Abstract
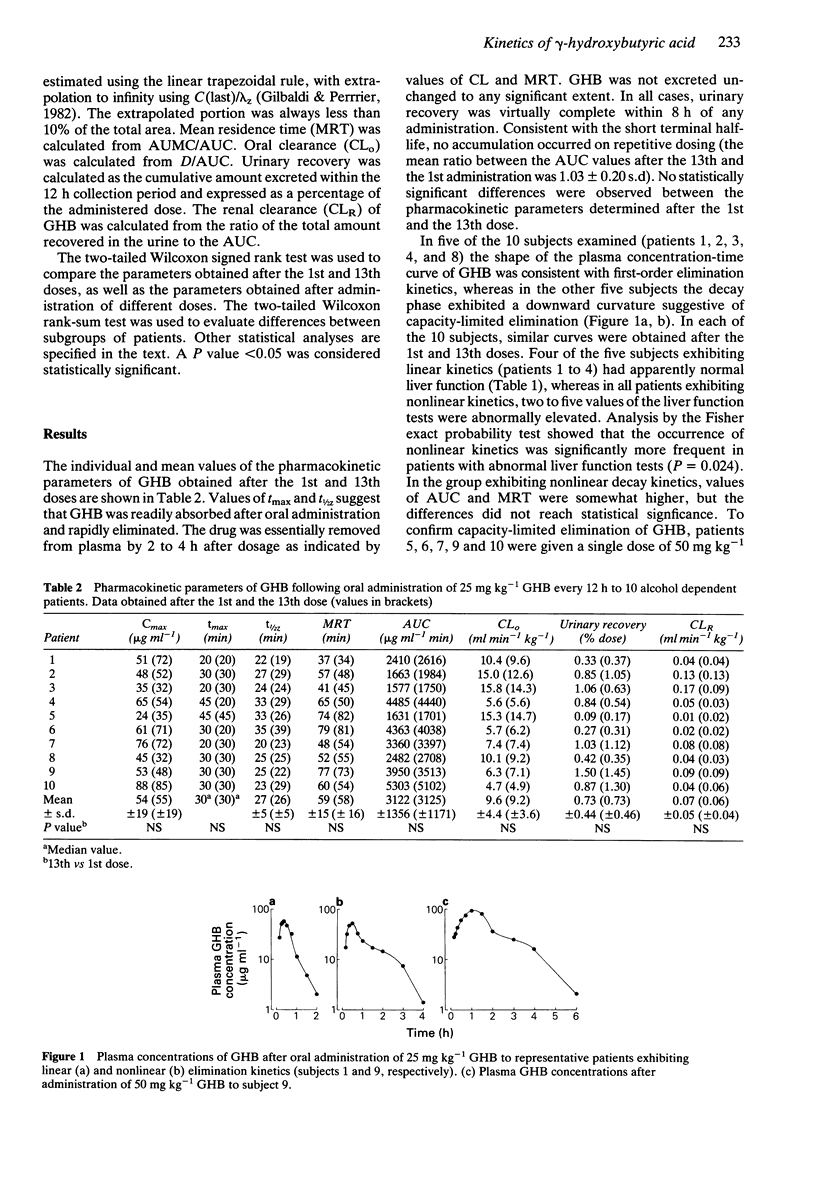
1. The pharmacokinetics of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) were studied in 10 alcohol dependent subjects after single and repeated therapeutic oral doses (25 mg kg-1 every 12 h for 7 days). 2. GHB was readily absorbed and rapidly eliminated (tmax = 20-45 min; mean t1/2z 27 +/- 5 s.d. min). Urinary recovery of unchanged GHB was negligible (less than 1% of the dose). gamma-butyrolactone was not detected in either plasma or urine, indicating that lactonization of GHB does not occur in vivo. 3. The multiple-dose regimen resulted neither in accumulation of GHB nor in time-dependent modification of its pharmacokinetics. 4. In five subjects, the data were consistent with nonlinear elimination kinetics of GHB. Administration of a 50 mg kg-1 dose to these subjects resulted in significant increases in dose-normalized AUC, t1/2z and mean residence time. 5. Doubling of the dose also resulted in a significant increase in tmax with little change in Cmax. 6. At the administered doses, GHB did not accumulate in the plasma and caused no serious side effects.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andén N. E., Stock G. Inhibitory effect of gammahydroxybutyric acid and gammaaminobutyric acid on the dopamine cells in the substantia nigra. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1973;279(1):89–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00502071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arena C., Fung H. L. Absorption of sodium gamma-hydroxybutyrate and its prodrug gamma-butyrolactone: relationship between in vitro transport and in vivo absorption. J Pharm Sci. 1980 Mar;69(3):356–358. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600690331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BESSMAN S. P., SKOLNIK S. J. GAMMA HYDROXYBUTYRATE AND GAMMA BUTYROLACTONE: CONCENTRATION IN RAT TISSUES DURING ANESTHESIA. Science. 1964 Mar 6;143(3610):1045–1047. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3610.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
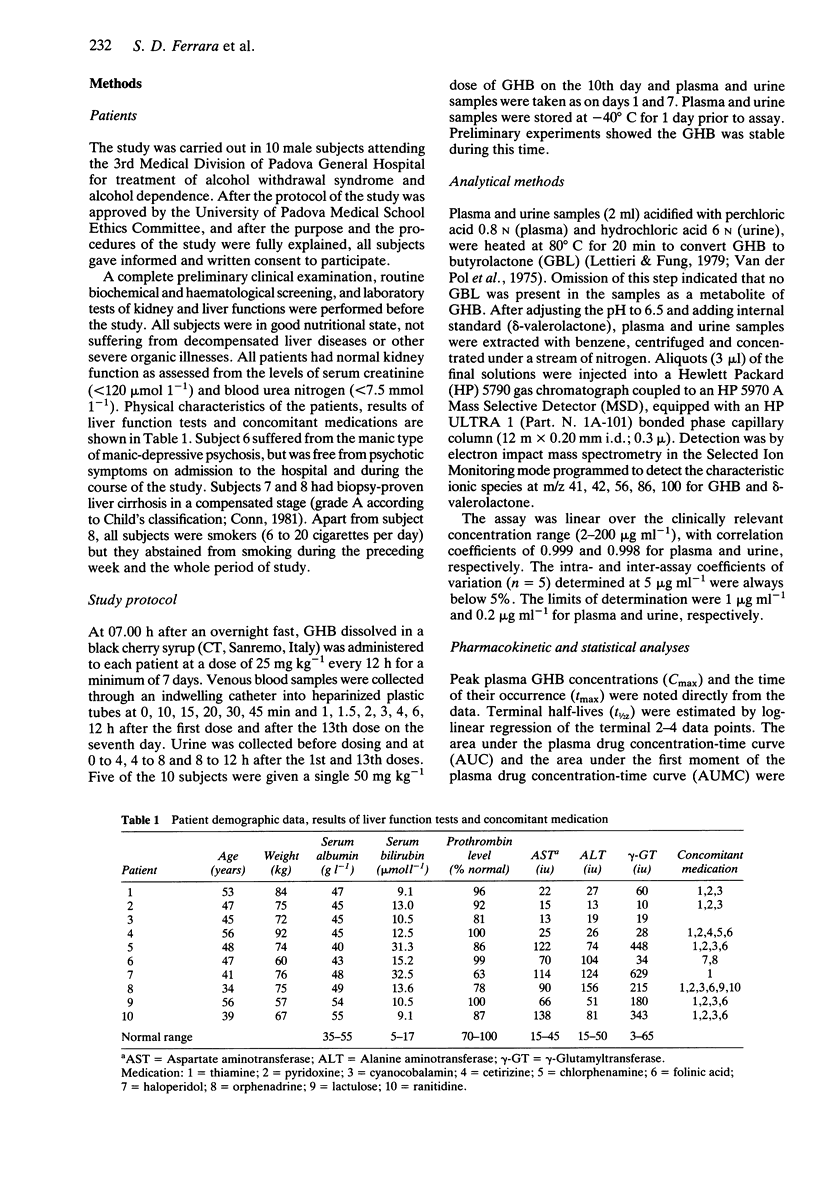
- Conn H. O. A peek at the Child-Turcotte classification. Hepatology. 1981 Nov-Dec;1(6):673–676. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fadda F., Argiolas A., Melis M. R., De Montis G., Gessa G. L. Suppression of voluntary ethanol consumption in rats by gamma-butyrolactone. Life Sci. 1983 Mar 28;32(13):1471–1477. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90913-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fadda F., Colombo G., Mosca E., Gessa G. L. Suppression by gamma-hydroxybutyric acid of ethanol withdrawal syndrome in rats. Alcohol Alcohol. 1989;24(5):447–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIARMAN N. J., ROTH R. H. DIFFERENTIAL ESTIMATION OF GAMMA-BUTYROLACTONE AND GAMMA-HYDROXYBUTYRIC ACID IN RAT BLOOD AND BRAIN. Science. 1964 Aug 7;145(3632):583–584. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3632.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallimberti L., Canton G., Gentile N., Ferri M., Cibin M., Ferrara S. D., Fadda F., Gessa G. L. Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid for treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Lancet. 1989 Sep 30;2(8666):787–789. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90842-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LABORIT H., JOUANY J. M., GERARD J., FABIANI F. [Summary of an experimental and clinical study on a metabolic substrate with inhibitory central action: sodium 4-hydroxybutyrate]. Presse Med. 1960 Nov 12;68:1867–1869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lettieri J. T., Fung H. L. Dose-dependent pharmacokinetics and hypnotic effects of sodium gamma-hydroxybutyrate in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Jan;208(1):7–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lettieri J., Fung H. L. Improved pharmacological activity via pro-drug modification: comparative pharmacokinetics of sodium gamma-hydroxybutyrate and gamma-butyrolactone. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1978 Oct;22(1):107–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamelak M., Scharf M. B., Woods M. Treatment of narcolepsy with gamma-hydroxybutyrate. A review of clinical and sleep laboratory findings. Sleep. 1986;9(1 Pt 2):285–289. doi: 10.1093/sleep/9.1.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pol W., Kleijn E., Lauw M. Gas chromatographic determination and pharmacokinetics of 4-hydroxybutrate in dog and mouse. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1975 Apr;3(2):99–113. doi: 10.1007/BF01066018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. H., Nowycky M. C. Dopaminergic neurons: effects elicited by gamma-hydroxybutyrate are reversed by picrotoxin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Nov 1;26(21):2079–2082. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shumate J. S., Snead O. C., 3rd Plasma and central nervous system kinetics of gamma-hydroxybutyrate. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1979 Aug;25(2):241–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snead O. C., 3rd, Furner R., Liu C. C. In vivo conversion of gamma-aminobutyric acid and 1,4-butanediol to gamma-hydroxybutyric acid in rat brain. Studies using stable isotopes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Dec 15;38(24):4375–4380. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90645-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snead O. C., 3rd, Morley B. J. Ontogeny of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid. I. Regional concentration in developing rat, monkey and human brain. Brain Res. 1981 Jul;227(4):579–589. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(81)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler H., Lloyd K. G., Bartholini G. Dopaminergic inhibition of striatal cholinergic neurons: synergistic blocking action of gamma-butyrolactone and neuroleptic drugs. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1974;283(2):129–134. doi: 10.1007/BF00501139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vayer P., Mandel P., Maitre M. Gamma-hydroxybutyrate, a possible neurotransmitter. Life Sci. 1987 Sep 28;41(13):1547–1557. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90721-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vree T. B., van der Kleijn E. Rapid determination of 4-hydroxybutyric acid (Gamma OH) and 2-propyl pentanoate (Depakine) in human plasma be means of gas-liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1976 Jun 9;121(1):150–152. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)82317-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters J. R., Roth R. H., Aghajanian G. K. Dopaminergic neurons: similar biochemical and histochemical effects of gamma-hydroxybutyrate and acute lesions of the nigro-neostriatal pathway. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Sep;186(3):630–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


