Abstract
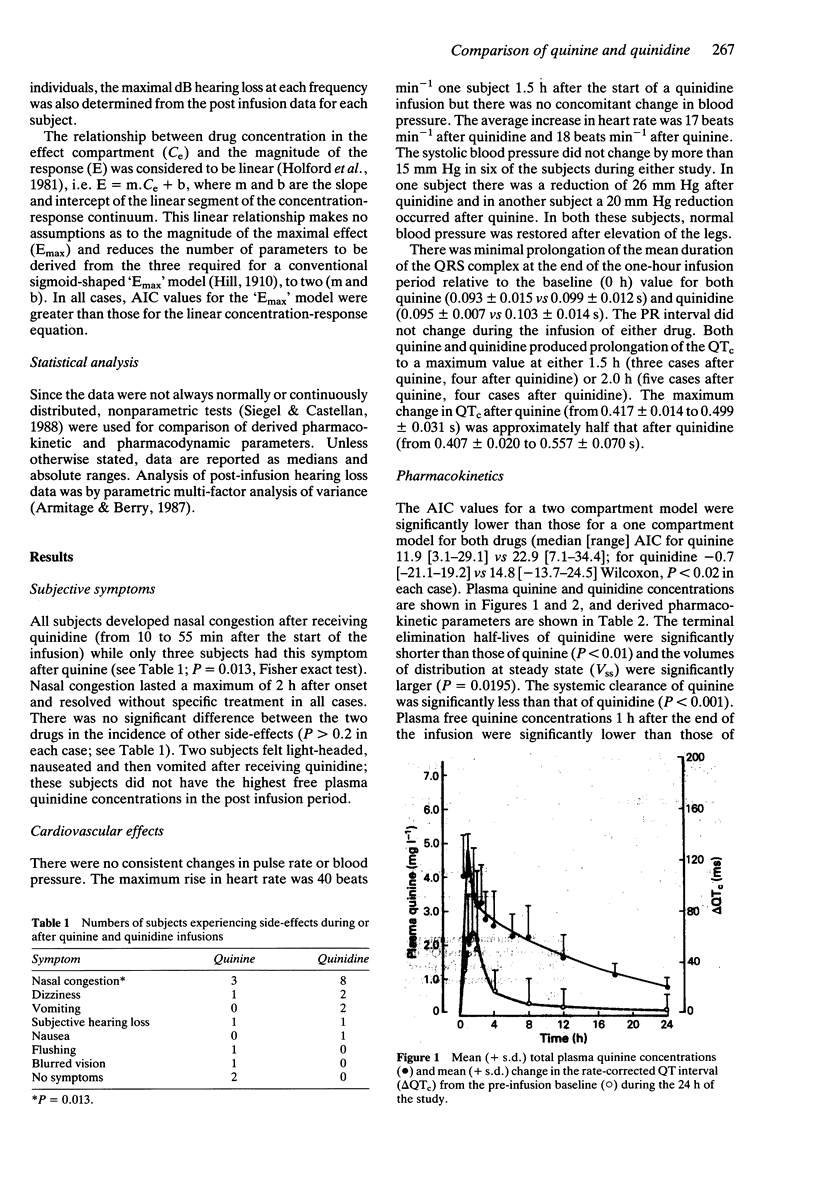
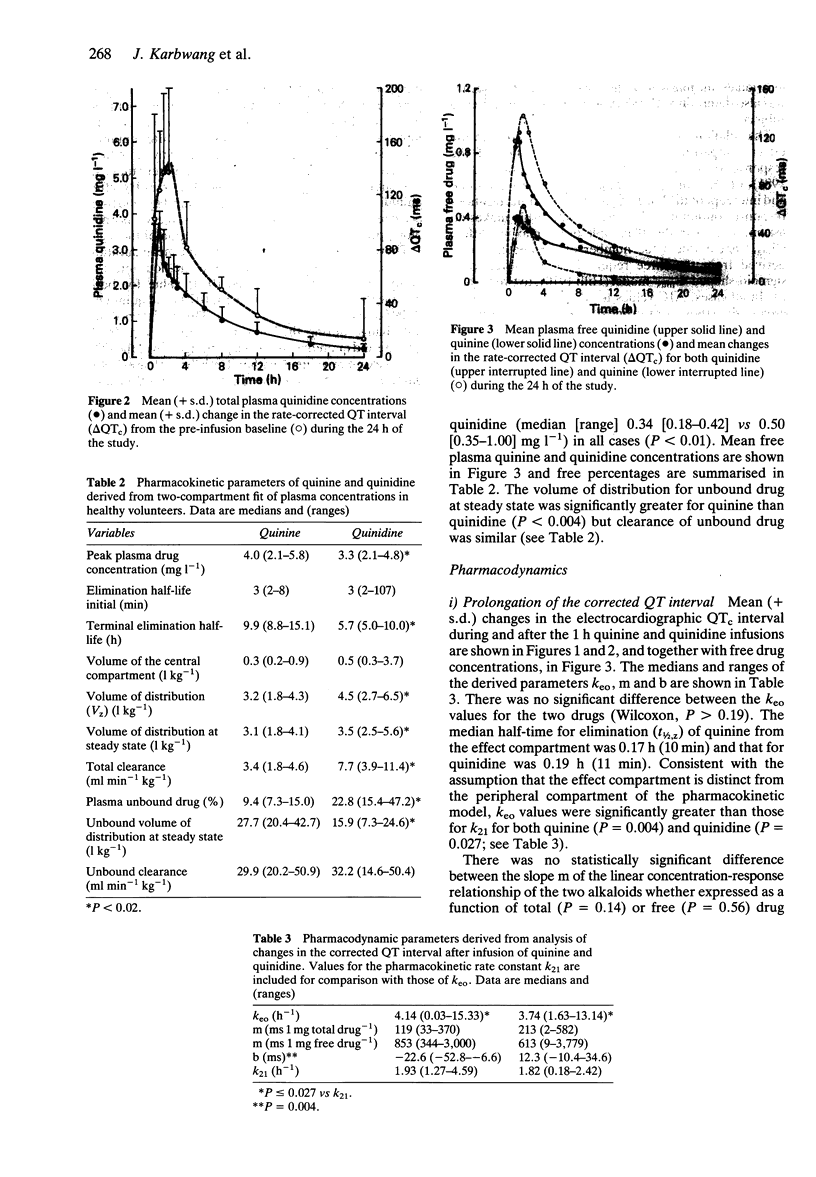
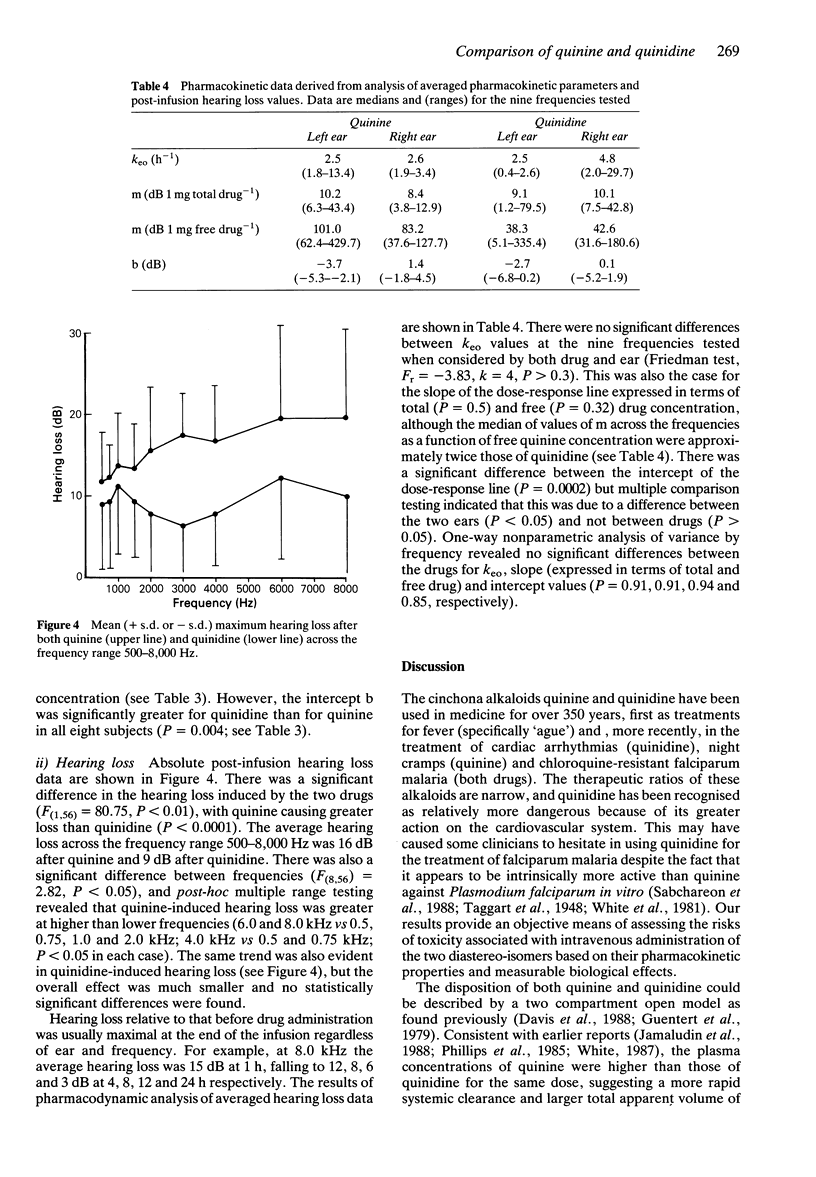
1. Eight healthy Thai males, aged 19-27 years, received quinine or quinidine dihydrochloride 10 mg kg-1 body weight by intravenous infusion over 1 h. At least 1 week later, the alternative alkaloid was administered. 2. The terminal elimination half-time of quinidine was shorter than that of quinine (median [range]; 5.7 [5.0-10.0] vs 9.9 [8.8-15.1] h, P < 0.01), the volume of distribution at steady state (Vss) for quinidine was larger than that for quinine (3.5 [2.5-5.6] vs 3.1 [1.8-4.1] 1 kg-1; P = 0.02) and quinidine was less bound to plasma proteins (% free drug: 22.8 [15.4-47.2] vs 9.4 [7.3-15.0]%, P < 0.01). Total clearance was greater for quinidine (7.7 [3.9-11.4] vs 3.4 [1.8-4.6] ml min-1 kg-1, P < 0.01) but not for clearance of unbound drug (32.2 [14.6-50.4] vs 29.9 [20.2-50.9] ml min-1 kg-1 respectively, P > 0.2). 3. Side-effects, including transient hypotension after quinidine in two cases, were mild. 4. Both drugs produced prolongation of the rate-corrected QT interval (QTc), with similar rates of elimination from the cardiac conduction 'effect' compartment (keo; 4.14 [0.03-15.33] h-1 for quinine, 3.74 [1.63-13.14] h-1 for quinidine, P > 0.19). Using a linear concentration-response model, the intercept ('threshold') for quinidine effect was lower than that for quinine (P = 0.004) but the slopes (change in QTc for a given change in free drug concentration) were similar (P = 0.56).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bunnag D., Harinasuta T., Vanijanonta S., Looareesuwan S., Chittamas S., Punnavut W., Jochims E. Slow-release quinidine in the treatment of chloroquine resistant falciparum malaria: a double-blind trial. Acta Leiden. 1987;55:129–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAMER G., ISAKSSON B. QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF QUINIDINE IN PLASMA. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1963;15:553–556. doi: 10.1080/00365516309079786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad K. A., Molk B. L., Chidsey C. A. Pharmacokinetic studies of quinidine in patients with arrhythmias. Circulation. 1977 Jan;55(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis T. M., Supanaranond W., Pukrittayakamee S., Karbwang J., Molunto P., Mekthon S., White N. J. A safe and effective consecutive-infusion regimen for rapid quinine loading in severe falciparum malaria. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1305–1308. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis T. M., White N. J., Looareesuwan S., Silamut K., Warrell D. A. Quinine pharmacokinetics in cerebral malaria: predicted plasma concentrations after rapid intravenous loading using a two-compartment model. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1988;82(4):542–547. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(88)90498-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guentert T. W., Holford N. H., Coates P. E., Upton R. A., Riegelman S. Quinidine pharmacokinetics in man: choice of a disposition model and absolute bioavailability studies. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1979 Aug;7(4):315–330. doi: 10.1007/BF01062532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holford N. H., Coates P. E., Guentert T. W., Riegelman S., Sheiner L. B. The effect of quinidine and its metabolites on the electrocardiogram and systolic time intervals: concentration--effect relationships. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 Feb;11(2):187–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01123.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamaludin A., Mohamed M., Navaratnam V., Mohamed N., Yeoh E., Wernsdorfer W. Single-dose comparative kinetics and bioavailability study of quinine hydrochloride, quinidine sulfate and quinidine bisulfate sustained-release in healthy male volunteers. Acta Leiden. 1988;57(1):39–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karbwang J., Na Bangchang K., Molunto P., Bunnag D. Determination of quinine and quinidine in biological fluids by high performance liquid chromatography. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1989 Mar;20(1):65–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihaly G. W., Ching M. S., Klejn M. B., Paull J., Smallwood R. A. Differences in the binding of quinine and quinidine to plasma proteins. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1987 Dec;24(6):769–774. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1987.tb03244.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. D., Greenberg A. E., Campbell C. C. Treatment of severe malaria in the United States with a continuous infusion of quinidine gluconate and exchange transfusion. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 13;321(2):65–70. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907133210201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs H. R., Greenblatt D. J., Woo E. Clinical pharmacokinetics of quinidine. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1980 Mar-Apr;5(2):150–168. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198005020-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. E., Warrell D. A., White N. J., Looareesuwan S., Karbwang J. Intravenous quinidine for the treatment of severe falciparum malaria. Clinical and pharmacokinetic studies. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 16;312(20):1273–1278. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505163122001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riegelman S., Loo J., Rowland M. Concept of a volume of distribution and possible errors in evaluation of this parameter. J Pharm Sci. 1968 Jan;57(1):128–133. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600570125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche R. J., Silamut K., Pukrittayakamee S., Looareesuwan S., Molunto P., Boonamrung S., White N. J. Quinine induces reversible high-tone hearing loss. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;29(6):780–782. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1990.tb03704.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabchareon A., Chongsuphajaisiddhi T., Sinhasivanon V., Chanthavanich P., Attanath P. In vivo and in vitro responses to quinine and quinidine of Plasmodium falciparum. Bull World Health Organ. 1988;66(3):347–352. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiner L. B., Stanski D. R., Vozeh S., Miller R. D., Ham J. Simultaneous modeling of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: application to d-tubocurarine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979 Mar;25(3):358–371. doi: 10.1002/cpt1979253358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silamut K., Molunto P., Ho M., Davis T. M., White N. J. Alpha 1-acid glycoprotein (orosomucoid) and plasma protein binding of quinine in falciparum malaria. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;32(3):311–315. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1991.tb03904.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silamut K., White N. J., Looareesuwan S., Warrell D. A. Binding of quinine to plasma proteins in falciparum malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Jul;34(4):681–686. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swerdlow C. D., Yu J. O., Jacobson E., Mann S., Winkle R. A., Griffin J. C., Ross D. L., Mason J. W. Safety and efficacy of intravenous quinidine. Am J Med. 1983 Jul;75(1):36–42. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)91165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taggart J. V., Earle D. P., Berliner R. W., Zubrod C. G., Welch W. J., Wise N. B., Schroeder E. F., London I. M., Shannon J. A. STUDIES ON THE CHEMOTHERAPY OF THE HUMAN MALARIAS. III. THE PHYSIOLOGICAL DISPOSITION AND ANTIMALARIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CINCHONA ALKALOIDS. J Clin Invest. 1948 May;27(3 Pt 2):80–86. doi: 10.1172/JCI101977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White N. J., Chanthavanich P., Krishna S., Bunch C., Silamut K. Quinine disposition kinetics. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Oct;16(4):399–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb02184.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White N. J., Looareesuwan S., Warrell D. A., Chongsuphajaisiddhi T., Bunnag D., Harinasuta T. Quinidine in falciparum malaria. Lancet. 1981 Nov 14;2(8255):1069–1071. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White N. J., Looareesuwan S., Warrell D. A., Warrell M. J., Bunnag D., Harinasuta T. Quinine pharmacokinetics and toxicity in cerebral and uncomplicated Falciparum malaria. Am J Med. 1982 Oct;73(4):564–572. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90337-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White N. J. The pharmacokinetics of quinine and quinidine in malaria. Acta Leiden. 1987;55:65–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka K., Nakagawa T., Uno T. Application of Akaike's information criterion (AIC) in the evaluation of linear pharmacokinetic equations. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1978 Apr;6(2):165–175. doi: 10.1007/BF01117450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


