Abstract
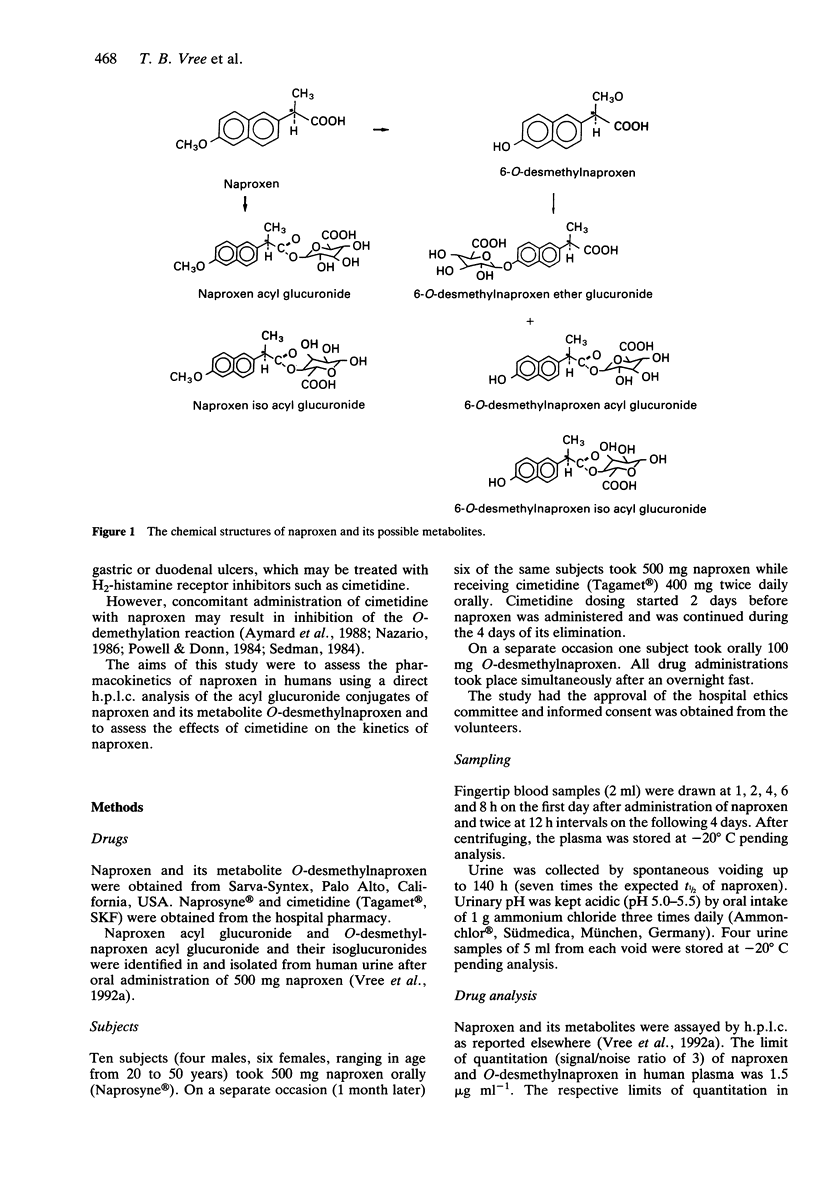
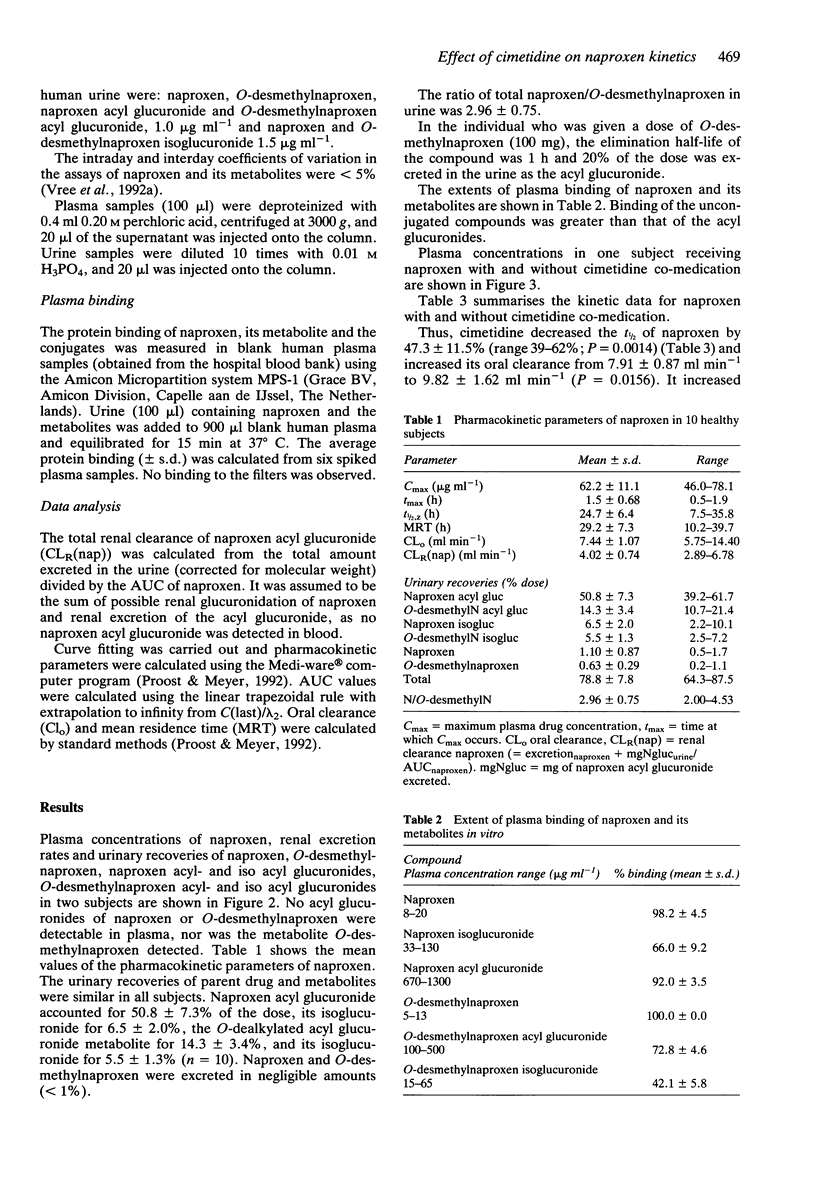
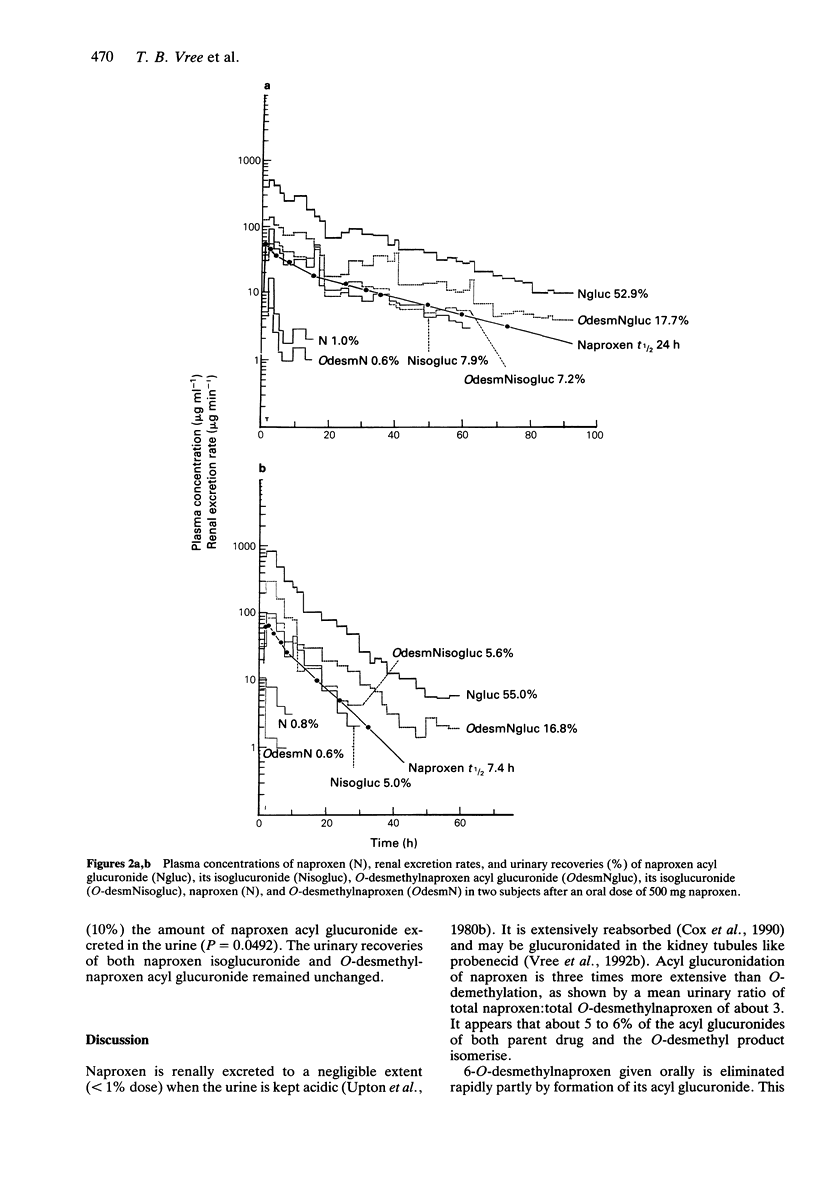
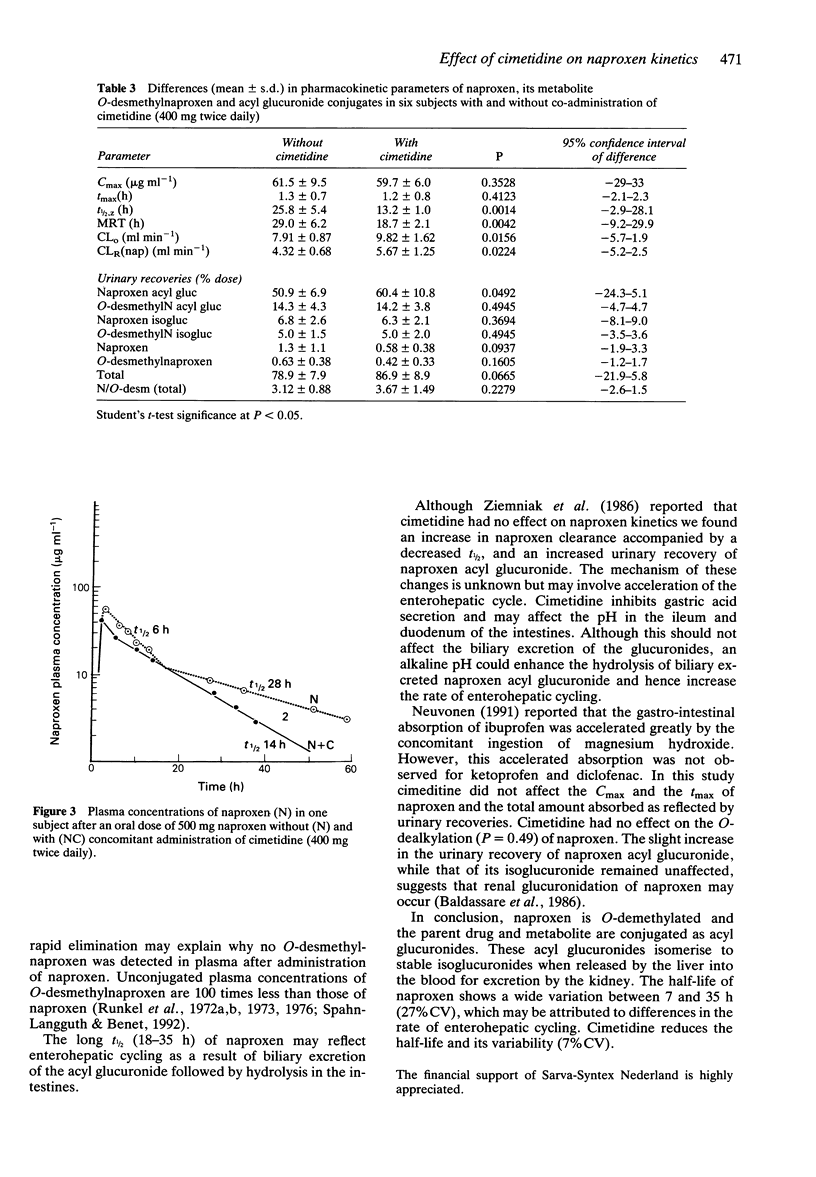
1. The pharmacokinetics of 500 mg naproxen given orally were described in 10 subjects using a direct h.p.l.c. analysis of the acyl glucuronide conjugates of naproxen and its metabolite O-desmethylnaproxen. 2. The mean elimination half-life of naproxen was 24.7 +/- 6.4 h (range 7 to 36 h). 3. Naproxen acyl glucuronide accounted for 50.8 +/- 7.3% of the dose recovered in the urine, its isomerised conjugate isoglucuronide for 6.5 +/- 2.0%, O-desmethylnaproxen acyl glucuronide for 14.3 +/- 3.4%, and its isoglucuronide for 5.5 +/- 1.3%. Naproxen and O-desmethylnaproxen were excreted in negligible amounts (< 1%). 4. Even though the urine pH of the subjects was kept acid in order to stabilize the acyl glucuronides, isomerisation took place in blood. 5. The extents of plasma binding of the unconjugated compounds were 98% (naproxen) and 100% (O-desmethylnaproxen), while naproxen acyl glucuronide binding was 92%; that of its isomer isoglucuronide 66%. O-desmethylnaproxen acyl glucuronide was 72% bound and its isoglucuronide was 42% bound. 6. Cimetidine (400 mg twice daily) decreased the t1/2 of naproxen by 39-60% (mean 47.3 +/- 11.5%; P = 0.0014) from 24.7 +/- 6.4 h to 13.2 +/- 1.0 h. It increased (10%) the urinary recovery of naproxen acyl glucuronide (P = 0.0492). The urinary recoveries of naproxen isoglucuronide and O-desmethylnaproxen acyl glucuronide remained unchanged.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aarbakke J., Gadeholt G., Høylandskjaer A. Pharmacokinetics of naproxen after oral administration of two tablet formulations in healthy volunteers. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1983 Jun;21(6):281–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Moety E. M., Al-Obaid A. M., Jado A. I., Lotfi E. A. Coupling of TLC and UV-measurement for quantification of naproxen and its main metabolite in urine. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 1988 Oct-Dec;13(4):267–271. doi: 10.1007/BF03190090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anttila M. Fluorometric determination of naproxen in serum. J Pharm Sci. 1977 Mar;66(3):433–434. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600660333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anttila M., Haataja M., Kasanen A. Pharmacokinetics of naproxen in subjects with normal and impaired renal function. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Oct;18(3):263–268. doi: 10.1007/BF00563009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aymard J. P., Aymard B., Netter P., Bannwarth B., Trechot P., Streiff F. Haematological adverse effects of histamine H2-receptor antagonists. Med Toxicol Adverse Drug Exp. 1988 Nov-Dec;3(6):430–448. doi: 10.1007/BF03259895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox P. G., Moons M. M., Russel F. G., van Ginneken C. A. Naproxen and indomethacin: disposition and effects in the isolated perfused rat kidney. Toxicol Lett. 1990 Sep;53(1-2):175–177. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(90)90119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faed E. M. Properties of acyl glucuronides: implications for studies of the pharmacokinetics and metabolism of acidic drugs. Drug Metab Rev. 1984;15(5-6):1213–1249. doi: 10.3109/03602538409033562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guelen P. J., Janssen T. J., Brueren M. M., Vree T. B., Lipperts G. J. The pharmacokinetic profile of naproxen suppository in man. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1988 Apr;26(4):190–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen N. E., Marinelli K. Mass fragmentographic quantification of naproxen in human plasma. J Chromatogr. 1981 Mar 13;222(3):482–485. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)84151-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen A., Jensen E. B., Petersen P. B., Husted S., Andreasen F. The determination of naproxen by spectrofluorometry and its binding to serum proteins. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1979 Apr;44(4):277–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1979.tb02330.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazario M. The hepatic and renal mechanisms of drug interactions with cimetidine. Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 1986 May;20(5):342–348. doi: 10.1177/106002808602000502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuvonen P. J. The effect of magnesium hydroxide on the oral absorption of ibuprofen, ketoprofen and diclofenac. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;31(3):263–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1991.tb05527.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J. R., Donn K. H. Histamine H2-antagonist drug interactions in perspective: mechanistic concepts and clinical implications. Am J Med. 1984 Nov 19;77(5B):57–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proost J. H., Meijer D. K. MW/Pharm, an integrated software package for drug dosage regimen calculation and therapeutic drug monitoring. Comput Biol Med. 1992 May;22(3):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0010-4825(92)90011-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runkel R. A., Kraft K. S., Boost G., Sevelius H., Forchielli E., Hill R., Magoun R., Szakacs J. B., Segre E. Naproxen oral absorption characteristics. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1972 Jul;20(7):1457–1466. doi: 10.1248/cpb.20.1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runkel R., Chaplin M. D., Sevelius H., Ortega E., Segre E. Pharmacokinetics of naproxen overdoses. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Sep;20(3):269–277. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976203269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runkel R., Chaplin M., Boost G., Segre E., Forchielli E. Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of naproxen in various laboratory animals and human subjects. J Pharm Sci. 1972 May;61(5):703–708. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600610507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runkel R., Forchielli E., Boost G., Chaplin M., Hill R., Sevelius H., Thompson G., Segre E. Naproxen-metabolism, excretion and comparative pharmacokinetics. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1973;2:24–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runkel R., Forchielli E., Sevelius H., Chaplin M., Segre E. Nonlinear plasma level response to high doses of naproxen. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1974 Mar;15(3):261–266. doi: 10.1002/cpt1974153261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runkel R., Mroszczak E., Chaplin M., Sevelius H., Segre E. Naproxen-probenecid interaction. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978 Dec;24(6):706–713. doi: 10.1002/cpt1978246706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedman A. J. Cimetidine-drug interactions. Am J Med. 1984 Jan;76(1):109–114. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90758-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimek J. L., Rao N. G., Khalil S. K. An isocratic high-pressure liquid chromatographic determination of naproxen and desmethylnaproxen in human plasma. J Pharm Sci. 1982 Apr;71(4):436–439. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600710415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spahn-Langguth H., Benet L. Z. Acyl glucuronides revisited: is the glucuronidation process a toxification as well as a detoxification mechanism? Drug Metab Rev. 1992;24(1):5–47. doi: 10.3109/03602539208996289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd P. A., Clissold S. P. Naproxen. A reappraisal of its pharmacology, and therapeutic use in rheumatic diseases and pain states. Drugs. 1990 Jul;40(1):91–137. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199040010-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton R. A., Buskin J. N., Guentert T. W., Williams R. L., Riegelman S. Convenient and sensitive high-performance liquid chromatography assay for ketoprofen, naproxen and other allied drugs in plasma or urine. J Chromatogr. 1980 Mar 21;190(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)85518-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton R. A., Buskin J. N., Williams R. L., Holford N. H., Riegelman S. Negligible excretion of unchanged ketoprofen, naproxen, and probenecid in urine. J Pharm Sci. 1980 Nov;69(11):1254–1257. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600691105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vree T. B., van den Biggelaar-Martea M., Verwey-van Wissen C. P. Determination of naproxen and its metabolite O-desmethylnaproxen with their acyl glucuronides in human plasma and urine by means of direct gradient high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1992 Jul 24;578(2):239–249. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(92)80422-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber S. S., Bankhurst A. D., Mroszczak E., Ding T. L. Effect of Mylanta on naproxen bioavailability. Ther Drug Monit. 1981;3(1):75–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



