Abstract
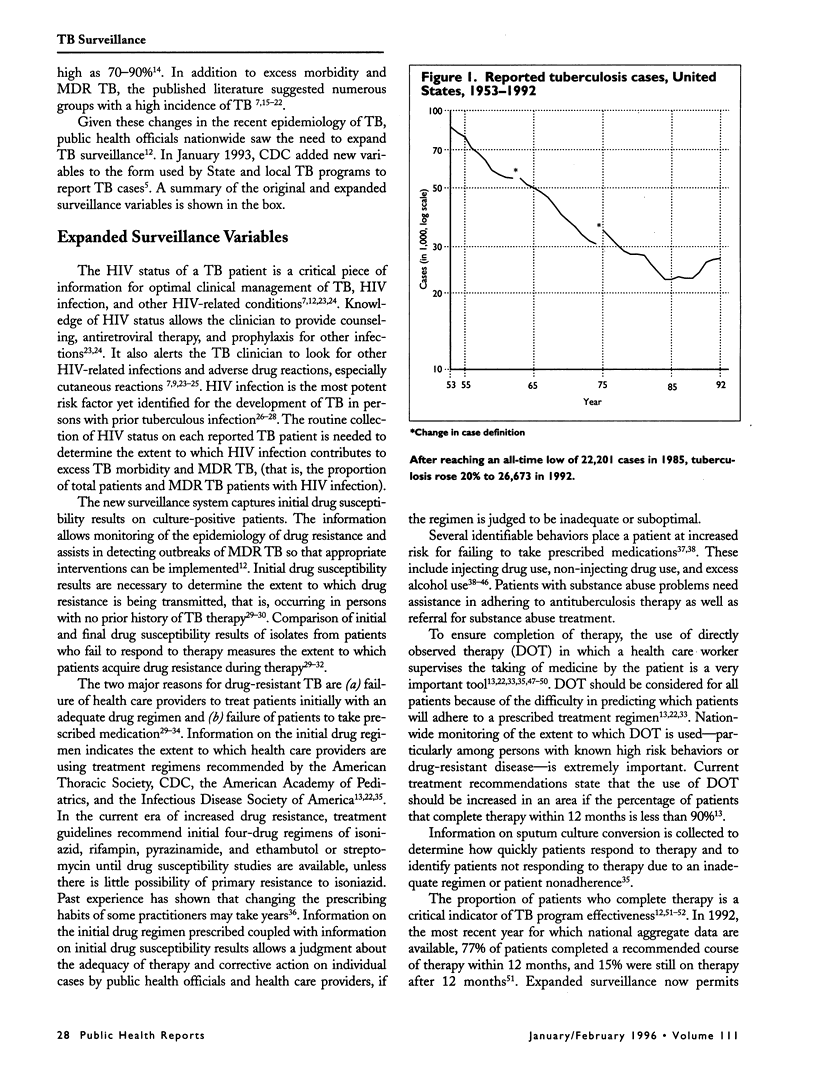
The past decade has witnessed an unprecedented upturn in tuberculosis morbidity and outbreaks of difficult- to-treat and highly lethal multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. In the early 1990s, a national consensus developed among public health officials to define more comprehensively the problem, and in January 1993, expanded tuberculosis surveillance was implemented nationwide. Carefully selected epidemiologic and case management variables were added to the Report of Verified Case of Tuberculosis form. Information is collected on the health status and treatment of patients, including human immunodeficiency virus status, drug susceptibility test results, and the initial drug regimen. Completion of therapy and use of directly observed therapy are also monitored. The new surveillance system allows a comparison of the quality of care of patients in the public and private sectors. Additional epidemiologic variables include membership in high-risk groups (the homeless, residents of correctional or long-term care facilities, migrant workers, health care workers, and correctional employees) and substance abuse (injecting drug use, non-injecting drug use, and excess alcohol use). The additional information derived from expanded tuberculosis surveillance is crucial to optimal patient management, policy development, resource allocation, as well as program planning, implementation, and evaluation at Federal, State, and local levels.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez S., Shell C., Berk S. L. Pulmonary tuberculosis in elderly men. Am J Med. 1987 Mar 23;82(3 Spec No):602–606. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. F., Bloch A. B., Davidson P. T., Snider D. E., Jr Tuberculosis in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jun 6;324(23):1644–1650. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199106063242307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. F., Leedom J. M., Chan L. S., Wong S. F., Shah J., Vachon L. A., Overturf G. D., Modlin R. L. Predictors of short-term prognosis in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Aug;158(2):366–371. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.2.366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer R., Dubler N. N., Landesman S. The dual epidemics of tuberculosis and AIDS: ethical and policy issues in screening and treatment. Am J Public Health. 1993 May;83(5):649–654. doi: 10.2105/ajph.83.5.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer R., Wilkinson D. Directly observed therapy for tuberculosis: history of an idea. Lancet. 1995 Jun 17;345(8964):1545–1548. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91090-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch A. B., Rieder H. L., Kelly G. D., Cauthen G. M., Hayden C. H., Snider D. E. The epidemiology of tuberculosis in the United States. Semin Respir Infect. 1989 Sep;4(3):157–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun M. M., Byers R. H., Heyward W. L., Ciesielski C. A., Bloch A. B., Berkelman R. L., Snider D. E. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and extrapulmonary tuberculosis in the United States. Arch Intern Med. 1990 Sep;150(9):1913–1916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brudney K., Dobkin J. Resurgent tuberculosis in New York City. Human immunodeficiency virus, homelessness, and the decline of tuberculosis control programs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Oct;144(4):745–749. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.4.745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantwell M. F., Snider D. E., Jr, Cauthen G. M., Onorato I. M. Epidemiology of tuberculosis in the United States, 1985 through 1992. JAMA. 1994 Aug 17;272(7):535–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantwell M. F., Snider D. E., Jr, Cauthen G. M., Onorato I. M. Epidemiology of tuberculosis in the United States, 1985 through 1992. JAMA. 1994 Aug 17;272(7):535–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLDI M., KOVACH A. G., SOLTI F., REV J., REFI Z., HERMANN R., KOLTEY E. Uber Crataeguswirkungen auf die Nierenfunktion beim Menschen. Dtsch Med J. 1959 Apr 1;10(6):164–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold A. O. Association of tuberculosis with alcoholism. South Med J. 1976 Oct;69(10):1336–1337. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197610000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieden T. R., Fujiwara P. I., Washko R. M., Hamburg M. A. Tuberculosis in New York City--turning the tide. N Engl J Med. 1995 Jul 27;333(4):229–233. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199507273330406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman L. N., Sullivan G. M., Bevilaqua R. P., Loscos R. Tuberculosis screening in alcoholics and drug addicts. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Nov;136(5):1188–1192. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.5.1188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goble M., Iseman M. D., Madsen L. A., Waite D., Ackerson L., Horsburgh C. R., Jr Treatment of 171 patients with pulmonary tuberculosis resistant to isoniazid and rifampin. N Engl J Med. 1993 Feb 25;328(8):527–532. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199302253280802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gostin L. O. Controlling the resurgent tuberculosis epidemic. A 50-state survey of TB statutes and proposals for reform. JAMA. 1993 Jan 13;269(2):255–261. doi: 10.1001/jama.269.2.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iseman M. D., Cohn D. L., Sbarbaro J. A. Directly observed treatment of tuberculosis. We can't afford not to try it. N Engl J Med. 1993 Feb 25;328(8):576–578. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199302253280811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iseman M. D., Sbarbaro J. A. The increasing prevalence of resistance to antituberculosis chemotherapeutic agents: implications for global tuberculosis control. Curr Clin Top Infect Dis. 1992;12:188–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iseman M. D. Treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 1993 Sep 9;329(11):784–791. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199309093291108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent J. H. The epidemiology of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in the United States. Med Clin North Am. 1993 Nov;77(6):1391–1409. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)30200-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoudi A., Iseman M. D. Pitfalls in the care of patients with tuberculosis. Common errors and their association with the acquisition of drug resistance. JAMA. 1993 Jul 7;270(1):65–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardell E. A. Beyond four drugs. Public health policy and the treatment of the individual patient with tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Jul;148(1):2–5. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/148.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan C. M. Incorporation of pyrazinamide into community-wide treatment of tuberculosis. Am J Public Health. 1990 Dec;80(12):1525–1526. doi: 10.2105/ajph.80.12.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichman L. B., Felton C. P., Edsall J. R. Drug dependence, a possible new risk factor for tuberculosis disease. Arch Intern Med. 1979 Mar;139(3):337–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder H. L., Cauthen G. M., Comstock G. W., Snider D. E., Jr Epidemiology of tuberculosis in the United States. Epidemiol Rev. 1989;11:79–98. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder H. L., Cauthen G. M., Kelly G. D., Bloch A. B., Snider D. E., Jr Tuberculosis in the United States. JAMA. 1989 Jul 21;262(3):385–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn P. A., Hartel D., Lewis V. A., Schoenbaum E. E., Vermund S. H., Klein R. S., Walker A. T., Friedland G. H. A prospective study of the risk of tuberculosis among intravenous drug users with human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1989 Mar 2;320(9):545–550. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198903023200901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small P. M., Schecter G. F., Goodman P. C., Sande M. A., Chaisson R. E., Hopewell P. C. Treatment of tuberculosis in patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jan 31;324(5):289–294. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199101313240503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider D. E., Jr, Roper W. L. The new tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 1992 Mar 5;326(10):703–705. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199203053261011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider D. E., Jr, Roper W. L. The new tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 1992 Mar 5;326(10):703–705. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199203053261011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacker S. B., Berkelman R. L. Public health surveillance in the United States. Epidemiol Rev. 1988;10:164–190. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis S. E., Slocum P. C., Blais F. X., King B., Nunn M., Matney G. B., Gomez E., Foresman B. H. The effect of directly observed therapy on the rates of drug resistance and relapse in tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 1994 Apr 28;330(17):1179–1184. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199404283301702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




