. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198700341-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander A. Influence of food on the bioavailability of drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1978 Sep-Oct;3(5):337–351. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197803050-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuvonen P. J., Kivistö K. T., Lehto P. Interference of dairy products with the absorption of ciprofloxacin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1991 Nov;50(5 Pt 1):498–502. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1991.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuvonen P. J., Kivistö K. T. The clinical significance of food-drug interactions: a review. Med J Aust. 1989 Jan 2;150(1):36–40. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1989.tb136321.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nix D. E., Watson W. A., Lener M. E., Frost R. W., Krol G., Goldstein H., Lettieri J., Schentag J. J. Effects of aluminum and magnesium antacids and ranitidine on the absorption of ciprofloxacin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1989 Dec;46(6):700–705. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1989.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmers K., Sternglanz R. Ionization and divalent cation dissociation constants of nalidixic and oxolinic acids. Bioinorg Chem. 1978 Aug;9(2):145–155. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3061(00)80286-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welling P. G. Interactions affecting drug absorption. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1984 Sep-Oct;9(5):404–434. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198409050-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuk J. H., Nightingale C. H., Quintiliani R., Sweeney K. R. Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin in healthy volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Feb;35(2):384–386. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.2.384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


