Abstract
OBJECTIVE. This study was designed to evaluate an innovative program of high speed radiographic screening for pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) at a large urban correctional institution, Cook County Jail in Chicago. METHODS. From March 1992 to February 1994, 126,608 inmates were screened on intake with a 100-mm mini-chest radiograph. RESULTS. Sixty-seven cases of active TB were identified by radiograph and 19 others from diagnostic work-up. The case finding rate for active disease with radiographic screening was approximately double the rate previously achieved with Mantoux skin testing. Mean time from jail entry to isolation was reduced from 17.6 days with Mantoux skin testing to 2.3 days with radiographic screening. CONCLUSIONS. In large jail facilities, high speed X-ray screening for TB can minimize disruption of the intake process and lead to dramatic improvements in the efficiency of medical follow-up and isolation.
Full text
PDF

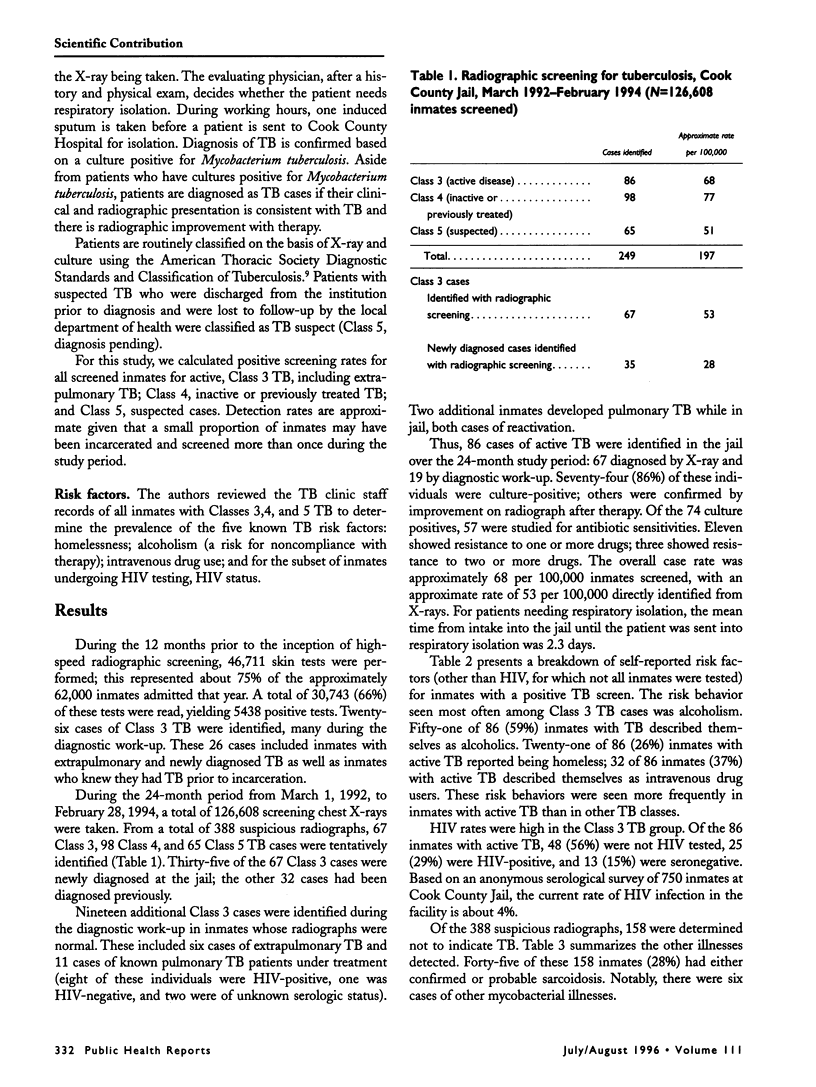
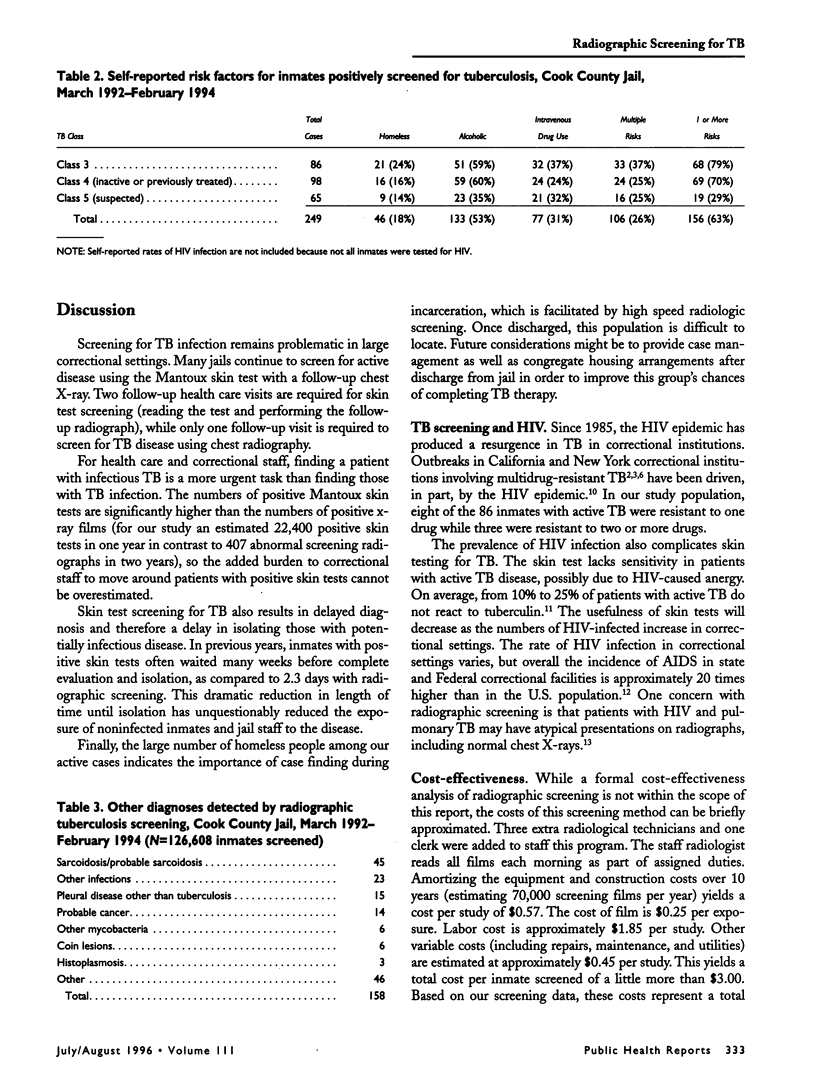

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- American Thoracic Society. Diagnostic standards and classification of tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Sep;142(3):725–735. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.3.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellin E. Y., Fletcher D. D., Safyer S. M. Association of tuberculosis infection with increased time in or admission to the New York City jail system. JAMA. 1993 May 5;269(17):2228–2231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun M. M., Truman B. I., Maguire B., DiFerdinando G. T., Jr, Wormser G., Broaddus R., Morse D. L. Increasing incidence of tuberculosis in a prison inmate population. Association with HIV infection. JAMA. 1989 Jan 20;261(3):393–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser J. B., Greifinger R. B. Correctional health care: a public health opportunity. Ann Intern Med. 1993 Jan 15;118(2):139–145. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-118-2-199301150-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huebner R. E., Schein M. F., Bass J. B., Jr The tuberculin skin test. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Dec;17(6):968–975. doi: 10.1093/clinids/17.6.968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keiper M. D., Beumont M., Elshami A., Langlotz C. P., Miller W. T., Jr CD4 T lymphocyte count and the radiographic presentation of pulmonary tuberculosis. A study of the relationship between these factors in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Chest. 1995 Jan;107(1):74–80. doi: 10.1378/chest.107.1.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King L., Geis G. Tuberculosis transmission in a large urban jail. JAMA. 1977 Feb 21;237(8):791–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead W. W. Undetected tuberculosis in prison. Source of infection for community at large. JAMA. 1978 Dec 1;240(23):2544–2547. doi: 10.1001/jama.240.23.2544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valway S. E., Greifinger R. B., Papania M., Kilburn J. O., Woodley C., DiFerdinando G. T., Dooley S. W. Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in the New York State prison system, 1990-1991. J Infect Dis. 1994 Jul;170(1):151–156. doi: 10.1093/infdis/170.1.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valway S. E., Richards S. B., Kovacovich J., Greifinger R. B., Crawford J. T., Dooley S. W. Outbreak of multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis in a New York State prison, 1991. Am J Epidemiol. 1994 Jul 15;140(2):113–122. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a117222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


