Abstract
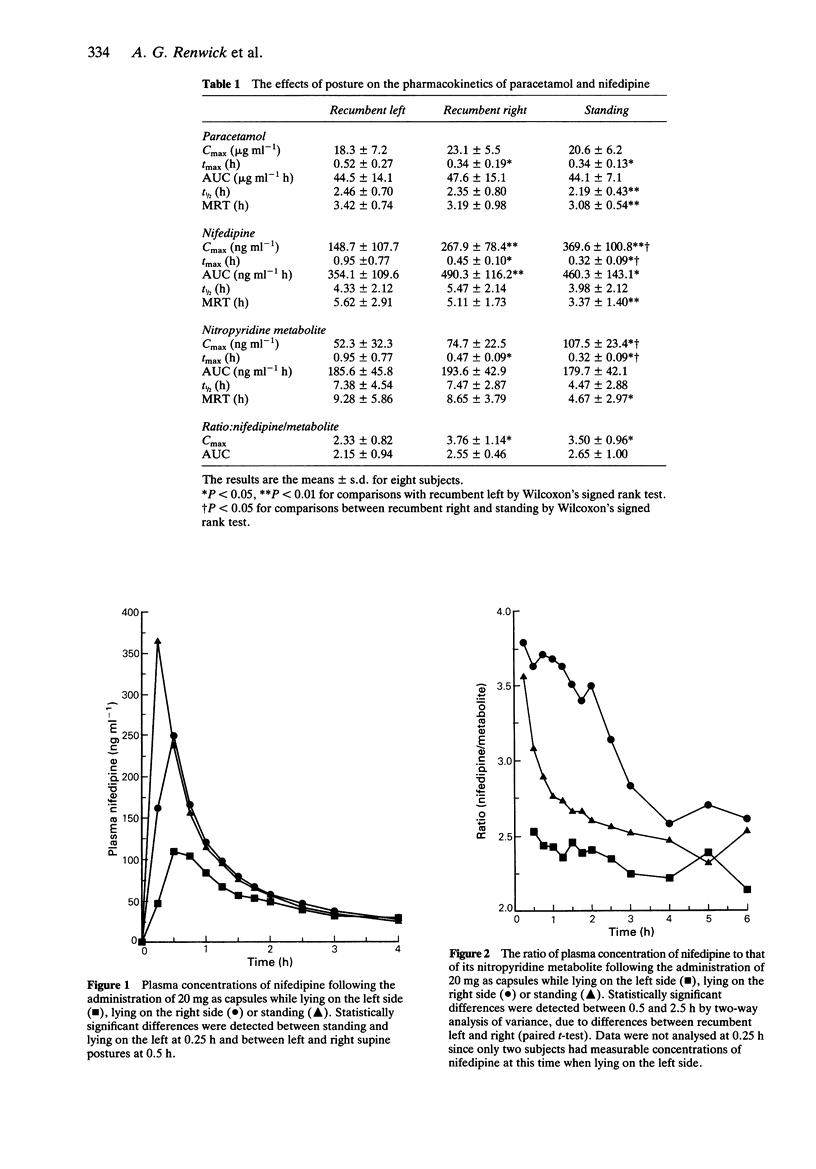
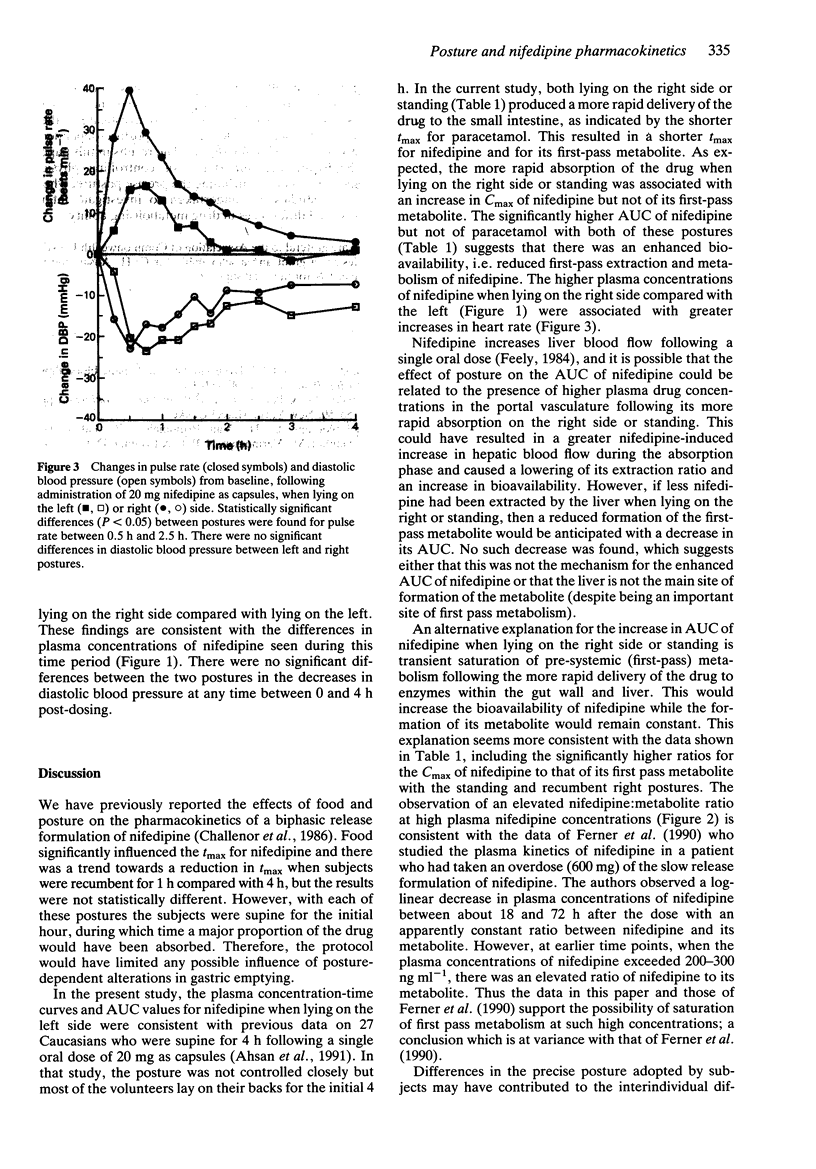
1. Nifedipine (20 mg as capsules) and soluble paracetamol (1 g) were co-administered to eight healthy young volunteers on three separate occasions, following which in random order they stood, lay on their left side or lay on their right side for 4 h. 2. The time to maximum plasma concentration of paracetamol was significantly lower when standing or lying on the right side compared with recumbent left, indicating more rapid gastric emptying. 3. The times to maximum plasma concentrations of nifedipine and its metabolite produced at first pass were reduced when standing or lying on the right side. These postures were associated with significantly higher peak plasma concentrations and AUC values of nifedipine but not of its nitropyridine metabolite. 4. The increase in heart rate following nifedipine administration was significantly greater when lying on the right side compared with the left. 5. The data are consistent with transient saturation of first pass metabolism of nifedipine with postures which favour rapid gastric emptying. The results demonstrate the importance of defining the precise posture in studies in which pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic measurements are made on drugs which are absorbed rapidly and are subject to presystemic elimination.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahsan C. H., Renwick A. G., Macklin B., Challenor V. F., Waller D. G., George C. F. Ethnic differences in the pharmacokinetics of oral nifedipine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;31(4):399–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1991.tb05552.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ameer B., Greenblatt D. J., Divoll M., Abernethy D. R., Shargel L. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of acetaminophen in plasma: single-dose pharmacokinetic studies. J Chromatogr. 1981 Nov 13;226(1):224–230. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)84226-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY S. E., CHILDS A. W., COMBES B., COURNAND A., WADE O. L., WHEELER H. O. The effect of exercise on the splanchnic blood flow and splanchnic blood volume in normal man. Clin Sci. 1956 Aug;15(3):457–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backon J., Hoffman A. The lateral decubitus position may affect gastric emptying through an autonomic mechanism: the skin pressure-vegetative reflex. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1991 Jul;32(1):138–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1991.tb05631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burn-Murdoch R., Fisher M. A., Hunt J. N. Does lying on the right side increase the rate of gastric emptying? J Physiol. 1980 May;302:395–398. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CULBERTSON J. W., WILKINS R. W., INGELFINGER F. J., BRADLEY S. E. The effect of the upright posture upon hepatic blood flow in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. J Clin Invest. 1951 Mar;30(3):305–311. doi: 10.1172/JCI102445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challenor V., Waller D. G., Gruchy B. S., Renwick A. G., George C. F., McMurdo E. T., McEwen J. The effects of food and posture on the pharmacokinetics of a biphasic release preparation of nifedipine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;22(5):565–570. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb02936.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feely J. Nifedipine increases and glyceryl trinitrate decreases apparent liver blood flow in normal subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1984 Jan;17(1):83–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1984.tb05003.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferner R. E., Monkman S., Riley J., Cholerton S., Idle J. R., Bateman D. N. Pharmacokinetics and toxic effects of nifedipine in massive overdose. Hum Exp Toxicol. 1990 Sep;9(5):309–311. doi: 10.1177/096032719000900507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George C. F. Drug kinetics and hepatic blood flow. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1979 Nov-Dec;4(6):433–448. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197904060-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinbloesem C. H., van Brummelen P., Faber H., Danhof M., Vermeulen N. P., Breimer D. D. Variability in nifedipine pharmacokinetics and dynamics: a new oxidation polymorphism in man. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Nov 15;33(22):3721–3724. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90165-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renwick A. G., Robertson D. R., Macklin B., Challenor V., Waller D. G., George C. F. The pharmacokinetics of oral nifedipine--a population study. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;25(6):701–708. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1988.tb05256.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumble R. H., Roberts M. S., Denton M. J. Effects of posture and sleep on the pharmacokinetics of paracetamol (acetaminophen) and its metabolites. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1991 Feb;20(2):167–173. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199120020-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellens J. H., Soons P. A., Breimer D. D. Lack of bimodality in nifedipine plasma kinetics in a large population of healthy subjects. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 1;37(13):2507–2510. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90238-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Victor Y. H. Effect of body position on gastric emptying in the neonate. Arch Dis Child. 1975 Jul;50(7):500–504. doi: 10.1136/adc.50.7.500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller D. G., Renwick A. G., Gruchy B. S., George C. F. The first pass metabolism of nifedipine in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1984 Dec;18(6):951–954. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1984.tb02569.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. B., Cuss F., Barnes P. J. Posture and theophylline kinetics. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1985 May;19(5):707–709. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1985.tb02701.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


