Abstract
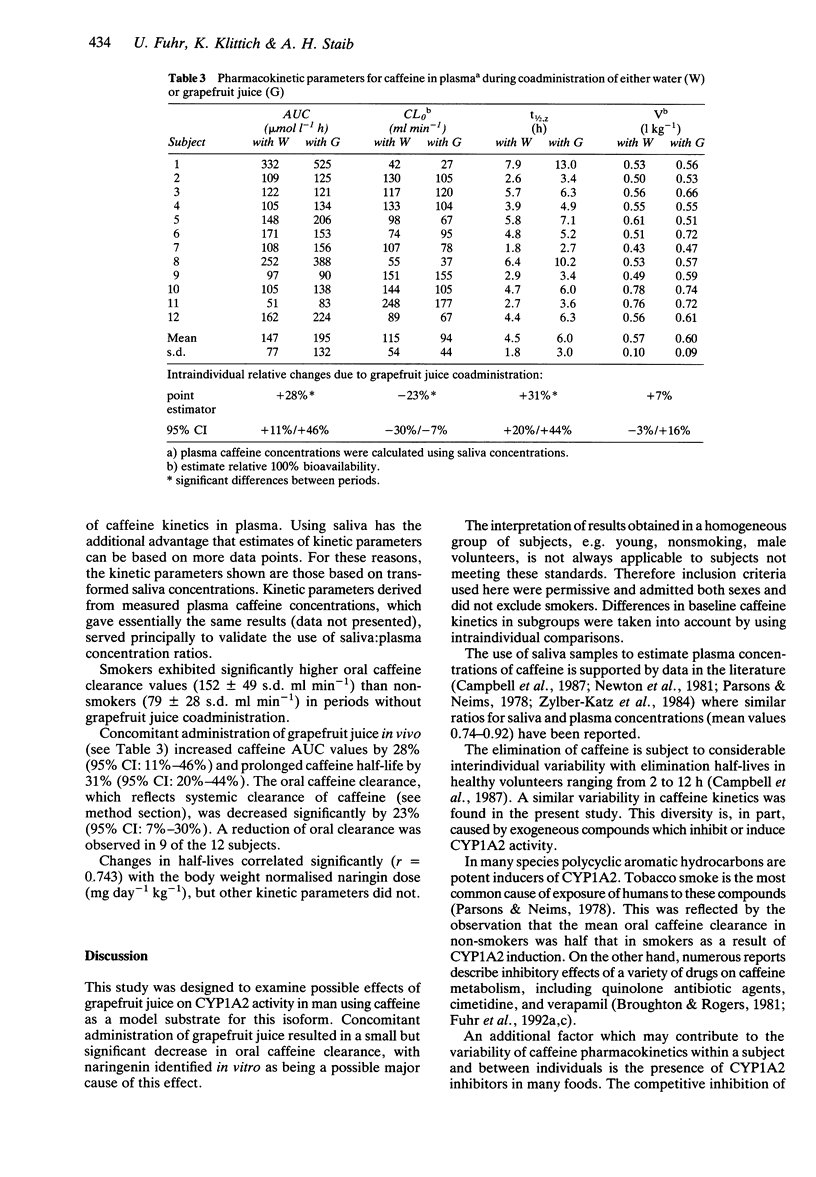
1. The effects of grapefruit juice and naringenin on the activity of the human cytochrome P450 isoform CYP1A2 were evaluated using caffeine as a probe substrate. 2. In vitro naringin was a potent competitive inhibitor of caffeine 3-demethylation by human liver microsomes (Ki = 7-29 microM). 3. In vivo grapefruit juice (1.2 l day-1 containing 0.5 g l-1 naringin, the glycone form of naringenin) decreased the oral clearance of caffeine by 23% (95% CI: 7%-30%) and prolonged its half-life by 31% (95% CI: 20%-44%) (n = 12). 4. We conclude that grapefruit juice and naringenin inhibit CYP1A2 activity in man. However, the small effect on caffeine clearance in vivo suggests that in general the ingestion of grapefruit juice should not cause clinically significant inhibition of the metabolism of other drugs that are substrates of CYPIA2.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOOTH A. N., JONES F. T., DEEDS F. Metabolic and glucosuria studies on naringin and phloridzin. J Biol Chem. 1958 Aug;233(2):280–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey D. G., Spence J. D., Munoz C., Arnold J. M. Interaction of citrus juices with felodipine and nifedipine. Lancet. 1991 Feb 2;337(8736):268–269. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90872-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broughton L. J., Rogers H. J. Decreased systemic clearance of caffeine due to cimetidine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 Aug;12(2):155–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01194.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
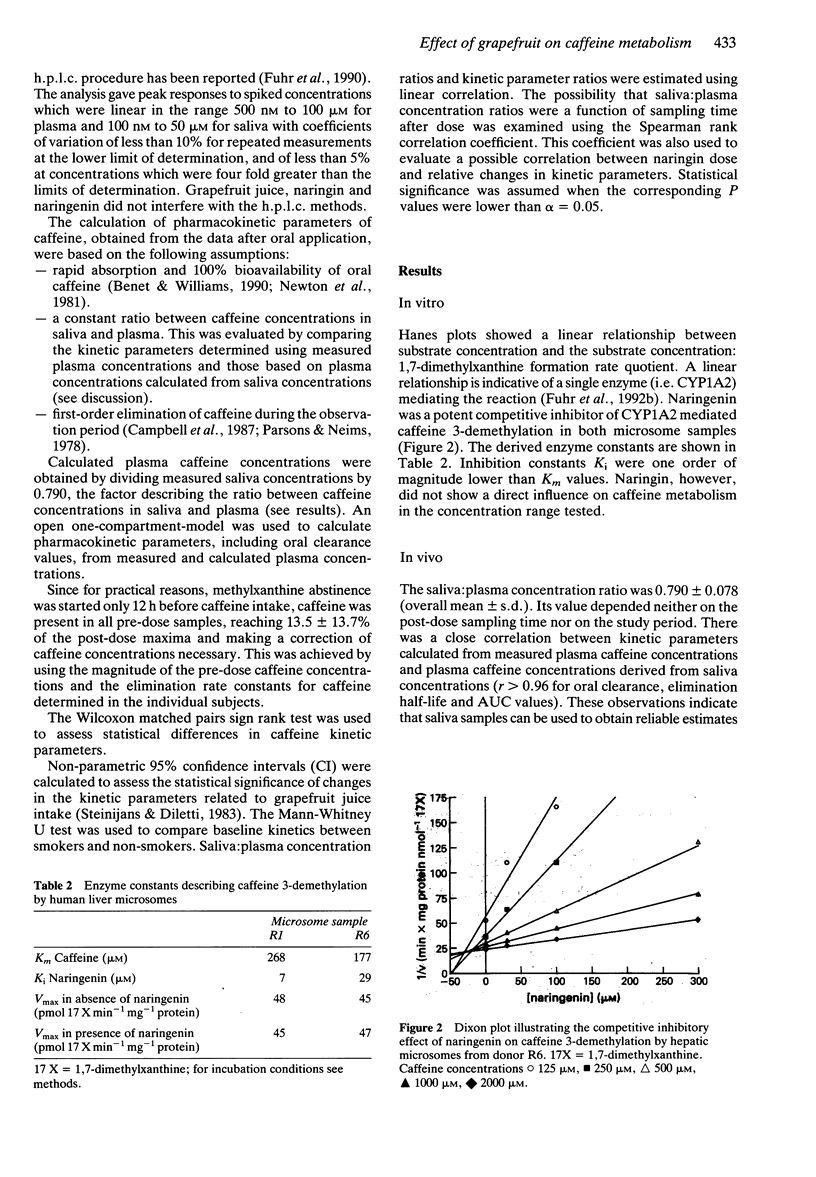
- Buening M. K., Chang R. L., Huang M. T., Fortner J. G., Wood A. W., Conney A. H. Activation and inhibition of benzo(a)pyrene and aflatoxin B1 metabolism in human liver microsomes by naturally occurring flavonoids. Cancer Res. 1981 Jan;41(1):67–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M. A., Iwasaki M., Guengerich F. P., Kadlubar F. F. Human cytochrome P-450PA (P-450IA2), the phenacetin O-deethylase, is primarily responsible for the hepatic 3-demethylation of caffeine and N-oxidation of carcinogenic arylamines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7696–7700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böcker R. H., Guengerich F. P. Oxidation of 4-aryl- and 4-alkyl-substituted 2,6-dimethyl-3,5-bis(alkoxycarbonyl)-1,4-dihydropyridines by human liver microsomes and immunochemical evidence for the involvement of a form of cytochrome P-450. J Med Chem. 1986 Sep;29(9):1596–1603. doi: 10.1021/jm00159a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Spielberg S. P., Kalow W. A urinary metabolite ratio that reflects systemic caffeine clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1987 Aug;42(2):157–165. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1987.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis A. R., Shetty T. K., Bhattacharya R. K. Modulating effect of plant flavonoids on the mutagenicity of N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine. Carcinogenesis. 1989 Oct;10(10):1953–1955. doi: 10.1093/carcin/10.10.1953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhr U., Anders E. M., Mahr G., Sörgel F., Staib A. H. Inhibitory potency of quinolone antibacterial agents against cytochrome P450IA2 activity in vivo and in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 May;36(5):942–948. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.5.942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhr U., Doehmer J., Battula N., Wölfel C., Kudla C., Keita Y., Staib A. H. Biotransformation of caffeine and theophylline in mammalian cell lines genetically engineered for expression of single cytochrome P450 isoforms. Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 22;43(2):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90282-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhr U., Wolff T., Harder S., Schymanski P., Staib A. H. Quinolone inhibition of cytochrome P-450-dependent caffeine metabolism in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos. 1990 Nov-Dec;18(6):1005–1010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhr U., Woodcock B. G., Siewert M. Verapamil and drug metabolism by the cytochrome P450 isoform CYP1A2. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1992;42(4):463–464. doi: 10.1007/BF00280138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths R. R., Woodson P. P. Caffeine physical dependence: a review of human and laboratory animal studies. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1988;94(4):437–451. doi: 10.1007/BF00212836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Kim D. H. In vitro inhibition of dihydropyridine oxidation and aflatoxin B1 activation in human liver microsomes by naringenin and other flavonoids. Carcinogenesis. 1990 Dec;11(12):2275–2279. doi: 10.1093/carcin/11.12.2275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Shimada T., Iwasaki M., Martin M. V. Activation of mutagens by human cytochrome P-450 enzymes. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;340B:87–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazaki M., Ishii T., Uyeta M. Mutagenicity of hydrolysates of citrus fruit juices. Mutat Res. 1982 Jun;101(4):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(82)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton R., Broughton L. J., Lind M. J., Morrison P. J., Rogers H. J., Bradbrook I. D. Plasma and salivary pharmacokinetics of caffeine in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1981;21(1):45–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00609587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons W. D., Neims A. H. Effect of smoking on caffeine clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978 Jul;24(1):40–45. doi: 10.1002/cpt197824140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinijans V. W., Diletti E. Statistical analysis of bioavailability studies: parametric and nonparametric confidence intervals. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1983;24(1):127–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00613939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylber-Katz E., Granit L., Levy M. Relationship between caffeine concentrations in plasma and saliva. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1984 Jul;36(1):133–137. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1984.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


