Abstract
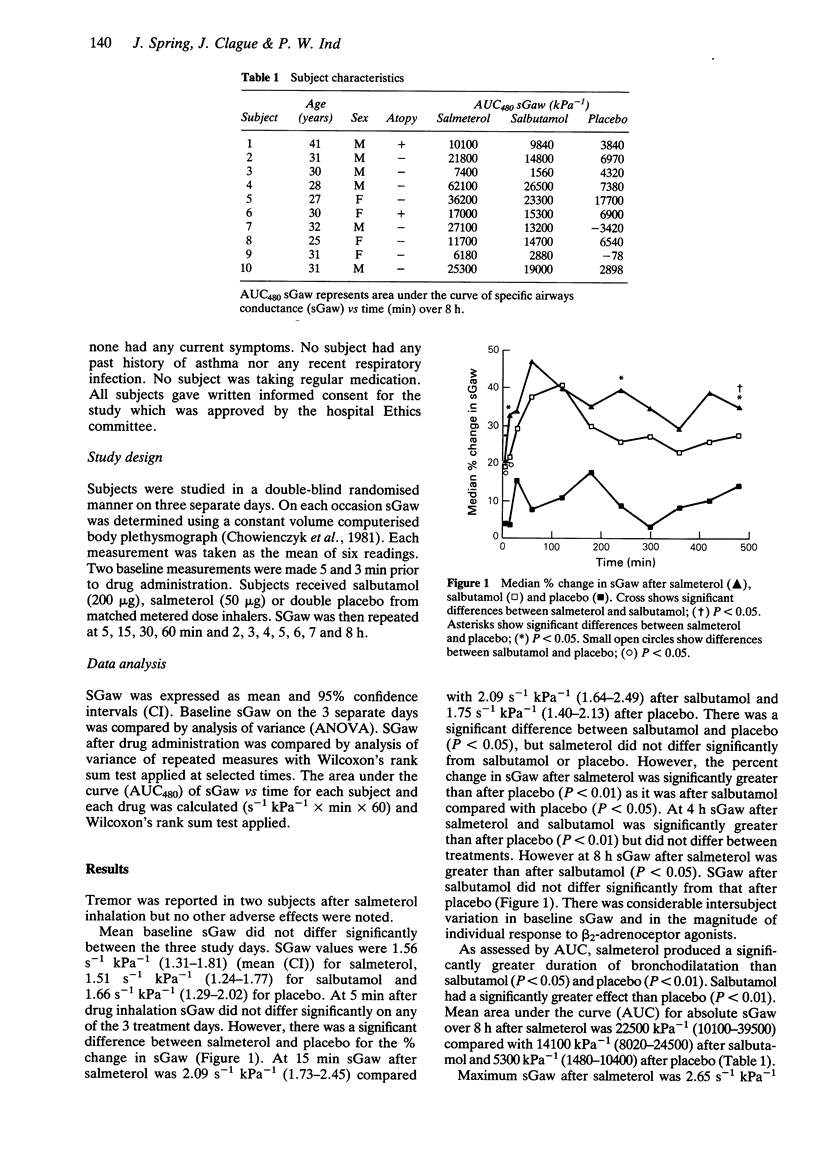
1. The effects of salmeterol hydroxynaphthoate (50 micrograms, 8.3 x 10(-8) M) and salbutamol (200 micrograms, 3.5 x 10(-7) M) on sGaw were compared in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised study in 10 normal subjects. 2. SGaw increased by 29% (14-43) (mean (CI)), 5 min after salmeterol and by 35% (19-51) at 15 min compared with an increase of 32% (14-51) and 37% (10-63) after salbutamol and 4% (-3-11) and 8% (0-16) after placebo. 3. The mean area under the sGaw-time curve (AUC480) after salmeterol inhalation was 22,500 kPa-1 (10,100-39,500) compared with 14100 kPa-1 (8020-24,500) after salbutamol and 5300 kPa-1 (1500-10,400) after placebo. 4. Salmeterol produced a significantly prolonged bronchodilator effect compared with salbutamol in normals.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carstairs J. R., Nimmo A. J., Barnes P. J. Autoradiographic visualization of beta-adrenoceptor subtypes in human lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Sep;132(3):541–547. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.3.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choonara I. A., Malia R. G., Haynes B. P., Hay C. R., Cholerton S., Breckenridge A. M., Preston F. E., Park B. K. The relationship between inhibition of vitamin K1 2,3-epoxide reductase and reduction of clotting factor activity with warfarin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Jan;25(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1988.tb03274.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowienczyk P. J., Rees P. J., Payne J., Clark T. J. A new method for computer-assisted determination of airways resistance. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Mar;50(3):672–678. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.50.3.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick M. F., Mackay T., Driver H., Douglas N. J. Salmeterol in nocturnal asthma: a double blind, placebo controlled trial of a long acting inhaled beta 2 agonist. BMJ. 1990 Dec 15;301(6765):1365–1368. doi: 10.1136/bmj.301.6765.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribbin H. R., Baldwin C. J., Tattersfield A. E. Quantitative assessment of bronchial beta-adrenoceptor blockade in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Jun;7(6):551–556. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb04641.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. The pharmacology of salmeterol. Lung. 1990;168 (Suppl):115–119. doi: 10.1007/BF02718123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner C., Palmer K. N. Changes in specific airways conductance and forced expiratory volume in one second after a bronchodilator in normal subjects and patients with airways obstruction. Thorax. 1974 Sep;29(5):574–577. doi: 10.1136/thx.29.5.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman A., Hedner J., Svedmyr N. Inhaled salmeterol and salbutamol in asthmatic patients. An evaluation of asthma symptoms and the possible development of tachyphylaxis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Sep;142(3):571–575. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.3.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman A., Svedmyr N. Salmeterol, a new long acting inhaled beta 2 adrenoceptor agonist: comparison with salbutamol in adult asthmatic patients. Thorax. 1988 Sep;43(9):674–678. doi: 10.1136/thx.43.9.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


